Credit: POSTECH
Alchemy, which attempted to turn cheap metals such as lead and copper into gold, has not yet succeeded. However, with the development of alloys in which two or three auxiliary elements are mixed with the best elements of the times, modern alchemy can produce high-tech metal materials with high strength, such as high entropy alloys. Now, together with artificial intelligence, the era of predicting the crystal structure of high-tech materials has arrived without requiring repetitive experiments.
A joint research team of Professor Ji Hoon Shim and Dr. Taewon Jin (first author, currently at KAIST) of POSTECH’s Department of Chemistry, and Professor Jaesik Park of POSTECH Graduate School of Artificial Intelligence have together developed a system that predicts the crystal structures of multi-element alloys with expandable features without needing massive training data. These research findings were recently published in Scientific Reports.
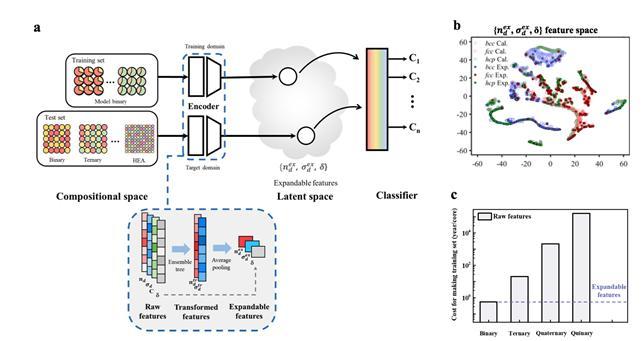
Properties of solid-state materials depend on their crystal structures. In solid solution high entropy alloy (HEA) – a material that has the same crystal structure but continuously changes its chemical composition within a certain range – mechanical properties such as strength and ductility vary depending on the structural phase. Therefore, predicting the crystal structure of a material plays a crucial role in finding new functional materials. Methods to predict the crystal structure through machine learning have been studied recently, but there is an enormous cost attached to prepare the data necessary for training.
To this, the research team designed an artificial intelligence model that predicts the crystal structure of HEAs through expandable features and binary alloy data instead of the conventional models that use more than 80% of the HEA data in the training process. This is the first study to predict the crystal structure of multi-element alloys, including HEAs, with an artificial intelligence model trained only with the compositions and structural phase data of binary alloys.
Through experiments, the researchers confirmed that the structural phase of the multi-element alloy was predicted with an accuracy of 80.56%, even though the multi-element alloy data were not involved in the training process. In the case of HEAs, it was predicted with an accuracy of 84.20%. According to the method developed by the research team, it is anticipated that the calculation cost can be saved by about 1,000 times compared to previous methods.
“An immense dataset is required to apply an artificial intelligence methodology to the development of new materials,” explained Professor Ji Hoon Shim who led the research. “This study is significant in that it enables to effectively predict the crystal structure of advanced materials without securing a huge data set.”
###
The research was conducted with the support from the National Research Foundation, POSTECH Graduate School of Artificial Intelligence Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP) and the SRC Center for Quantum Dynamics.
Media Contact
Jinyoung Huh
[email protected]
Original Source
http://postech.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




