Coupled terahertz device significantly improves electron beam quality
Credit: DESY, Gesine Born
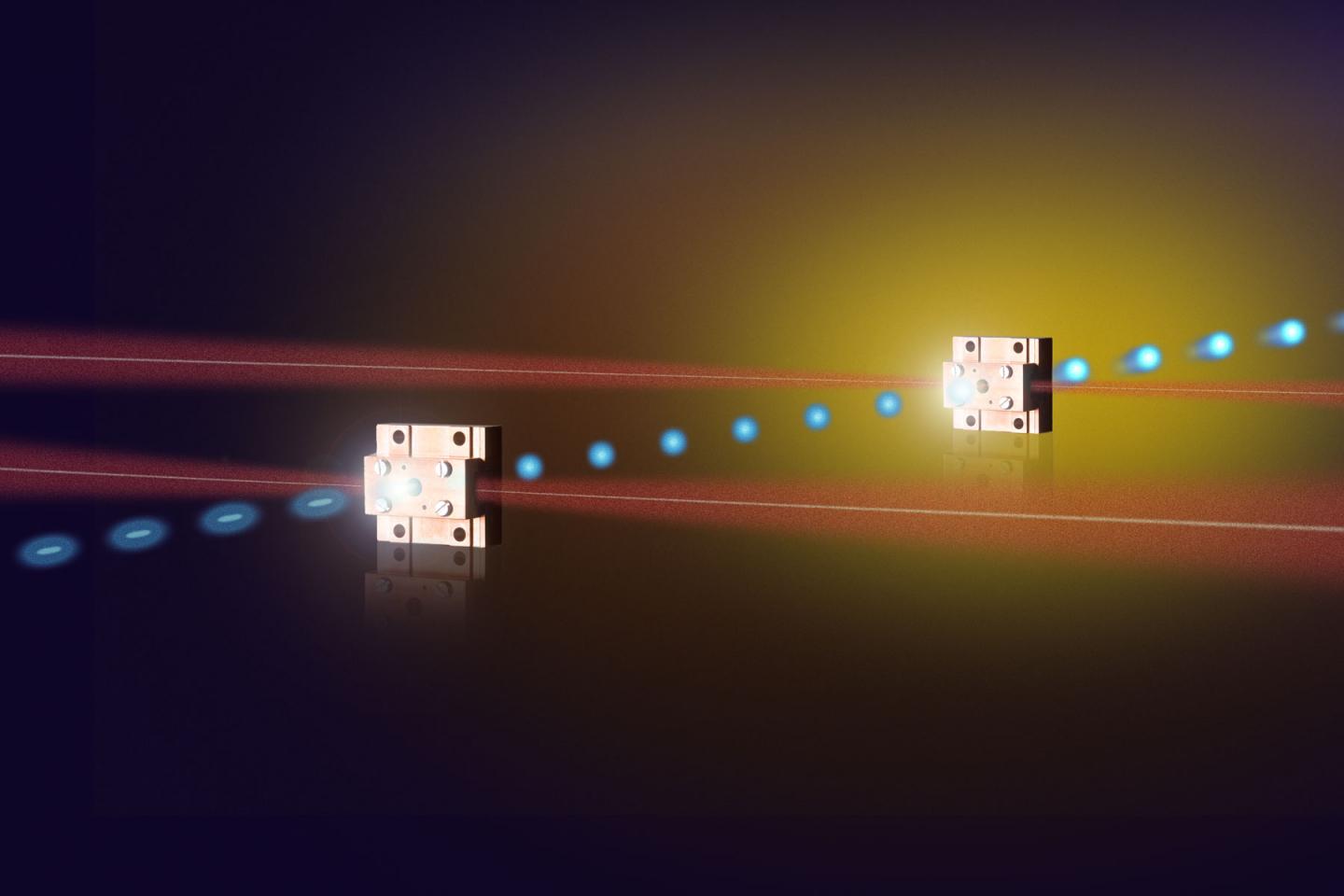
Scientists at DESY have achieved a new world record for an experimental type of miniature particle accelerator: For the first time, a terahertz powered accelerator more than doubled the energy of the injected electrons. At the same time, the setup significantly improved the electron beam quality compared to earlier experiments with the technique, as Dongfang Zhang and his colleagues from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science (CFEL) at DESY report in the journal Optica. “We have achieved the best beam parameters yet for terahertz accelerators,” said Zhang.
“This result represents a critical step forward for the practical implementation of terahertz-powered accelerators,” emphasized Franz Kärtner, who heads the ultrafast optics and X-rays group at DESY. Terahertz radiation lies between infrared and microwave frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum and promises a new generation of compact particle accelerators. “The wavelength of terahertz radiation is about a hundred times shorter than the radio waves currently used to accelerate particles,” explained Kärtner. “This means that the components of the accelerator can also be built to be around a hundred times smaller.” The terahertz approach promises lab-sized accelerators that will enable completely new applications for instance as compact X-ray sources for materials science and maybe even for medical imaging. The technology is currently under development.
Since terahertz waves oscillate so fast, every component and every step has to be precisely synchronized. “For instance, to achieve the best energy gain, the electrons have to hit the terahertz field exactly during its accelerating half cycle,” explained Zhang. In accelerators, particles usually do not fly in a continuous beam, but are packed in bunches. Because of the fast-changing field, in terahertz accelerators these bunches have to be very short to ensure even acceleration conditions along the bunch.
“In previous experiments the electron bunches were too long”, said Zhang. “Since the terahertz field oscillates so quickly, some of the electrons in the bunch were accelerated, while others were even slowed down. So, in total there was just a moderate average energy gain, and, what is more important, a wide energy spread, resulting in what we call poor beam quality.” To make things worse, this effect strongly increased the emittance, a measure for how well a particle beam is bundled transversally. The tighter, the better – the smaller the emittance.
To improve the beam quality, Zhang and his colleagues built a two-step accelerator from a multi-purpose device they had developed earlier: The Segmented Terahertz Electron Accelerator and Manipulator (STEAM) can compress, focus, accelerate and analyze electron bunches with terahertz radiation. The researchers combined two STEAM devices in line. They first compressed the incoming electron bunches from about 0.3 millimetres in length to just 0.1 millimetres. With the second STEAM device, they accelerated the compressed bunches. “This scheme requires control on the level of quadrillionths of a second, which we achieved,” said Zhang “This led to a fourfold reduction of the energy spread and improved the emittance sixfold, yielding the best beam parameters of a terahertz accelerator so far.”
The net energy gain of the electrons that were injected with an energy of 55 kiloelectron volts (keV) was 70 keV. “This is the first energy boost greater than 100 percent in a terahertz powered accelerator,” emphasised Zhang. The coupled device produced an accelerating field with a peak strength of 200 million Volts per metre (MV/m) – close to state-of-the-art strongest conventional accelerators. For practical applications this still has to be significantly improved. “Our work shows that even a more than three times stronger compression of the electron bunches is possible. Together with a higher terahertz energy, acceleration gradients in the regime of gigavolts per metre seem feasible,” summarized Zhang. “The terahertz concept thus appears increasingly promising as a realistic option for the design of compact electron accelerators.”
###
The achieved progress is also central for the ERC funded project AXSIS (frontiers in Attosecond X-ray Science: Imaging and Spectroscopy) at CFEL, which pursues short pulse X-ray spectroscopy and imaging of complex biophysical processes, where the short X-ray pulses are generated with THz based electron accelerators. CFEL is a joint venture of DESY, the University of Hamburg and the Max Planck Society.
DESY is one of the world’s leading particle accelerator centres. Researchers use the large?scale facilities at DESY to explore the microcosm in all its variety – ranging from the interaction of tiny elementary particles to the behaviour of innovative nanomaterials and the vital processes that take place between biomolecules to the great mysteries of the universe. The accelerators and detectors that DESY develops and builds at its locations in Hamburg and Zeuthen are unique research tools. DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association, and receives its funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (90 per cent) and the German federal states of Hamburg and Brandenburg (10 per cent).
Reference:
Femtosecond phase control in high field Terahertz driven ultrafast electron sources; Dongfang Zhang, Arya Fallahi, Michael Hemmer, Hong Ye, Moein Fakhari, Yi Hua, Huseyin Cankaya, Anne-Laure Calendron, Luis E. Zapata, Nicholas H. Matlis, Franz X. Kärtner; Optica, 2019; DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000872
Media Contact
Dr. Thomas Zoufal
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




