Credit: JAIST
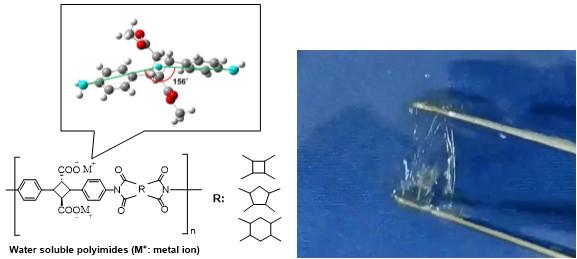
This is the first report for the syntheses of water-soluble polyimides which are Interestingly derived from bio-based resources, showing high transparency, tunable mechanical strength and the highest thermoresistance in water-soluble polymers reported ever.
Water-soluble polymers are of great interest in many areas of soft materials. These soft materials have been widely used in application related to aqueous solutions, such as dispersants, aggregation agents, thickeners, moisturizers, binders, and hydrogels. With increase in global awareness about environmental concerns, the importance of water-soluble materials has been highlighted and thereby have expanded their application windows to electronics, functional coatings, advanced adhesives and biomedical materials. Most of natural polymers such as polysaccharides, polypeptides, or their derivatives are water-soluble while synthetic water-soluble polymers are also available such as poly(ethylene oxide), poly(vinyl alcohol), polyacrylates, polyacrylamide, and their derivatives. However, the conventional water-soluble polymers have limited applications due to their low thermal distortion temperatures (ca. 200 °C). On the other hand, polymers exhibiting ultrahigh thermal stability, such as polyimides, possess poor solubility. Particularly, in literature there is little effective molecular engineering strategy for designing the polyimide with water solubility features due to the rigid polymer backbone and study interchain interactions and thereby limits processability and post-polymerization functionalization. A precise molecular engineering induced in the polyimide backbone through multifunctional monomers could play a game changer role in developing water-soluble polymers with ultrahigh thermal stability.
Here we have reported the preparation of a new diamine 4,4′-diamino truxillic acid as photodimer of bio-derived amino acid, 4-aminocinnamic acid, with a series of dianhydrides. The article demonstrates that a super-engineering plastic with very high thermo-mechanical properties bearing unprotected carboxylic acid groups can be utilized to incept the water solubility in the polymer. The synthesized biopolyimide were treated with alkaline metal hydroxide (or ammonium hydroxide) to yield biopolyimide salts. The resultant biopolyimide salts were dissolved in water to give an optically clear solution. The ion exchange reaction between monovalent cation with multivalent cation or with proton resulted in insoluble biopolyimide formation. The degradation temperatures of biopolyimide salts were found to keep very high temperatures (nearly= 366 °C), which is much higher than conventional water-soluble polymers. Furthermore, it was observed that biopolyimide salt self-standing film exhibited high transparency and an interesting trend for greater cationic size of the metal ion yielding more elastic film. In other words, change in cation size provides an opportunity for precise tuning of the tensile properties. The synthesized water-soluble biopolyimide are attractive building blocks for the soft materials and may be utilized for specialty applications such as drug delivery, polychelatogens etc. A preliminary study into polyureas and polyamides by following similar strategy also resulted the induction of water-solubility features, which indicates the wide versatility of this building block methodology.
Professor Tatsuo Kaneko of JAIST said that “I and Dr. Sumant Dwivedi developed the ideation process and then led experiments with very hardworker students and researchers to synthesize these wonderful materials with plausible waterborne applications, like coatings, biomedical device etc.”
###
Media Contact
Tatsuo Kaneko
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




