‘An experiment of nature’ after the end-Cretaceous mass extinction
Credit: © Giuseppe Marramà
An international research team led by Giuseppe Marramà from the Institute of Paleontology of the University of Vienna discovered a new and well-preserved fossil stingray with an exceptional anatomy, which greatly differs from living species. The find provides new insights into the evolution of these animals and sheds light on the recovery of marine ecosystems after the mass extinction occurred 66 million years ago. The study was recently published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Stingrays (Myliobatiformes) are a very diverse group of cartilaginous fishes which are known for their venomous and serrated tail stings, which they use against other predatory fish, and occasionally against humans. These rays have a rounded or wing-like pectoral disc and a long, whip-like tail that carries one or more serrated and venomous stings. The stingrays include the biggest rays of the world like the gigantic manta rays, which can reach a “wingspan” of up to seven meters and a weight of about three tons.
Fossil remains of stingrays are very common, especially their isolated teeth. Complete skeletons, however, exist only from a few extinct species coming from particular fossiliferous sites. Among these, Monte Bolca, in northeastern Italy, is one of the best known. So far, more than 230 species of fishes have been discovered that document a tropical marine coastal environment associated with coral reefs which dates back to about 50 million years ago in the period called Eocene.
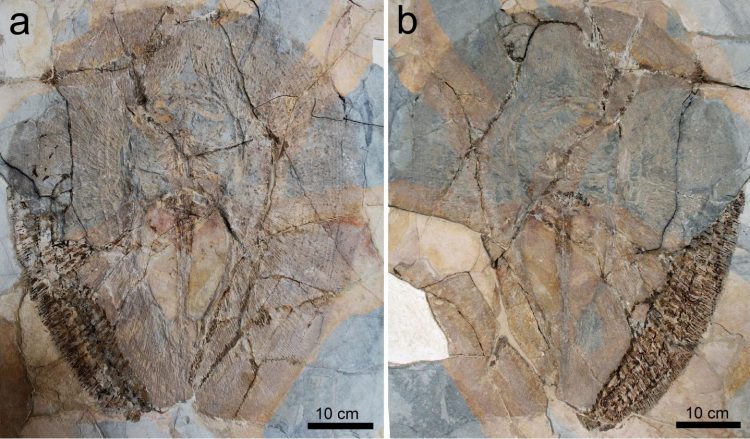
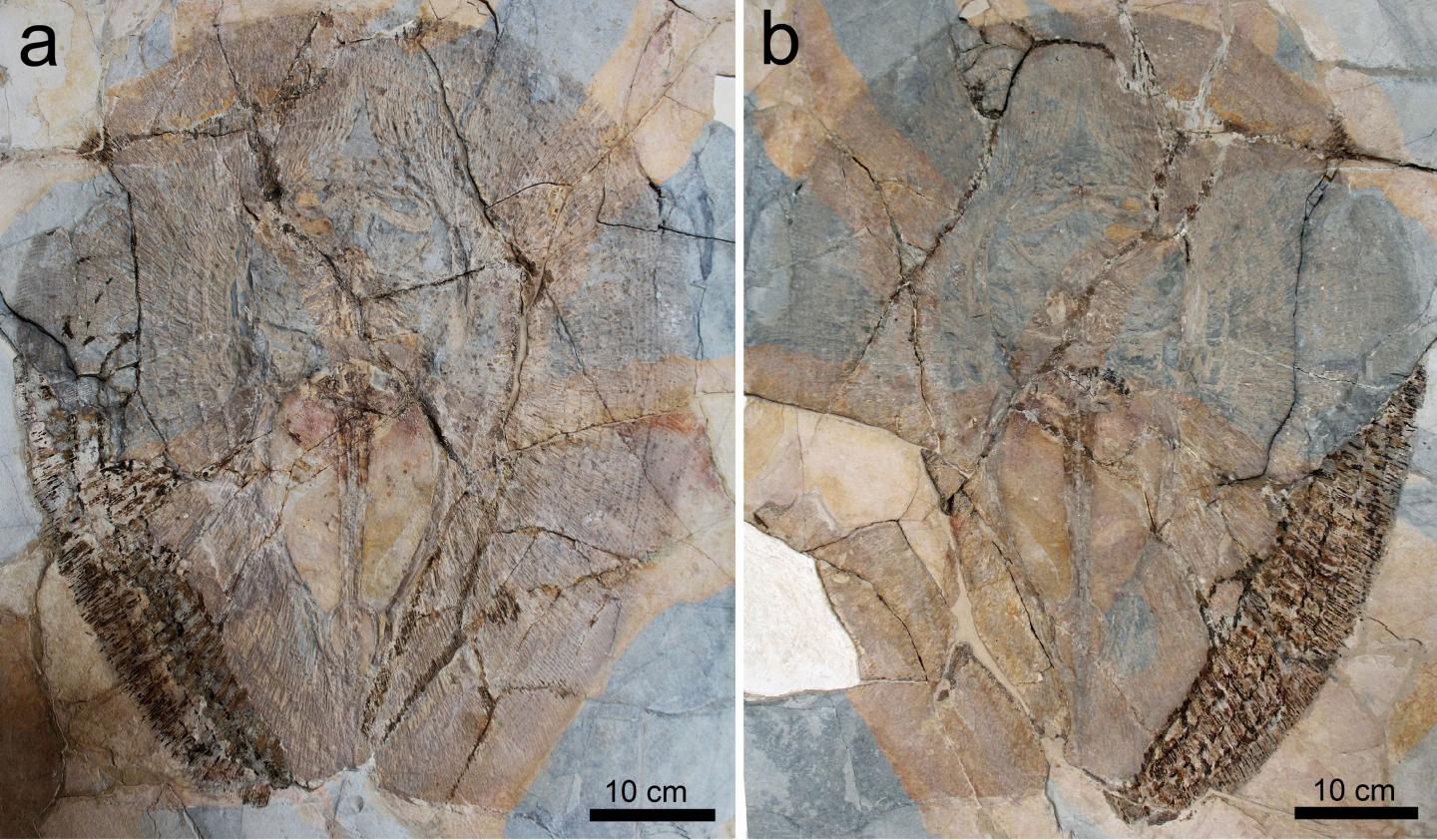
This new fossil stingray has a flattened body and a pectoral disc ovoid in shape. What is striking is the absence of sting and the extremely short tail, which is not long as in the other stingrays, and does not protrude posteriorly to the disc. This body plan is not known in any other fossil or living stingray. Since this animal is unique and peculiar, the researchers named the new stingray Lessiniabatis aenigmatica, which means “bizarre ray from Lessinia” (the Italian area where Bolca is located).
More than 70 percent of the organisms, such as dinosaurs, marine reptiles, several mammal groups, numerous birds, fish and invertebrates, disappeared during the fifth largest extinction event in the Earth’s history occurred about 66 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous. In marine environments, the time after this event is characterized by the emergence and diversification of new species and entire groups of bony and cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays), which reoccupied the ecological niches left vacant by the extinction’s victims. The new species experimented sometimes new body plans and new ecological strategies.
“From this perspective, the emergence of a new body plan in a 50-million-year-old stingray such as Lessiniabatis aenigmatica is particularly intriguing when viewed in the context of simultaneous, extensive diversification and emergence of new anatomical features within several fish groups, during the recovery of the life after the end-Cretaceous extinction event”, states Giuseppe Marramà.
###
Publication in Scientific Reports:
Marramà G., Carnevale G., Giusberti L., Naylor G., Kriwet J. 2019. A bizarre Eocene dasyatoid batomorph (Elasmobranchii, Myliobatiformes) from the Bolca Lagerstätte (Italy) reveals a new, extinct body plan for stingrays. Scientific Reports.
doi:10.1038/s41598-019-50544-y
Media Contact
Giuseppe Marramà
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.