Credit: Molecular Cell
An international and multidisciplinary team led by researchers at the University of Oxford, University of Glasgow, and University of Heidelberg, has uncovered the interactions that SARS-CoV-2 RNA establishes with the host cell, many of which are fundamental for infection. These discoveries pave the way for the development of new therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 with broad-range antiviral potential.
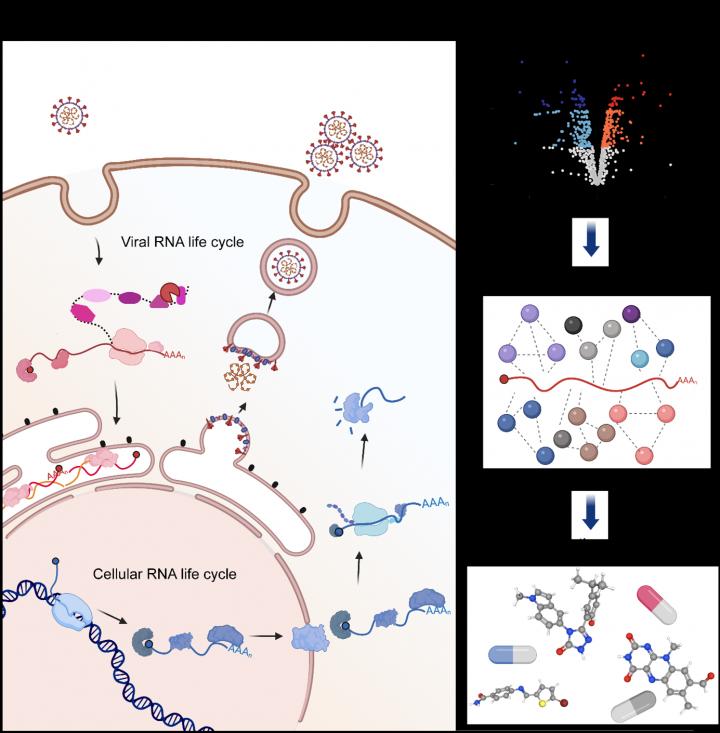
The genetic information of SARS-CoV-2 is encoded in an RNA molecule instead DNA. This RNA must be multiplied, translated, and packaged into new viral particles to produce the viral progeny. Despite the complexity of these processes, SARS-CoV-2 only encodes a handful of proteins able to engage with viral RNA. To circumvent this
limitation SARS-CoV-2 hijacks cellular proteins and repurposes it for its own benefit. However, the identity of these proteins has remained unknown until now.
Researchers from the University of Oxford in collaboration with other labs across UK and Europe have developed a new approach to discover in a comprehensive manner the proteins that ‘stick’ to SARS-CoV-2 RNA in infected cells. With this method, authors uncovered that SARS-CoV-2 RNA hijacks more than a hundred cellular proteins, which appear to play critical roles in the viral life cycle.
This work, published in Molecular Cell, identifies many potential therapeutic targets with hundreds of available drugs targeting them. In a proof-of-principle experiment, authors selected four drugs targeting four different cellular proteins. These drugs caused from moderate to strong effects in viral replication.
‘These exciting results are only the beginning,’ said Alfredo Castello, one of the researchers that has led the work. ‘With hundreds of compounds that target these critical cellular proteins, it will be possible to identify novel antivirals. Our efforts, together with those of the scientific community, should focus now on testing these drugs in infected cells and animal models to uncover which ones are the best antivirals.’
An unexpected observation of this study is that viruses from different origin such as SARS-CoV-2 and Sindbis, hijack a similar repertoire of cellular proteins. This discovery is very important, as cellular proteins with important and wide-spread roles in virus infection have potential as target for broad-spectrum antiviral treatments.
‘In this stage of the pandemic in which vaccines have proved their value,’ added Alfredo Castello. ‘It becomes fundamental to develop new therapeutic approach to counteract emergent vaccine-resistant variants or novel pathogenic viruses with pandemic potential.’
Professor Shabaz Mohammed adds: ‘These new methods to discover the interactors of viral RNA builds on nearly 6 years of joined effort between the Castello and Mohammed labs using Sindbis virus as discovery model. This pre-existent work allowed us to react rapidly at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic and study the interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and the host cell in a reduced timeframe. Our methodology will now be ready to respond rapidly to future viral threads.’
###
The paper ‘Global analysis of protein-RNA interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells reveals key regulators of infection’ is published in the journal Molecular Cell. The work was led by Dr Wael Kamel and Marko Noerenberg, postdoctoral researchers at Glasgow and Oxford, and Berati Cerikan, postdoctoral fellow at the University of Heidelberg.
Media Contact
Gen Juillet
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




