The group has realized a scanless 3D imaging system and an algorithm for high-speed measurement
Credit: National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Tohoku University, Toin University of Yokohama,
Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
[Abstract]
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Tohoku University, Toin University of Yokohama, and Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) have succeeded in developing a scanless high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution for a 3D space. The system is based on digital holography. The developed microscopy system has an algorithm to acquire 3D information of fluorescent objects toward scanless 3D measurement in less than 1 millisecond. Scanless 3D sensing with submicron resolution and color-multiplexed holographic fluorescence imaging have been demonstrated using the algorithm. The microscopy system will be further developed to achieve holographic 3D motion-picture sensing of specimens with incoherent light.
This achievement was published in Optics Letters as an open-access paper on January 29, 2021.
[Achievements]
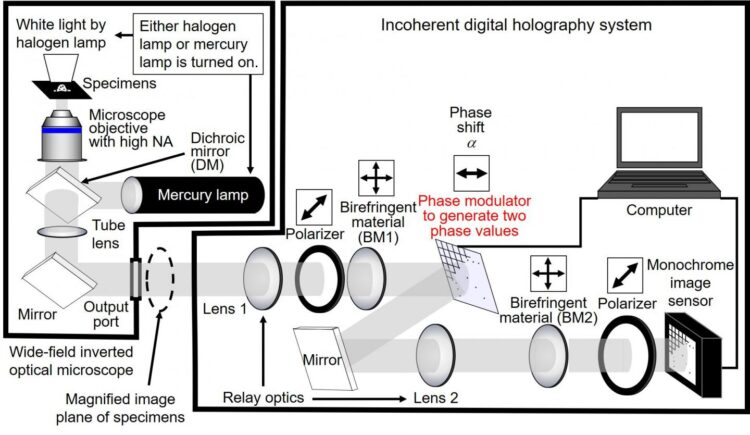
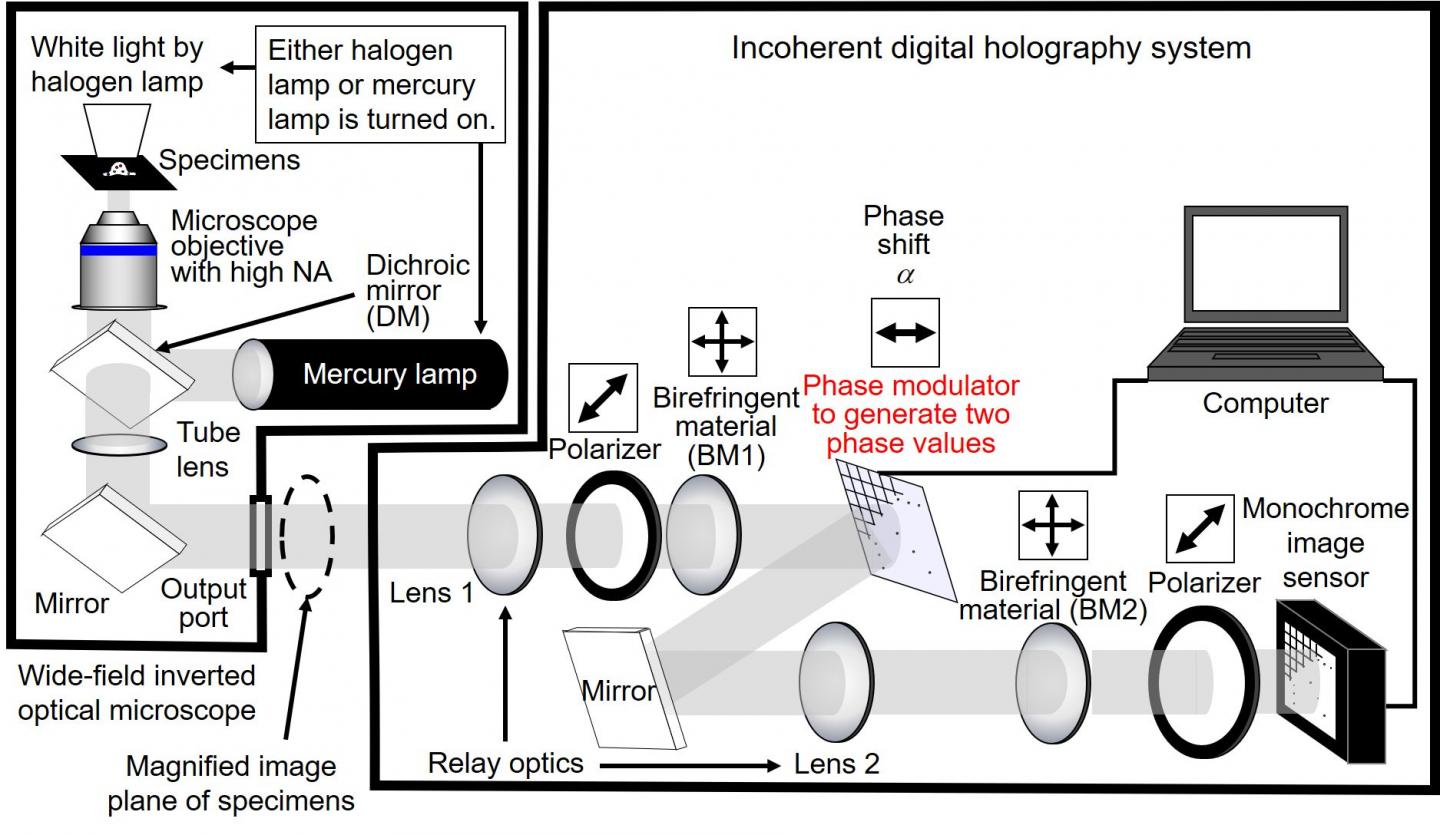
The scanless high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system shown in Figure 1 was constructed. The system is based on digital holography and is applicable to the sensing of incoherent light such as fluorescence light and natural light. The developed algorithm enables the adoption of a phase modulator to generate two phase values, which is expected to increase the measurement speed. Submicron resolution for a 3D space was successfully demonstrated using fluorescent objects with a diameter of 0.2 micron. The experimental results shown in Figure 2 indicate that the developed microscopy system achieves 3D sensing of nanoparticles and has submicron resolution quantitatively for a 3D space. Scanless 3D measurement in less than 1 millisecond is achievable by using the algorithm with either a ferroelectric liquid crystal on silicon (FLCOS) or an electro-optic (EO) device. Color-multiplexed holographic fluorescence imaging with the algorithm and only four exposures has also been demonstrated by combining the proposed algorithm and computational coherent superposition (CCS). The number of exposures is reduced by the algorithm, and the number of photons per hologram is increased even for ultimately weak light.
[Future prospects]
- High-speed holographic motion-picture imaging for 3D dynamics and multiple moving objects in a 3D space.
- Improvements of the system such as recording of a quantitative phase, sensing of ultimately weak light, and construction of a compact optical setup.
###
Media Contact
HIROTA Sachiko
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.