The new contrast agent offers a vast improvement over traditional gadolinium-based products
Credit: Institute for Basic Science
Heart attack and stroke are the first and second leading causes of death in developed countries, respectively. As the disease often results in sudden death with few special prognostic symptoms, early diagnosis is very important. For this purpose, imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are widely used to identify the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels.
In MRI, contrast agents improve the visibility of the structures such as smaller blood vessels within the body. Just as satellites or global positioning systems (GPS) give traffic congestion information, the MRI contrast agents can give accurate information of vascular conditions such as vascular blockage and stenosis. Commonly used products are the gadolinium-based contrast agents. Free gadolinium ions have high toxicity, and thus they must be administered in chelated forms. However, even then there are some health risks of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis for patients with poor kidney functions. There have been some attempts to use paramagnetic iron-based nanoparticles as contrasting agents, but their renal clearance profile must be improved to prevent undesirable accumulation in the liver and other organs.
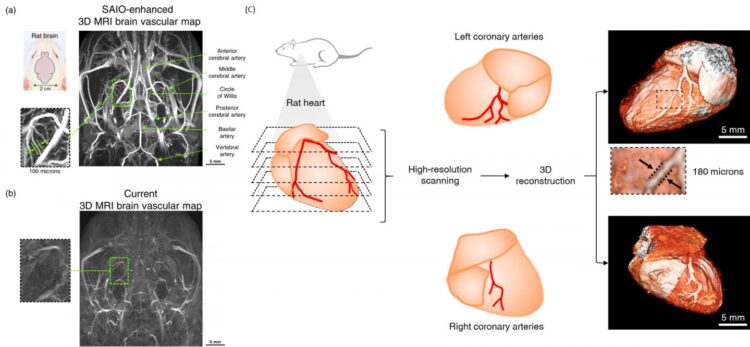
A collaborative research team led by Professor CHEON Jinwoo, the director of the Center for Nanomedicine (CNM), Institute for Basic Science (IBS) at Yonsei University, Seoul, South Korea and Professor CHOI Byoung Wook from Yonsei University College of Medicine developed a high-performance MRI contrast agent for 3D vascular mapping. The researchers developed a nanoparticle-based MRI contrast agent, called SAIO (Supramolecular Amorphous-like Iron Oxide). The particle is 5 nanometers in size, which is about 1,500 times smaller than the microvascular diameter. This allows it to circulate across blood vessels in the body.
The SAIO is a special nanoparticle that consist of a polysaccharide core made primarily with dextran cross-linked with other molecules. This core is then coated with an iron oxide surface to give it paramagnetic properties at room temperature. The hybrid nature of the SAIOs gives them both excellent biocompatibility and imaging performance. The researchers compared the contrast performance, retention, and renal clearance profile of the SAIO against Dotarem (a gadolinium-based agent) and iron oxide nanoparticles.
SAIO is one of the highest resolution imaging agents, which is 10 times more precise than the image generated using current contrast agents. It has achieved a 3D brain vascular mapping that can clearly identify brain microvessels as thin as a hair (100 microns) in animal experiments. In addition, to excellent resolution, the enhancement lasts substantially longer (>10 min) in comparison to Dotarem (
In addition to having high resolution, excretion of the contrasting agent through urine is especially important to avoid its accumulation within the body, which can cause various side effects. SAIO has an excellent renal clearance profile without accumulation in liver or spleen. It was also found that SAIO was stable without aggregation nor iron leaching for up to a year.
Director Cheon said, “SAIO is a next-generation contrast agent that satisfies both high resolution and safety at the same time” and professor Choi said, “SAIO is expected to play a vital role in increasing the accuracy of the diagnosis of cerebro-cardiovascular diseases such as stroke, myocardial infarction, angina, and dementia.”
###
The results of this study are supported by the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health & Welfare and Institute for Basic Science, Republic of Korea. The study was published on March 8th, 2021 in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Media Contact
William I. Suh
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.