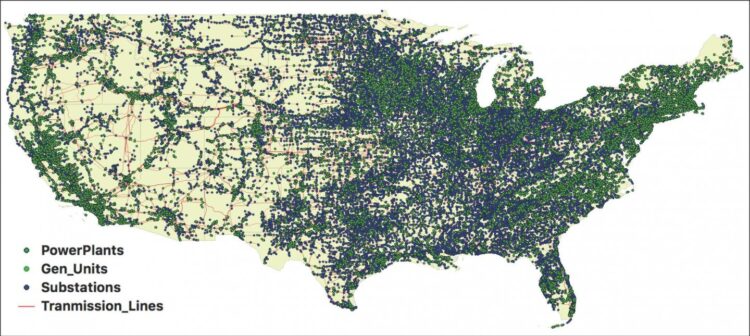
Credit: Dakota Thompson/Dartmouth
A new Dartmouth Engineering study shows that integrating renewable energy into the American Electric Power System (AEPS) would enhance the grid’s resilience, meaning a highly resilient and decarbonized energy system is possible. The researchers’ analysis is based upon the incremental incorporation of architectural changes that would be required to integrate renewable energy into AEPS.
The paper, “A Hetero-functional Graph Resilience Analysis of the Future American Electric Power System,” was recently published by IEEE Access.
“We concluded that there are no structural trade-offs between grid sustainability and resilience enhancements, meaning these strategic goals can be pursued simultaneously,” said Principal Investigator Amro Farid, a professor at Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth and research affiliate at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
“Whether you are of one political inclination or another, value resilience or sustainability, the efforts are entirely aligned and should serve as the basis for a bipartisan consensus on the transformation of the electric power grid,” said Farid.
The results of the structural analysis are the first to take into account the hetero-functionality of the grid’s resources, including renewable energy, using a new method that uniquely captures the true connectedness and capabilities of the grid. Using the novel hetero-functional graph theory, which Farid has been developing for over a decade, the researchers analyzed more than 175,000 energy resources throughout the United States such as power plants, substations, and transmission lines.
“Through the hetero-functional graph theory analysis of the American Electric Power Systems, we were better able to track the systems capabilities and structural resilience as the AEPS underwent both attacks and developments,” said first author Dakota Thompson, a Dartmouth Engineering PhD candidate. Dartmouth Engineering alumnus Wester Schoonenberg also contributed to the study.
The authors received funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF) as part of the American Multi-Modal Energy System (AMES) project, which supported this work.
The researchers are already working on their next project: developing a synthetic model of the AMES, including electric power, oil, natural gas, and coal infrastructure, so that the research community can study how the model can evolve to meet current and future needs.
###
Media Contact
Julie Bonette
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.