Credit: Akio Kimura, Hiroshima University
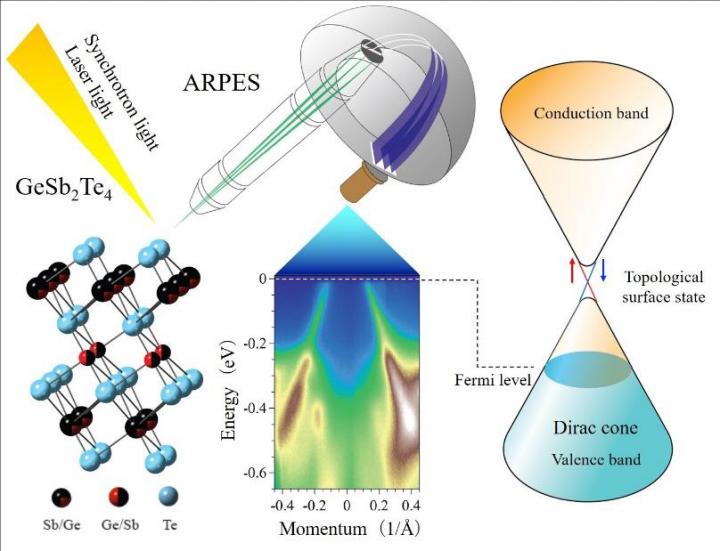
Researchers have found electrons that behave as if they have no mass, called Dirac electrons, in a compound used in rewritable discs, such as CDs and DVDs. The discovery of “massless” electrons in this phase-change material could lead to faster electronic devices.
The international team published their results on July 6 in ACS Nano, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The compound, GeSb2Te4, is a phase-change material, meaning its atomic structure shifts from amorphous to crystalline under heat. Each structure has individual properties and is reversible, making the compound an ideal material to use in electronic devices where information can be written and rewritten several times.
“Phase-change materials have attracted a great deal of attention owing to the sharp contrast in optical and electrical properties between their two phases,” said paper author Akio Kimura, professor in the Department of Physical Sciences in the Graduate School of Science and the Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering at Hiroshima University. “The electronic structure in the amorphous phase has already been addressed, but the experimental study of the electronic structure in the crystalline phase had not yet been investigated.”
The researchers found that the crystalline phase of GeSb2Te4 has Dirac electrons, meaning it behaves similarly to graphene, a conducting material that consists of a single layer of carbon atoms. They also found that the surface of the crystalline structure shares characteristics with a topological insulator, where the internal structure remains static while the surface conducts electrical activity.
“The amorphous phase shows a semiconducting behavior with a large electrical resistivity while the crystalline phase behaves like a metallic with a much lower electrical resistivity,” said Munisa Nurmamat, paper author and assistant professor in the Department of Physical Sciences in the Graduate School of Science and the Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering at Hiroshima University. “The crystalline phase of GeSb2Te4 can be viewed as a 3D analogue of graphene.”
Graphene is already considered by researchers to be a high-speed conducting material, according to Nurmamat and Kimura, but its inherently low on- and off-current ratio limits how it is applied in electronic devices. As a 3D version of graphene, GeSb2Te4 combines speed with flexibility to engineer the next generation of electrical switching devices.
###
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Tomsk State University competitiveness improvement program, Saint Petersburg University, the Russian Science Foundation and the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation.
Other contributors include Kazuaki Okamoto, Siyuan Zhu, Takeo Miyashita, Xiaoxiao Wang, Kazuki Sumida, all with the Department of Physical Sciences in the Graduate School of Science at Hiroshima University; Tatiana V. Menshchikova, Igor P. Rusinov and Vladislav O. Korostelev, all with Tomsk State University; Koji Miyamoto, Taichi Okuda, Eike F. Schwier and Keyna Shimada, all with the Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center at Hiroshima University; Yukiaki Ishida and Shik Shin, both with the Institute for Solid State Physics at the University of Tokyo; Mao Ye of the State Key Laboratory of Functional Materials for Informatics at the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences; Ziya S. Aliev of the Azerbaijan State Oil and Industry University in Azerbaijan; Mahammad B. Babanly of the Institute of Physics Catalysis and Inorganic Chemistry in Azerbaijan; Imamaddin R. Amiraslanov of the Institute of Physics and Baku State University in Azerbaijan; Evgueni V. Chulkov of Donostia International Physics Center; Konstantin A Kokh of V.S. Sobolev Institute of Geology and Minerology, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences; and Oleg E. Tereschenko of the A.V. Rzhanov Institute of Semiconductor Physics, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences.
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 4 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan. English website: https:/
Media Contact
Norifumi Miyoakwa
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




