Credit: Copyright © 2021, Yuji Enomoto, Shinshu University
It has been documented over hundreds of years that various electromagnetic anomalies occur during a few weeks before the occurrence of a large earthquake. These electromagnetic anomalies are variations that appear in telluric current, geomagnetism, electromagnetic waves etc. before the earthquake.
Although there are various models to explain the mechanism, the large current generated at the source was not fully explained. For example, many researchers thought that the stress applied to the fault produced an electric current, but the stress applied to the fault takes place over hundreds or thousands of years before the occurrence of the earthquake. It is a common belief among seismologists that it is impossible for the stress to suddenly increase and generate a large current just before the earthquake, and therefore the mechanism had not yet been explained.
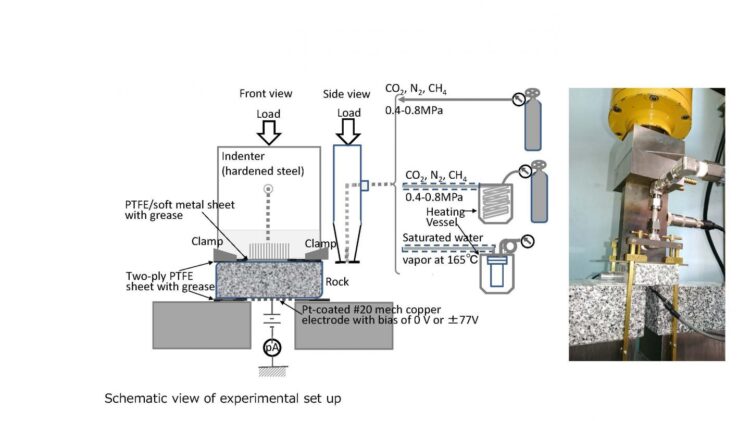
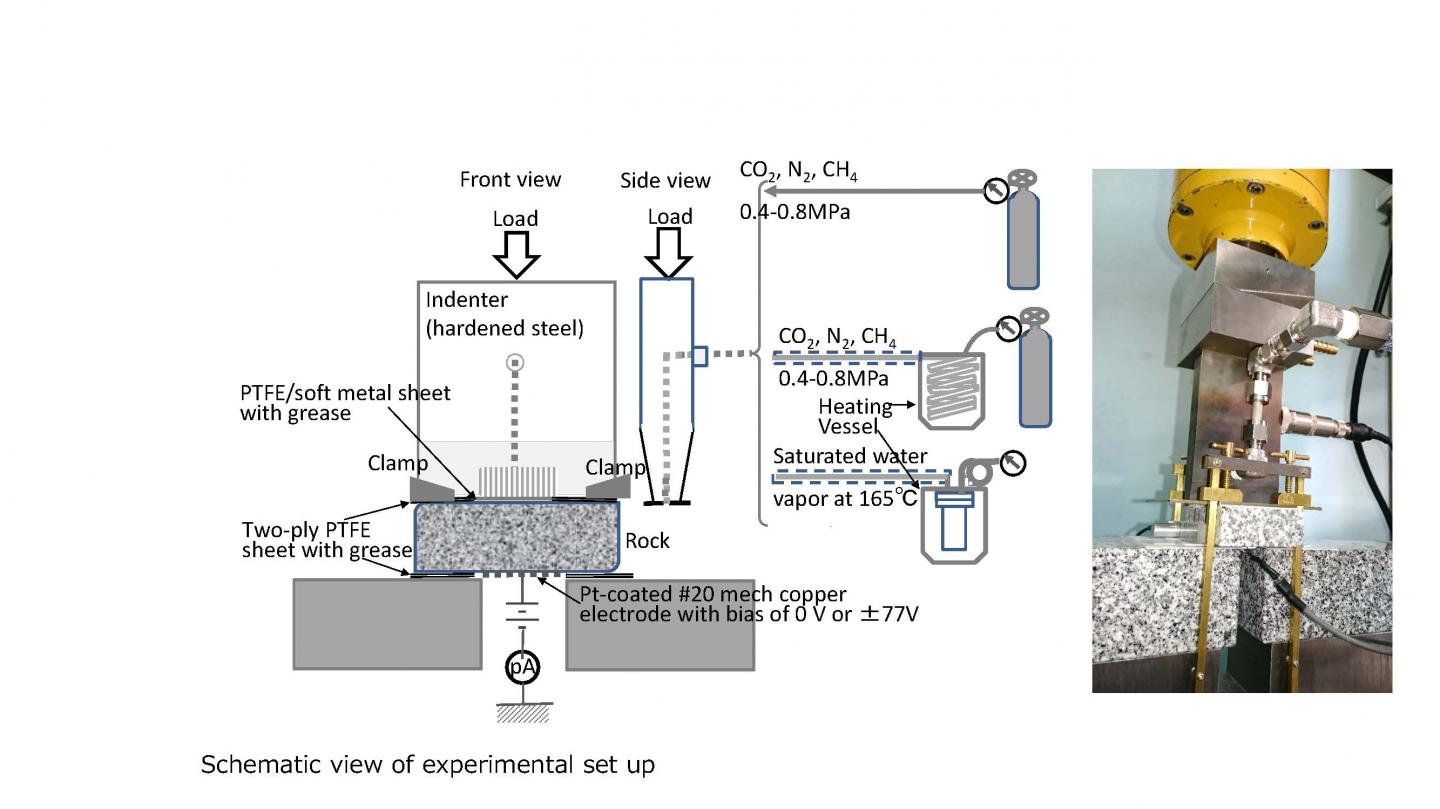
To resolve this mystery, Shinshu University and Genesis Research Institute, Inc. conducted a joint research project on earthquake-preceding phenomena under the leadership of Professor Emeritus of Shinshu University, Dr. Yuji Enomoto. The research group made the following hypothesis and conducted laboratory experiments on indoor rock fracture and gas-electric interactions to solve the mystery of electromagnetic anomalies.
In the area that is at the epicenter of a seismic fault, a fault-valve forms before the next earthquake occurs. It is believed that dense layers in the crust are formed over time. The fluid, including some gases such as water that springs up from the vicinity is trapped by the fault valve and stays there. When the shear stress applied to the fault or the pressure of the stagnant reserved fluid reaches criticality, the fault valve cracks, the high-pressure fluid rises along the fault, and the pressure gradually decreases.
As the pressure decreases, carbon dioxide or methane that are now dissolved in the fluid are degassed at once, expanding in volume and expanding the cracks. The model considers the fault becomes fragile and the rupture accelerates, leading to an earthquake. The gas becomes electrified in the process. That is, it is charged with electricity. The trapped electrons in the defects are suddenly released due to the thermal stimulus and attached to gas molecules. Because it is negatively charged, a current is generated as the gas moves.
In the lab, several types of rock, including granite, gabbro, quartz diorite and basalt were tested. A simple estimation found that there is a high possibility that a large current will be generated immediately before the earthquake, depending on the earthquake magnitude.
This supports the above-mentioned hypothesis that fault rupture progresses just before an earthquake, and the invading gas is charged and forms a large current, causing various electromagnetic anomalies. In the future, the group plan to carry out field observations to verify this model.
###
Media Contact
Hitomi Thompson
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.