A crucial player in genomic integrity maintenance, DNA Polymerase Theta (Polθ) provides a potential synthetic lethal relationship in BRCA-deficient tumors, which are particularly prevalent in certain tumor types including triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) and ovarian cancers. In fact, BRCA-deficient tumors account for 11-16% of TNBC cases, and 10-15% of ovarian cancers. Given limited treatment options and compromised efficacy due to resistance, alternative treatment strategies including Polθ inhibitors are urgently needed.
Credit: Insilico Medicine
- Building on the anti-tumor potential of Polθ inhibition in BRCA-deficient cancers, researchers at Insilico Medicine discovered a new class of orally bioavailable Polθ inhibitors designed using generative AI.
- For molecular generation, they used both ligand-based drug design (LBDD) and structure-based drug design (SBDD) strategies within the Chemistry42 generative chemistry engine.
- The new inhibitors demonstrated strong potency and promising druglike properties, highlighting AI’s potential in medicinal chemistry for precise molecular modifications.
A crucial player in genomic integrity maintenance, DNA Polymerase Theta (Polθ) provides a potential synthetic lethal relationship in BRCA-deficient tumors, which are particularly prevalent in certain tumor types including triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) and ovarian cancers. In fact, BRCA-deficient tumors account for 11-16% of TNBC cases, and 10-15% of ovarian cancers. Given limited treatment options and compromised efficacy due to resistance, alternative treatment strategies including Polθ inhibitors are urgently needed.
Now, researchers from Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, have discovered a new class of Polθ inhibitors featuring central scaffolding rings, designed using Chemistry42, the Company’s proprietary generative AI platform. According to the findings, the AI-enabled molecules exhibited significant enzymatic and cellular potency and promising druglike properties, pointing to a novel strategy for targeting Polθ. The research was published in Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, an Elsevier peer-reviewed journal focusing on molecular chemistry and biology.
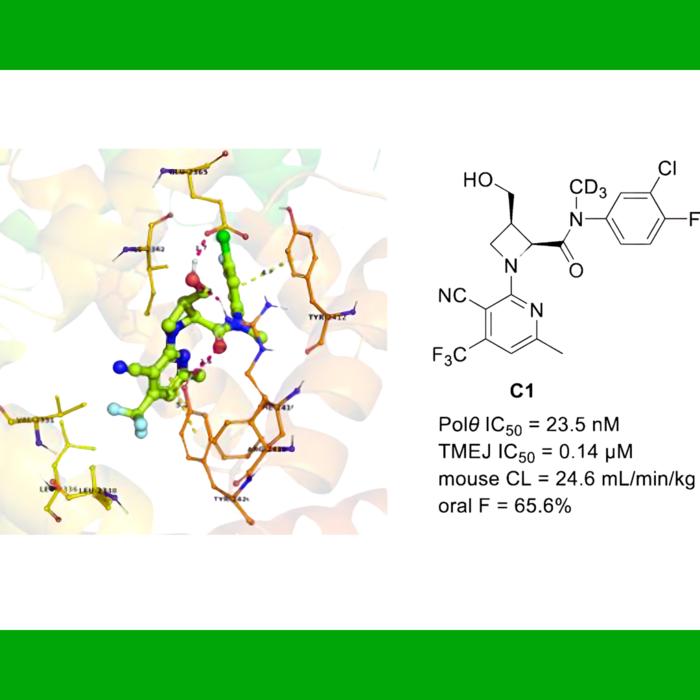
Aiming for a novel and potent Polθ inhibitor with new cores, the Insilico R&D team implemented both ligand-based drug design (LBDD) and structure-based drug design (SBDD) strategies. Based on novel central scaffold rings innovated with the help of Chemistry42, a promising lead compound was identified, and further optimization for improved potency and other druglike properties yielded 3-hydroxymethyl-azetidine derivatives as a novel class of Polθ inhibitors.
In consequent validation, a novel compound exhibited robust cellular potency in DNA repair-compromised cells, as well as favorable ADME profiles and pharmacokinetic properties in vivo. This orally bioavailable molecule shows potential as a possible treatment approach for solid cancers with BRCA1/2 mutations, and the findings demonstrate the potential of using AI in medicinal chemistry for precise molecular modifications.
Insilico Medicine is a pioneer in utilizing generative AI for drug discovery and development, and has delivered breakthroughs for healthcare in multiple disease areas, including fibrosis, cancer, immunology and aging-related diseases. Since 2021, Insilico has nominated 18 preclinical candidates in its comprehensive portfolio of over 30 assets and has advanced six pipelines to the clinical stage. Most recently, the company published a history of its lead AI-discovered and AI-designed drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, currently in Phase II clinical trials, in Nature Biotechnology.
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a global clinical-stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI, connects biology, chemistry, and clinical trial analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers, and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and generating novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases. www.insilico.com
Journal
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
DOI
10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117662
Article Title
Discovery of 3-hydroxymethyl-azetidine derivatives as potent polymerase theta inhibitors
Article Publication Date
1-Apr-2024




