The establishment of nasal mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 through a nasal vaccine could be the most efficient way to combat COVID-19 infection
Credit: Institute for Basic Science
Understanding how viral infection occurs can provide important clues for researchers to develop strategies to prevent viral transmission and develop effective therapeutic agents and vaccines. SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, enters the host cells through interaction between the virus’s spike protein and the extracellular receptor binding domain of ACE2. The viral entry into the cells is completed by various proteases, which allow the viral and cell membranes to fuse together. While it is known that the upper respiratory tract becomes compromised in the early infection, the exact types of the cells that the virus infects at the earliest stage have not yet been identified.
Led by Director KOH Gou Young, scientists from the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science, South Korea, have recently uncovered the processes involved in the earliest stages of COVID-19 infection. The group accomplished this by combining immunofluorescence staining (IFS) and single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) of the molecules that are involved in the viral entry process. Through this, Koh and his colleagues identified the exact target of the coronavirus at the cellular level by comparing the results of the subjects infected with COVID-19 with those of healthy controls.
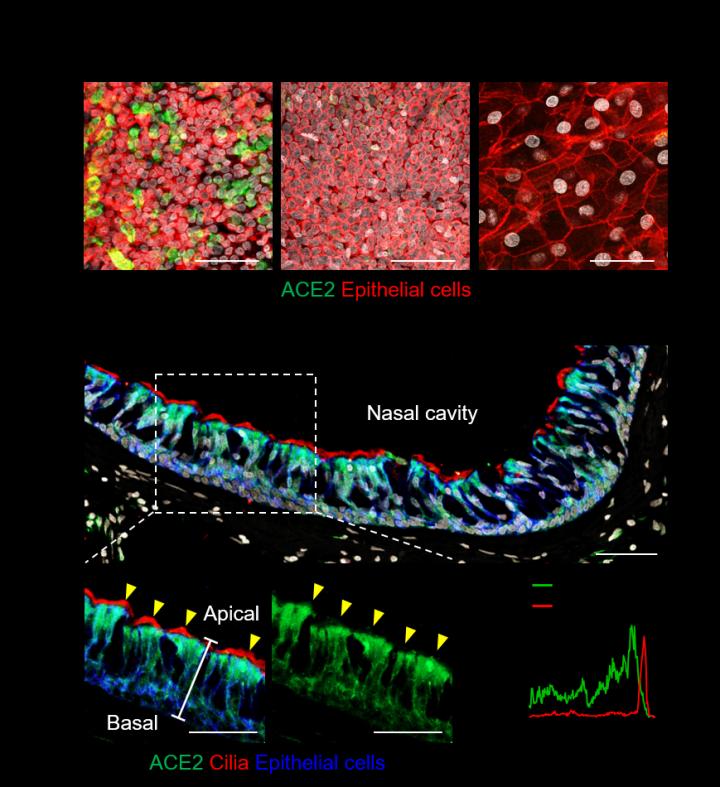
The researchers first looked for the presence of ACE2, TMPRSS2, and FURIN, which are the predominant SARS-CoV-2 entry-related molecules, on the surfaces of various types of cells in the nasal epithelium. It was found that these proteins were present in high quantities on ciliated cells. Moreover, the apical (upper) sides of these cells showed higher levels of these molecules in comparison to the basal (bottom) side. The levels of these proteins were highest in fully differentiated multiciliated cells. On the other hand, viral entry proteins were not found in the undifferentiated epithelial cells or secretory cells such as the goblet cells.
Next, the researchers further studied these nasal epithelial cells using scRNA-seq and visualized the cells into different clusters using UMAP. Samples were collected from 4 patients on the first day of their COVID-19 diagnosis, which were compared against 2 samples from healthy donors. It was found that the fraction of multicilial cells was greatly reduced in the samples from infected patients, while there was an increase in the secretory cells and differentiating cells. This hinted that multicilial cells were the first to be attacked and killed off by the virus, which are then replaced by the latter types of cells.
The study also measured the level of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA transcripts within the various types of cells. Among all the epithelial cells in COVID-19 infected patients, 38% of the cells were labeled as SARS-CoV-2hi cells. Up to 75% of the detected genes in these cells were of viral origin, compared to less than 1% for other clusters of cells. This means that these cells serve as the main factories for the mass production of SARS-CoV-2 viruses. While it was not possible to directly identify these cells through RNA seq due to the fact that they primarily produce viral mRNA, the researchers employed pseudo-time-trajectory analysis to predict their differentiation paths. The differentiation trajectory showed that SARS-CoV-2hi cells likely originated from ciliated cells. Further IFS analysis on the infected patients’ samples conclusively determined that up to 85% of SARS-CoV-2 factories were in fact multiciliated cells.
This study was able to determine that multiciliated cells in the nasal epithelium are the first cells that are targeted in the early COVID-19 infection. This implies that targeting these cells using specific treatments, such as through nasal sprays, can be an ideal strategy to curb COVID-19 infection in the early stages.
###
Media Contact
William I. Suh
[email protected]




