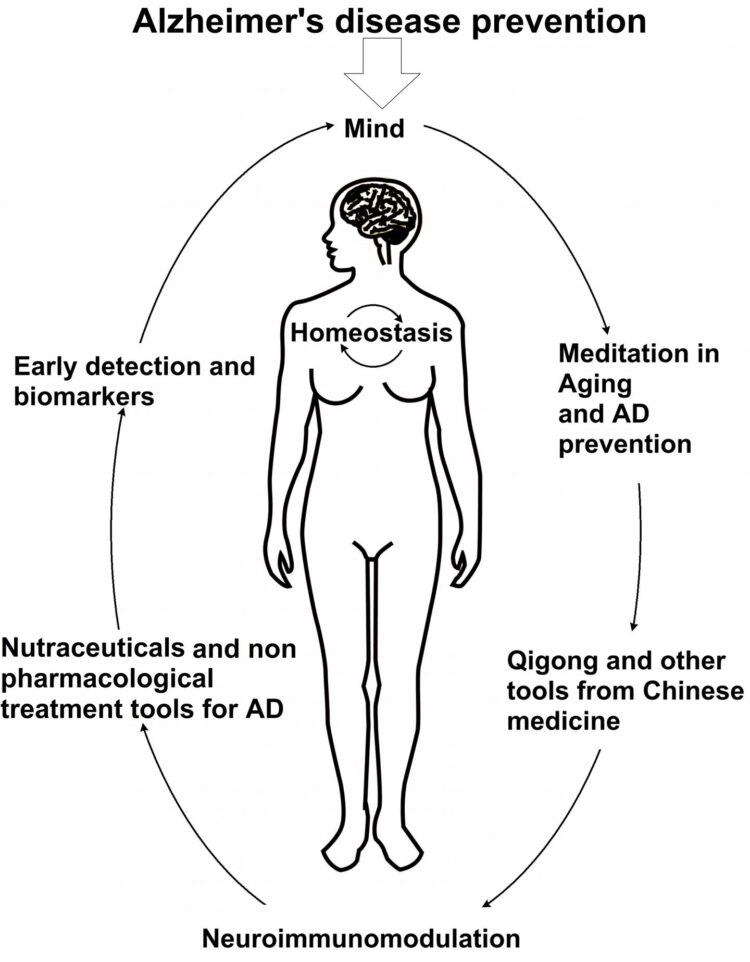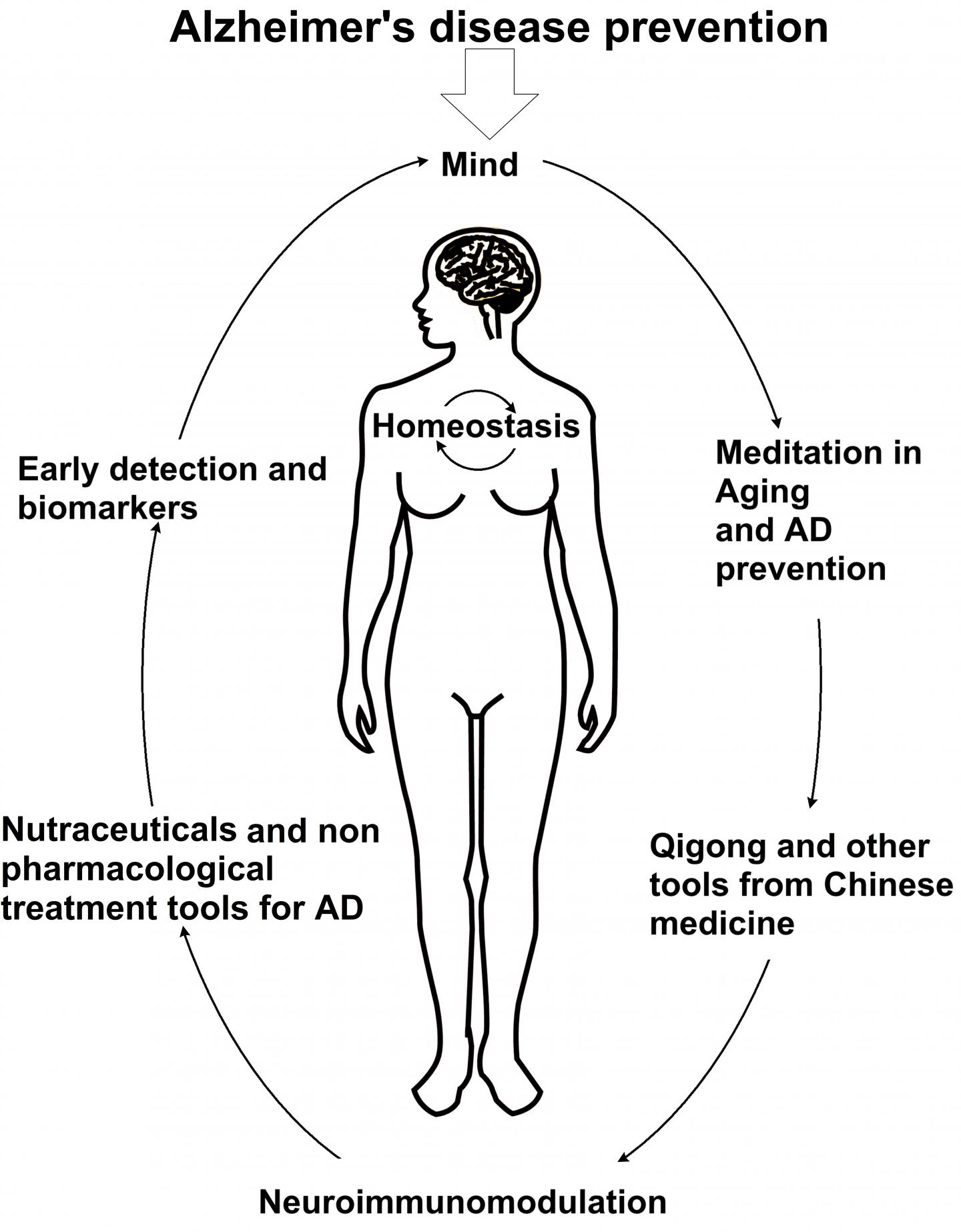
Credit: Dr. Ricardo B. Maccioni
Amsterdam, December 29, 2020 – This new pioneering study by Prof. Ricardo Maccioni and coworkers of the International Center for Biomedicine, “New Frontiers in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer´s disease” was published in the special issue of Latin American investigators of the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease(JAD). This supports a growing body of research on the Alzheimer’s prevention value of an integrated approach using daily exercise, nutraceuticals, oriental practices such as QiGong along with meditation, and social life. These elements of a healthy style of life are supplemented with the use of reliable biomarkers for early detection of this disease that allows the detection of Alzheimer up to 20 years before symptomatic phase of the disease.
One of the major puzzles in medical research and public health systems worldwide is Alzheimer’s disease (AD), reaching nowadays a prevalence of nearly 50 million people. AD is a multifactorial brain disorder characterized by progressive cognitive impairment, apathy, and mood disorders. The main risk of AD is aging. Studies suggest that AD is a break from normal aging with changes in the powerful functional capacities of neurons as well as in the mechanisms of neuronal protection. There are factors that are determinants of the functional losses during aging, an important part is played by epigenetic components. Thus, the action of genes that confer susceptibility to AD can be mitigated with healthy lifestyles, physical exercise, balanced nutrition, avoiding molecules harmful to health and drugs. An active social life and practicing activity during the latter years of aging, to achieve health in advanced age.
In this context, an important path has been opened towards AD prevention considering the factors mentioned above and the control of neuroinflammatoy events (Figure 1). On the basis of medical evidence we conclude that a rational integration of all these factor exert a preventive action against neuronal degeneration in AD providing a better quality of life. Prevention as well as innovative screening programs for an early detection of the disease using reliable biomarkers are becoming critical to control the disease. Our own data suggest that AD is a clear break with normal aging; understanding that this process requires a systems of a biology-based approach. In addition, the failure of traditional pharmacological treatments and search for new drugs has stimulated the emergence of nutraceutical compounds in the context of a “multitarget” therapy, as well as non-pharmacological approaches shown to be effective in aging, and applied to AD control. An integrated approach involving all these preventive factors combined with novel multitarget therapeutic approaches should pave the way for the future control of the disease.
###
Media Contact
Diana Murray
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.