Researchers from North Carolina State University, Duke University and the University of Copenhagen have created the world’s largest DNA origami, which are nanoscale constructions with applications ranging from biomedical research to nanoelectronics.
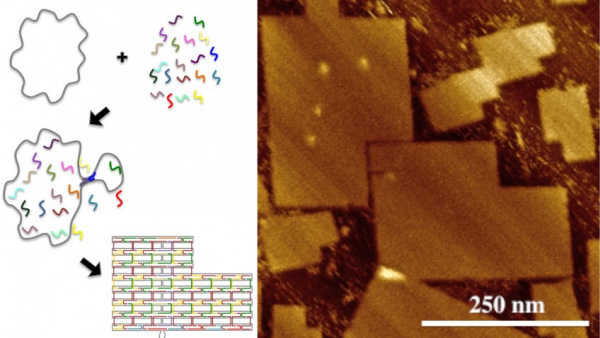
Scaffolded DNA origami utilizes numerous chemically synthesized, short DNA strands (staple strands) to direct the folding of a larger, biologically derived strand of DNA (scaffold strand). Molecular recognition (base pairing, i.e., A binds to T and G binds to C) directs the DNA to self-assemble into a specific structure as programed by the staple strand sequences. Unique staple strands produce a molecular pegboard with single-digit nanometer site-specificity precision. The atomic force microscopy image (right) demonstrates the final origami structure. Image credit: Alexandria Marchi.
“These origami can be customized for use in everything from studying cell behavior to creating templates for the nanofabrication of electronic components,” says Dr. Thom LaBean, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper describing the work.
DNA origami are self-assembling biochemical structures that are made up of two types of DNA. To make DNA origami, researchers begin with a biologically derived strand of DNA called the scaffold strand. The researchers then design customized synthetic strands of DNA, called staple strands. Each staple strand is made up of a specific sequence of bases (adenine, cytosine, thaline and guanine – the building blocks of DNA), which is designed to pair with specific subsequences on the scaffold strand.
The staple strands are introduced into a solution containing the scaffold strand, and the solution is then heated and cooled. During this process, each staple strand attaches to specific sections of the scaffold strand, pulling those sections together and folding the scaffold strand into a specific shape.
The standard for DNA origami has long been limited to a scaffold strand that is made up of 7,249 bases, creating structures that measure roughly 70 nanometers (nm) by 90 nm, though the shapes may vary.
However, the research team led by LaBean has now created DNA origami consisting of 51,466 bases, measuring approximately 200 nm by 300 nm.
“We had to do two things to make this viable,” says Dr. Alexandria Marchi, lead author of the paper and a postdoctoral researcher at Duke. “First we had to develop a custom scaffold strand that contained 51 kilobases. We did that with the help of molecular biologist Stanley Brown at the University of Copenhagen.
“Second, in order to make this economically feasible, we had to find a cost-effective way of synthesizing staple strands – because we went from needing 220 staple strands to needing more than 1,600,” Marchi says.
The researchers did this by using what is essentially a converted inkjet printer to synthesize DNA directly onto a plastic chip.
“The technique we used not only creates large DNA origami, but has a fairly uniform output,” LaBean says. “More than 90 percent of the origami are self-assembling properly.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by NC State University.