New software predicts cell fate
Credit: Helmholtz Zentrum München
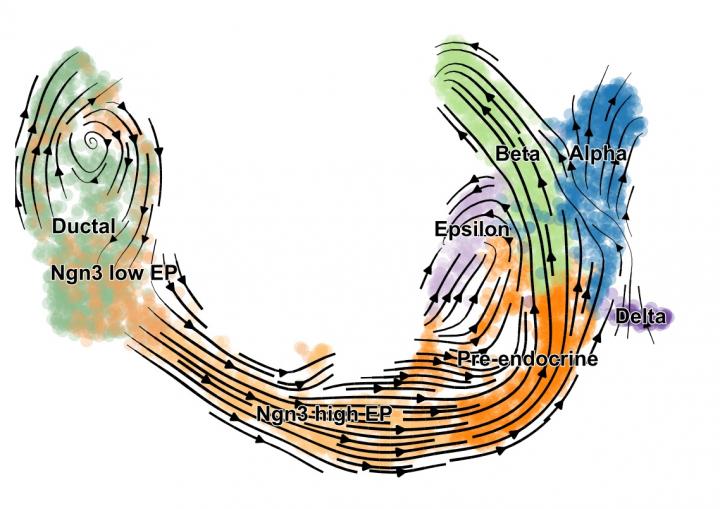
Traditional single-cell sequencing methods help to reveal insights about cellular differences and functions – but they do this with static snapshots only rather than time-lapse films. This limitation makes it difficult to draw conclusions about the dynamics of cell development and gene activity. The recently introduced method “RNA velocity” aims to reconstruct the developmental trajectory of a cell on a computational basis (leveraging ratios of unspliced and spliced transcripts). This method, however, is applicable to steady-state populations only. Researchers were therefore looking for ways to extend the concept of RNA velocity to dynamic populations which are of crucial importance to understand cell development and disease response.
Single-cell velocity
Researchers from the Institute of Computational Biology at Helmholtz Zentrum München and the Department of Mathematics at TUM developed “scVelo” (single-cell velocity). The method estimates RNA velocity with an AI-based model by solving the full gene-wise transcriptional dynamics. This allows them to generalize the concept of RNA velocity to a wide variety of biological systems including dynamic populations.
“We have used scVelo to reveal cell development in the endocrine pancreas, in the hippocampus, and to study dynamic processes in lung regeneration – and this is just the beginning”, says Volker Bergen, main creator of scVelo and first author of the corresponding study in Nature Biotechnology.
With scVelo researchers can estimate reaction rates of RNA transcription, splicing and degradation without the need of any experimental data. These rates can help to better understand the cell identity and phenotypic heterogeneity. Their introduction of a latent time reconstructs the unknown developmental time to position the cells along the trajectory of the underlying biological process. That is particularly useful to better understand cellular decision making. Moreover, scVelo reveals regulatory changes and putative driver genes therein. This helps to understand not only how but also why cells are developing the way they do.
Empowering personalized treatments
AI-based tools like scVelo give rise to personalized treatments. Going from static snapshots to full dynamics allows researchers to move from descriptive towards predictive models. In the future, this might help to better understand disease progression such as tumor formation, or to unravel cell signaling in response to cancer treatment.
“scVelo has been downloaded almost 60.000 times since its release last year. It has become a stepping-stone tooltowards the kinetic foundation for single-cell transcriptomics”, adds Prof. Fabian Theis, who conceived the study and serves as Director at the Institute for Computational Biology at Helmholtz Zentrums München and Chair for Mathematical Modeling of Biological Systems at TUM.
###
Media Contact
Volker Bergen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




