Just one well-placed slice into a particularly pungent onion can send even the most seasoned chef running for a box of tissues. Now, this humble root vegetable is proving its strength outside the culinary world as well — in an artificial muscle created from onion cells. Unlike previous artificial muscles, this one, created by a group of researchers from National Taiwan University, can either expand or contract to bend in different directions depending on the driving voltage applied. The finding is published this week in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
The concept of artificial muscle made from onion epidermal cell. Photo Credit: Shih Lab, National Taiwan University
“The initial goal was to develop an engineered microstructure in artificial muscles for increasing the actuation deformation [the amount the muscle can bend or stretch when triggered],” said lead researcher Wen-Pin Shih. “One day, we found that the onion’s cell structure and its dimensions were similar to what we had been making.” Shih lead the study along with graduate student Chien-Chun Chen and their colleagues.
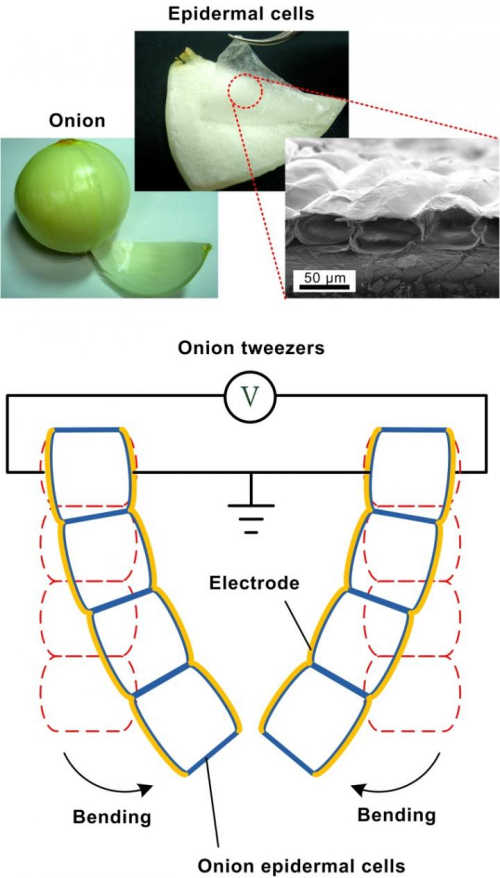
The onion epidermis — the fragile skin found just beneath the onion’s surface — is a thin, translucent layer of blocky cells arranged in a tightly-packed lattice. Shih and his colleagues thought that onion epidermal cells might be a viable candidate for the tricky task of creating a more versatile muscle that could expand or contract while bending. To date, Shih said, artificial muscles can either bend or contract, but not at the same time.
The researchers treated the cells with acid to remove the hemicellulose, a protein that makes the cell walls rigid. Then, they coated both sides of the onion layer with gold. When current flowed through the gold electrodes, the onion cells bent and stretched much like a muscle.
“We intentionally made the top and bottom electrodes a different thickness so that the cell stiffness becomes asymmetric from top to bottom,” said Shih. The asymmetry gave the researchers control over the muscle’s response: a low voltage made them expand and flex downwards, towards the thicker bottom layer. A high voltage, on the other hand, caused the cells to contract and flex upwards, towards the thinner top layer.
“We found that the single-layer lattice structure can generate unique actuation modes that engineered artificial muscle has never achieved before,” said Shih.
To demonstrate their device’s utility, the researchers combined two onion muscles into a pair of tweezers, which they used to pick up a cotton ball. In the future, they hope to increase the lifting power of their artificial muscles. “Our next step is to reduce the driving voltage and the actuating force,” said Shih.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by The American Institute of Physics.