Scientists at Kanazawa University combine continuum and molecular dynamics simulations to study the neutralization of excess charges during mass spectrometry, which may lead to more accurate medical, biological, and chemical tests
Credit: Kanazawa University
Mass spectrometers (MS) have become essential tools in chemistry and biology laboratories. The ability to quickly identify the chemical components in a sample allows them to take part in a diverse array of experiments, including radiocarbon dating, protein analysis, and monitoring drug metabolism.
MS instruments work by giving the analyte molecules an electric charge, and shooting them through a region of space with a uniform electric field, which curves their trajectory into a circle. The radius of the circle, which depends on the ratio of the molecule’s mass to its charge, is detected and compared with known samples. Because the method can only measure this ratio, not the mass itself, excess charges can lead to inaccurate or ambiguous results.
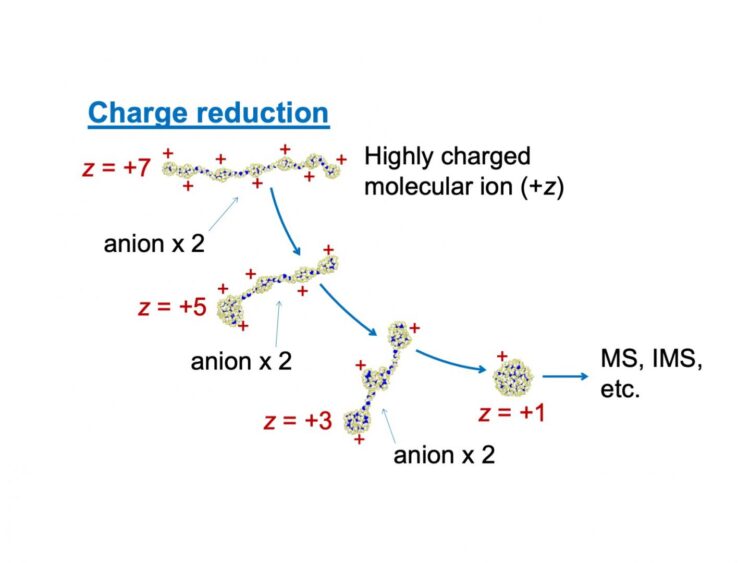
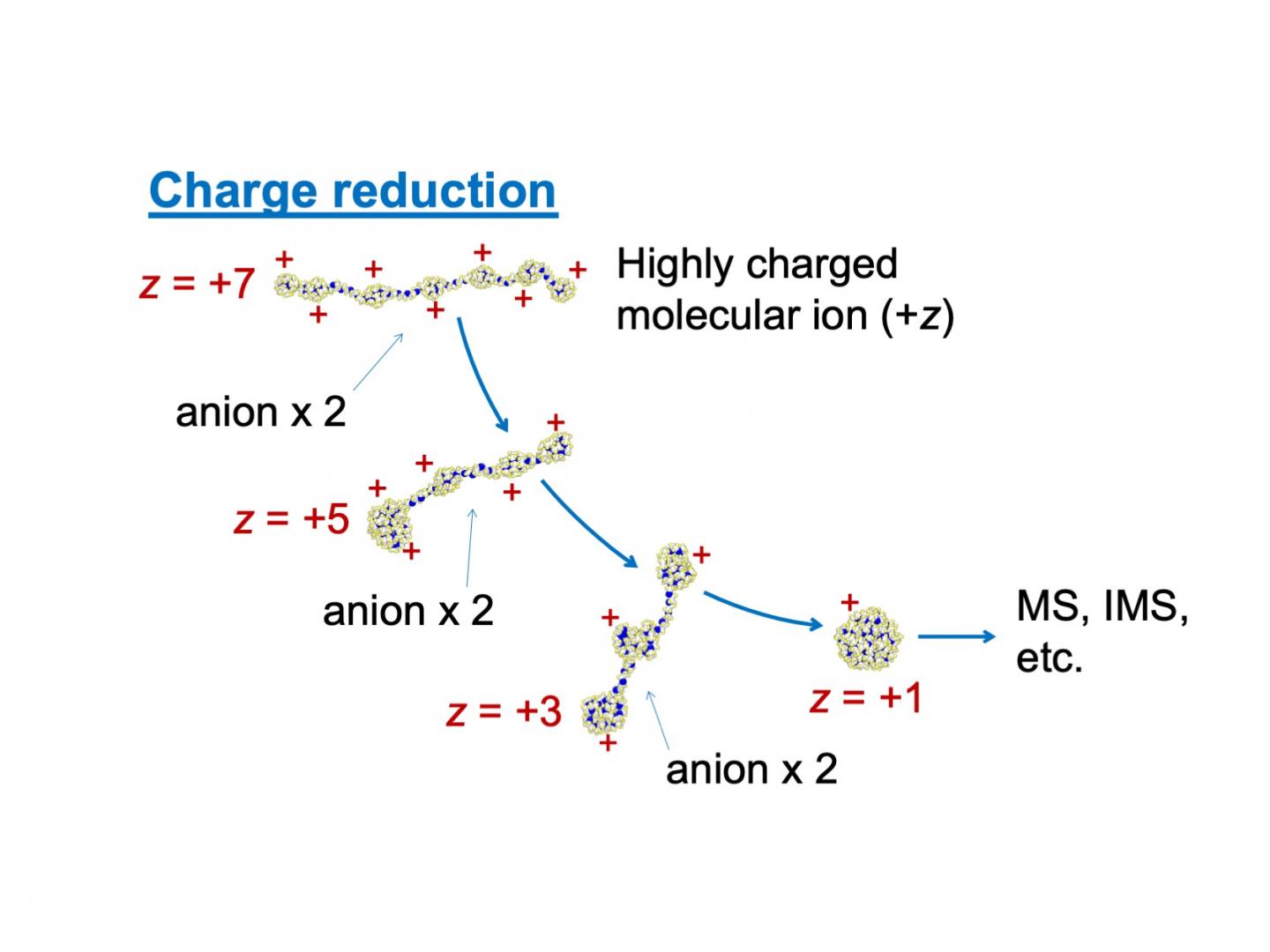
Now, a team of researchers lead by Kanazawa University used a powerful molecular dynamics simulation to better understand the effect of excess charges on molecules tested by a MS. They modeled the effect of adding molecules of the opposite charge in order to neutralize excess charge. In this case, the positive charge on polyethylene glycol (PEG) can be reduced via collision with negatively charged NO2– ions.
However, this is complicated by the fact that the likelihood of colliding depends on the amount of charge in the first place. “Charged polymers can adopt charge-state dependent structures because of electrostatic stretching,” first author Tomoya Tamadate says. For example, with small excess charge, PEG assumes a compact form. However, as the charge increased, the mutual repulsion between the positive charges causes it to straighten out.
To help speed up the calculations, the team used the “continuum approximation” method, which only started simulating all of the atoms in the NO2– molecule once it approached close enough to the PEG.
“The success of this project shows that hybrid continuum-molecular dynamics simulations can be used more generally to study collision-driven reactions molecules that can take on different conformations,” senior author Takafumi Seto says. The results can lead to more effective methods of controlling excess charge in sample molecules, which will allow for more accurate results.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.