Researchers from Kanazawa University find that propionic acid-class NSAIDs are conjugated with CoA by hepatic ACSL1, leading to liver toxicity via covalent binding with hepatic proteins
Credit: Kanazawa University
Kanazawa, Japan – Liver injury is a rare side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are frequently used for daily pain control. This toxicity has been regarded as a “black box” and is mainly managed by an empirical approach, but there is not a clear understanding of the mechanism. Now, researchers from Japan have found that a bit of attention to the types and frequencies of NSAIDs could help people avoid liver injury.
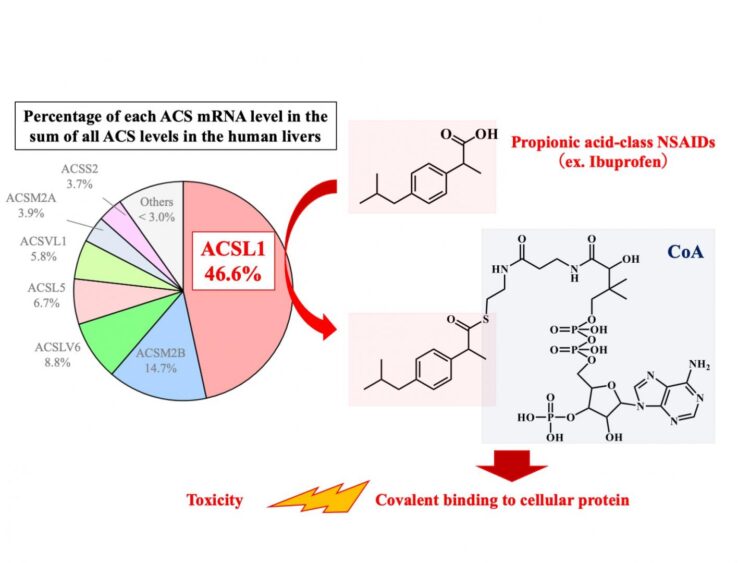
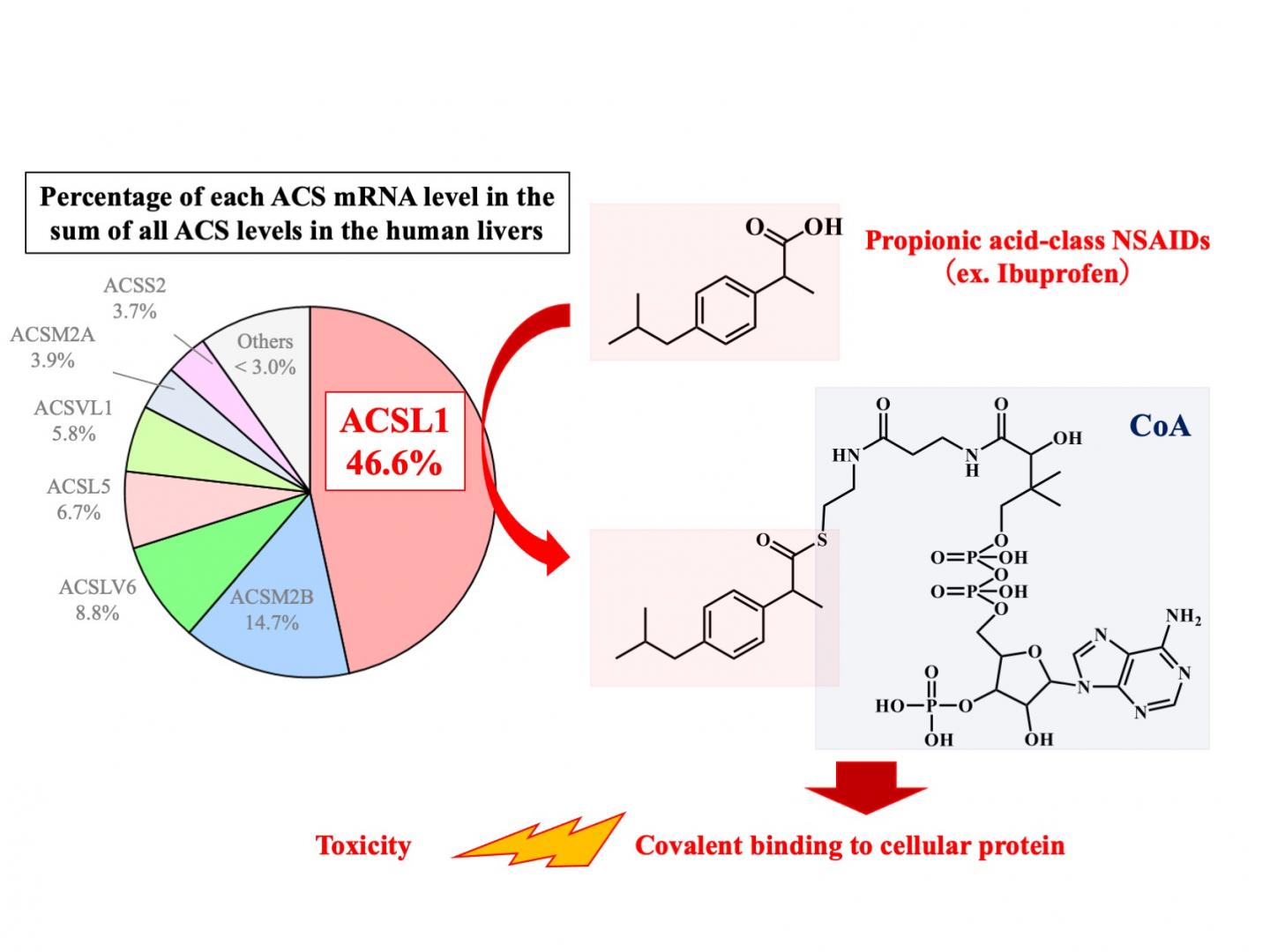
In a study published recently in Biochemical Pharmacology, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed that specific NSAIDs, including ibuprofen, are metabolized by one of the acyl-CoA synthetases, ACSL1, in a manner that can have toxic effects.
NSAIDs containing a specific chemical group, carboxylic acid, can form “conjugates” with coenzyme A (CoA) or glucuronic acid. Although these conjugates are suspected to cause toxicities, such as liver injury and anaphylaxis, the processes involved in CoA conjugation have been poorly understood, and researchers at Kanazawa University have aimed to address this.
“NSAID toxicities including liver injury and anaphylaxis had been considered to be caused by conjugates with glucuronic acid, another types of metabolite,” says senior author of the study, Miki Nakajima. “Because a recent study demonstrated a robust interaction between ibuprofen and CoA, we wanted to investigate how a range of NSAIDs conjugated with CoA in the presence of liver enzymes.”
To do this, the researchers performed enzymatic reactions involving human liver extracts, CoA, and representative medications from each of 10 classes of NSAIDs. They used a mass spectrometry method to identify interactions between the NSAIDs and CoA.
“The difference among NSAIDs was striking,” explains Tatsuki Fukami, corresponding author. “We found that propionic acid-class NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, had robust binding interactions with CoA, whereas other NSAIDs, such as salicylic acid, did not. This selectivity was likely determined by ACSL1.”
In addition, CoA conjugates of propionic acid-class NSAIDs could strongly bind with liver proteins, while glucuronic acid conjugates of those same NSAIDs formed weaker bonds with liver proteins.
“Our findings suggest that the high covalent binding of CoA-conjugate of propionic acid-class NSAIDs to hepatocellular proteins leads to liver injury. Because there is a large interindividual variation in the hepatic expression of ACSL1 catalyzing CoA conjugation with propionic acid-class NSAIDs, this variation may account for the susceptibility to their toxicities,” says Fukami.
Because pain control is an important medical problem for many people worldwide, this new information could help pharmaceutical companies to generate pain control options with fewer risks of severe side effects.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.