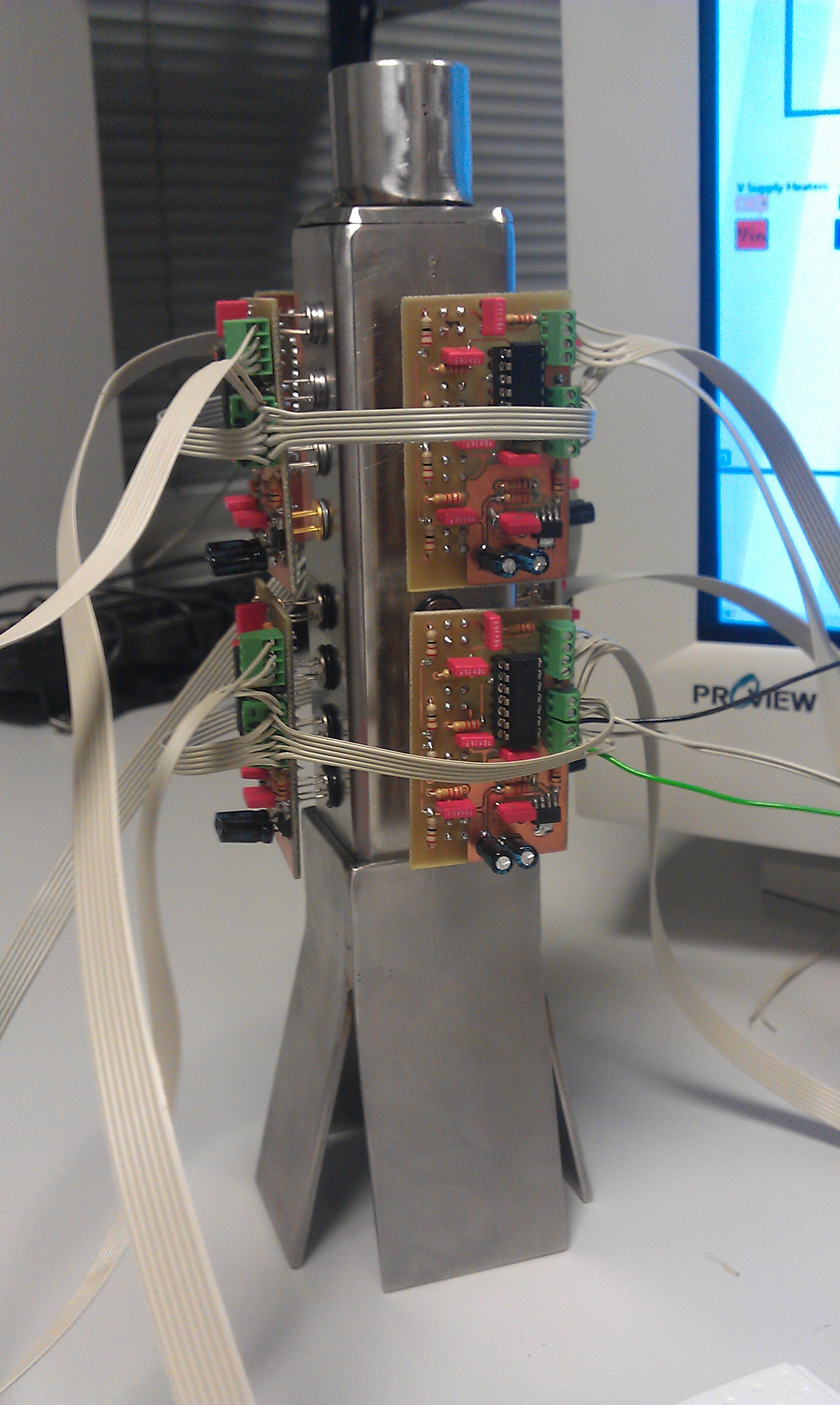
Swedish and Spanish engineers have created a system of sensors that detects fruit odours more effectively than the human sense of smell. For now, the device can distinguish between the odorous compounds emitted by pears and apples.
Researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV, Spain) and the University of Gävle (Sweden) have created an electronic nose with 32 sensors that can identify the odours given off by chopped pears and apples.
“The fruit samples are placed in a pre-chamber into which an air flow is injected which reaches the tower with the sensors which are metal oxide semiconductors that detect odorous compounds such as methane or butane,” explained José Pelegrí Sebastiá, UPV researcher at the Gandia campus and co-author of the paper.
Next, software is used to gather real time data and the information is processed through classification algorithms. The results can be viewed on a 3D graph which distinguishes between the pear and apple scores.
This study, which is published in the ‘Sensors and Actuators A’ journal, is the starting point for new research the team is already involved in to develop multisensor systems that increase the capacity to differentiate complex mixtures of volatile substances.
“One example would be the wine making sector,” Pelegrí commented, “where an electronic nose capable of distinguishing the quality or type of grape or recognising the vintage a wine belongs to would be very useful.”
Other lines of research focus on the field of biomedicine. Some studies have shown that trained dogs can detect cancerous tumours, such as lung cancer, by smelling a person’s breath.
If this is true, and an electronic nose can detect which substances the animals recognise, then we could diagnose the disease earlier and increase patients’ survival rates.
Story Source:
The above story is reprinted from materials provided by Plataforma SINC, via AlphaGalileo.