Credit: M. Johnson
New research has found as climate change causes the world’s oceans to warm, baby sharks are born smaller, exhausted, undernourished and into environments that are already difficult for them to survive in.
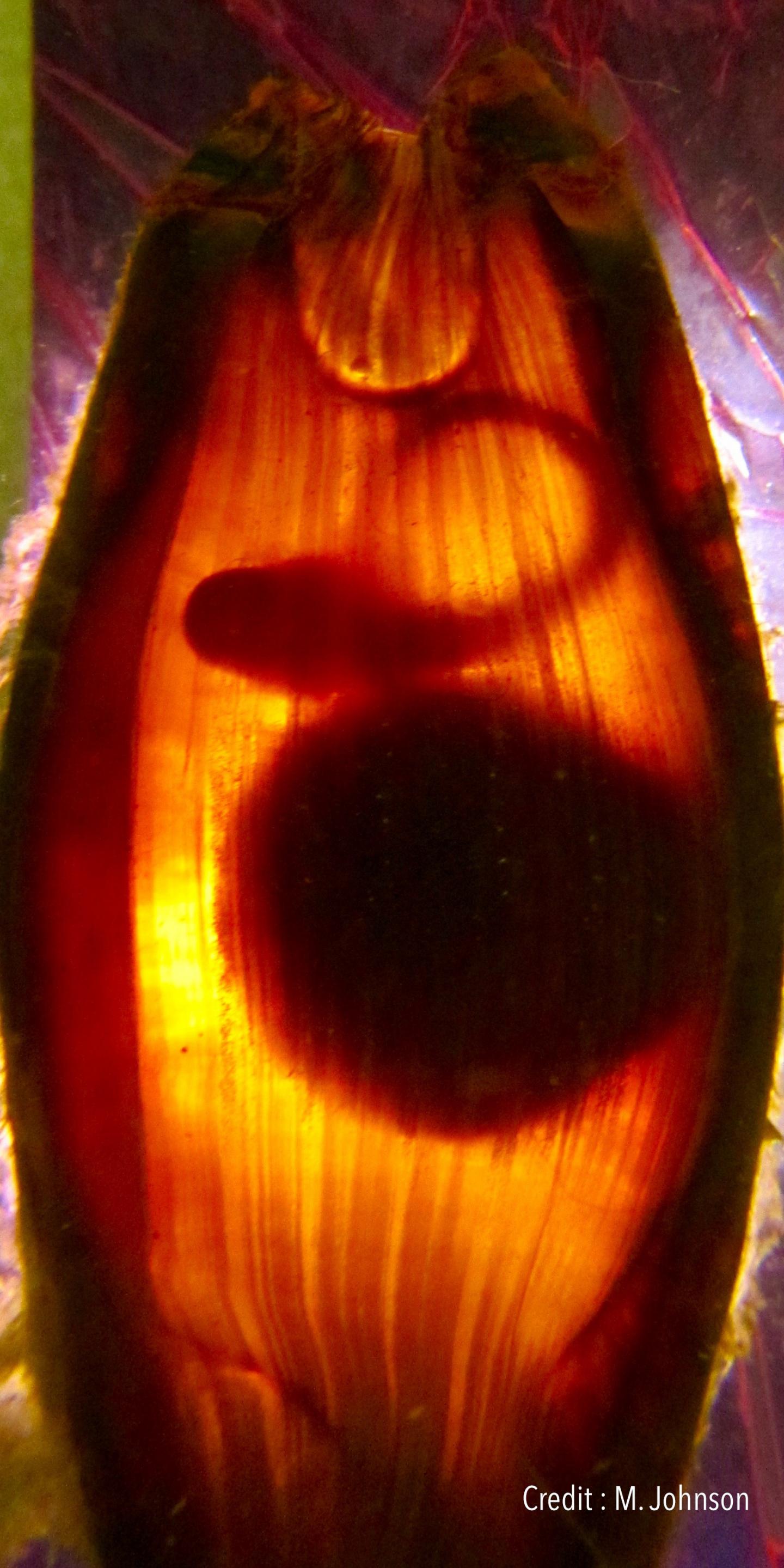
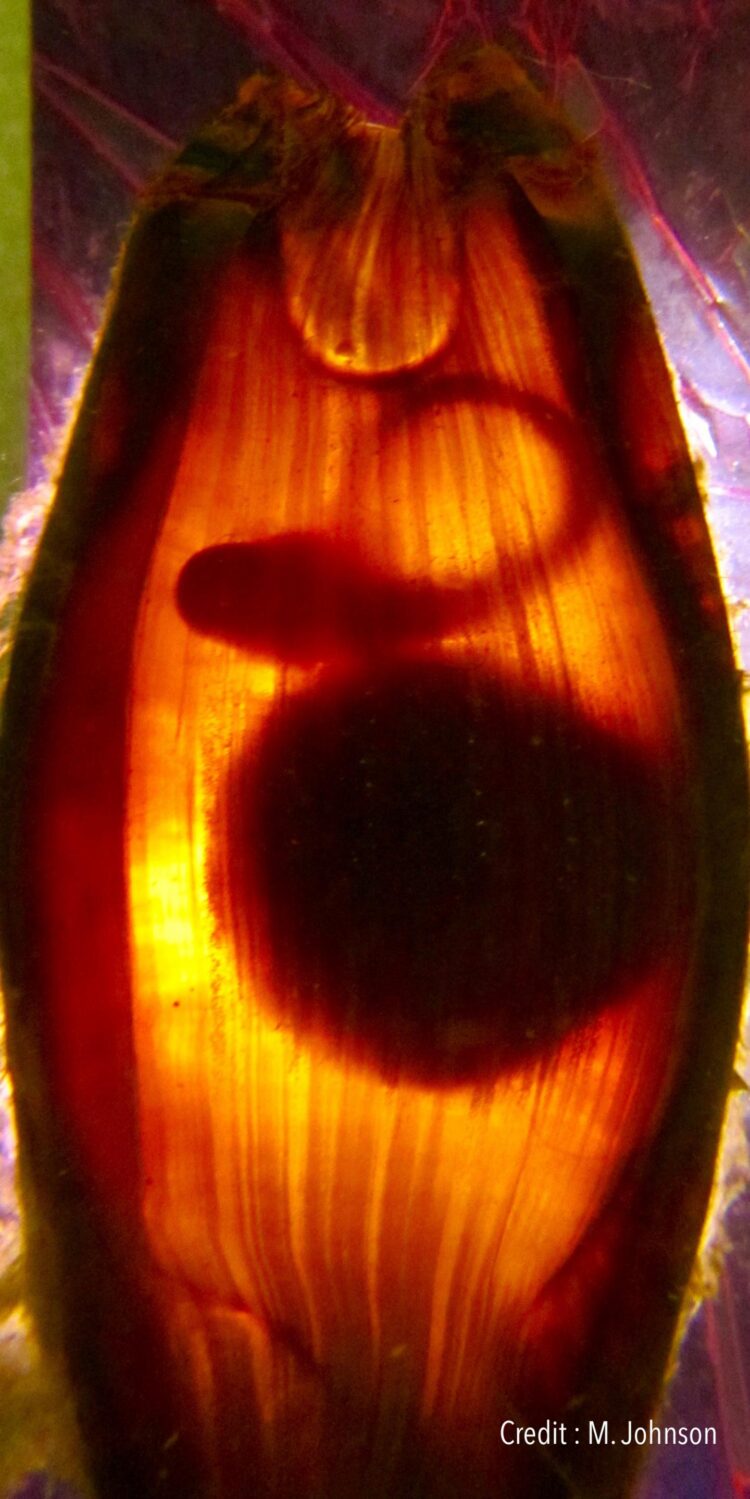
Lead author of the study Carolyn Wheeler is a PhD candidate at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University (Coral CoE at JCU) and the University of Massachusetts. She examined the effects of increased temperatures on the growth, development and physiological performance of epaulette sharks–an egg-laying species found only on the Great Barrier Reef. She and her team studied the sharks as embryos and as hatchlings.
“We tested shark embryos in waters up to 31°C,” Ms Wheeler said.
“The hotter the conditions, the faster everything happened, which could be a problem for the sharks. The embryos grew faster and used their yolk sac quicker, which is their only source of food as they develop in the egg case. This led to them hatching earlier than usual.”
This meant hatchlings were not only smaller, they needed to feed almost straight away–while lacking significant energy.
Co-author Associate Professor Jodie Rummer, also from Coral CoE at JCU, says the waters of the Great Barrier Reef will likely experience summer averages close to or even in excess of 31°C by the end of the century.
Since sharks don’t care for their eggs after they are laid, a shark egg must be able to survive unprotected for up to four months. Dr Rummer flags rising ocean temperatures as a major concern for the future of all sharks–both egg-laying and live-bearing species.
“The epaulette shark is known for its resilience to change, even to ocean acidification,” Dr Rummer said. “So, if this species can’t cope with warming waters then how will other, less tolerant species fare?” she said.
Sharks and the class of animals they belong to, which includes rays and skates, are slow growing. They also don’t reproduce that often compared to other fishes. The populations of these creatures are already threatened across the globe.
The study suggests the sharks of the future will be born–or hatch, in this case–not only at a disadvantage but into environments that are already at the warmest they can tolerate.
“The study presents a worrying future given that sharks are already threatened,” Ms Wheeler said.
“Sharks are important predators that keep ocean ecosystems healthy. Without predators, whole ecosystems can collapse, which is why we need to keep studying and protecting these creatures.”
“Our future ecosystems depend us taking urgent action to limit climate change,” Dr Rummer said.
###
The research was a collaborative effort between the Anderson Cabot Center for Ocean Life and the husbandry staff at the New England Aquarium in Boston. The New England Aquarium has a successful breeding program for epaulette sharks.
PAPER
Wheeler C, Rummer J, Bailey B, Lockwood J, Vance S, Mandelman J. (2020). ‘Future thermal regimes for epaulette sharks (Hemiscyllium ocellatum): growth and metabolic performance cease to be optimal’. Scientific Reports, 10: 79953. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79953-0
CONTACTS
Carolyn Wheeler
E: [email protected]
A/Prof Jodie Rummer
P: +61 (0)439 166 171
E: [email protected]
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
Melissa Lyne / Coral CoE
P: +61 (0)415 514 328
E: [email protected]
Media Contact
Melissa Lyne
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.