A paper by Kazan Federal University’s Sergey Kharintsev appeared in Optics Letters
Credit: Kazan Federal University
The research was supported by a Russian Science Foundation’s grant under the title “Synthesis and research of a new class of nanocomposite ceramics with degenerate dielectric permeability for opto-plasmonic applications.”
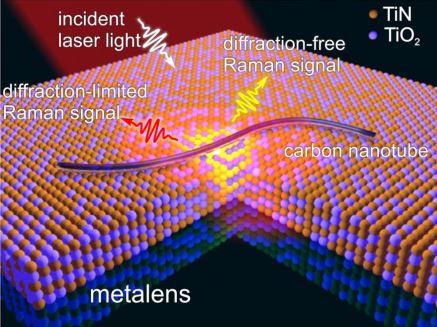
A metalens described in the article is a thin composite metal-dielectric film placed on a dielectric substrate; the width is several dozen nanometers.
“The light has a wave nature, so there is a diffraction limit which confines the resolution of traditional optical microscopy,” explains Kharintsev. “Our metalens is an optical device capable of surpassing that diffraction limit. Such a solution paves way for using optical technologies in nanoscale integral circuits and sensors.”
The ultra-high resolution is based on an unusual behavior of the metalens in optical and infrared ranges.
“The material part of the dielectric constant oscillates near zero. This property can be used to enhance stimulated Raman scattering of light in a spatially limited medium illuminated by low-intensity continuous laser light. For most materials found in nature, nonlinear effects are weak, and to observe them it is necessary to increase the length of the medium (for example, using optical fibers) and / or to increase the laser pump power (using high-power pulsed lasers).
“We used a 50 nm thick titanium oxy nitride (TiON) film as a disordered nonlinear medium. The film was synthesized by magnetron sputtering and subsequent oxidation in air. As a result of a two-stage procedure, metal (TiN) and dielectric (TiO2) nanoparticles were formed in the film. An increase in the amplitude of the Stokes wave in a TiN / TiO2 film occurs due to the enhancement of the cubic susceptibility because of localized plasmon resonance and a small refractive index of the effective medium. Such metal-insulator nanocomposite films having several epsilon-near-zero frequencies in the visible and infrared ramges have found application in creating broadband metal technologies providing resolution beyond the limits of light diffraction,” adds the author.
Kazan University employees have succeeded in visualizing 40 nm multiwall carbon nanotubes scattered along the surface of the metalens created by them, and the resolution was below 100 nm.
“Nanocomposite epsilon-near-zero film works as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate, and it helps not only enhance the scattered signal, but also achieve beyond-diffraction resolutions. Metalenses and ENZ films can be used to create broadband absorbers for solar panels,” concludes Dr. Kharintsev.
###
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




