Using an infrared photodiode pointed to the sky, a new device harvests energy from the temperature difference between Earth and near absolute zero temperatures of deep space.
Credit: Masashi Ono
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 6, 2019 — The obvious drawback of solar panels is that they require sunlight to generate electricity. Some have observed that for a device on Earth facing space, which has a frigid temperature, the chilling outflow of energy from the device can be harvested using the same kind of optoelectronic physics we have used to harness solar energy. New work, in a recent issue of Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, looks to provide a potential path to generating electricity like solar cells but that can power electronics at night.
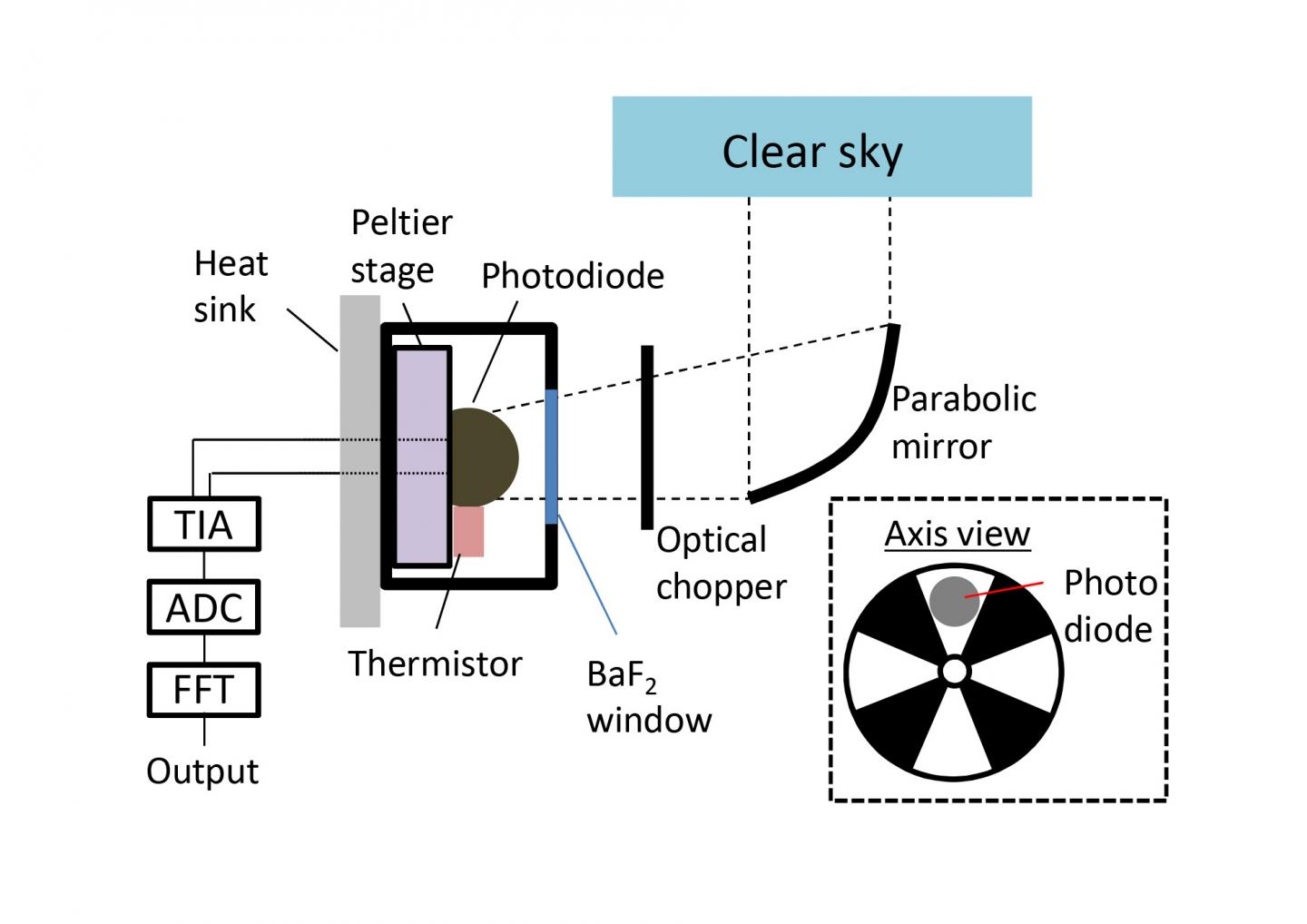
An international team of scientists has demonstrated for the first time that it is possible to generate a measurable amount of electricity in a diode directly from the coldness of the universe. The infrared semiconductor device faces the sky and uses the temperature difference between Earth and space to produce the electricity.
“The vastness of the universe is a thermodynamic resource,” said Shanhui Fan, an author on the paper. “In terms of optoelectronic physics, there is really this very beautiful symmetry between harvesting incoming radiation and harvesting outgoing radiation.”
In contrast to leveraging incoming energy as a normal solar cell would, the negative illumination effect allows electrical energy to be harvested as heat leaves a surface. Today’s technology, though, does not capture energy over these negative temperature differences as efficiently.
By pointing their device toward space, whose temperature approaches mere degrees from absolute zero, the group was able to find a great enough temperature difference to generate power through an early design.
“The amount of power that we can generate with this experiment, at the moment, is far below what the theoretical limit is,” said Masashi Ono, another author on the paper.
The group found that their negative illumination diode generated about 64 nanowatts per square meter, a tiny amount of electricity, but an important proof of concept, that the authors can improve on by enhancing the quantum optoelectronic properties of the materials they use.
Calculations made after the diode created electricity showed that, when atmospheric effects are taken into consideration, the current device can theoretically generate almost 4 watts per square meter, roughly one million times what the group’s device generated and enough to help power machinery that is required to run at night.
By comparison, today’s solar panels generate 100 to 200 watts per square meter.
While the results show promise for ground-based devices directed to the sky, Fan said the same principle could be used to recover waste heat from machines. For now, he and his group are focusing on improving their device’s performance.
###
The article, “Experimental demonstration of energy harvesting from sky using the negative illumination effect of a semiconductor photodiode,” is authored by Masashi Ono, Parthiban Santhanam, Wei Li, Bo Zhao and Shanhui Fan. The article appeared in Applied Physics Letters on April 23, 2019 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5089783). It can be accessed at http://aip.
Media Contact
Wendy Beatty
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




