Credit: RUDN University
Biotechnologists from RUDN University in collaboration with Lomonosov MSU and Kurchatov institute made an important contribution to the technology of phosphate and nitrate biocapture from wastewater using Lobosphaera algae fixed on the filters.The biomass obtained in the course of this process can be used as a fertilizer. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering.
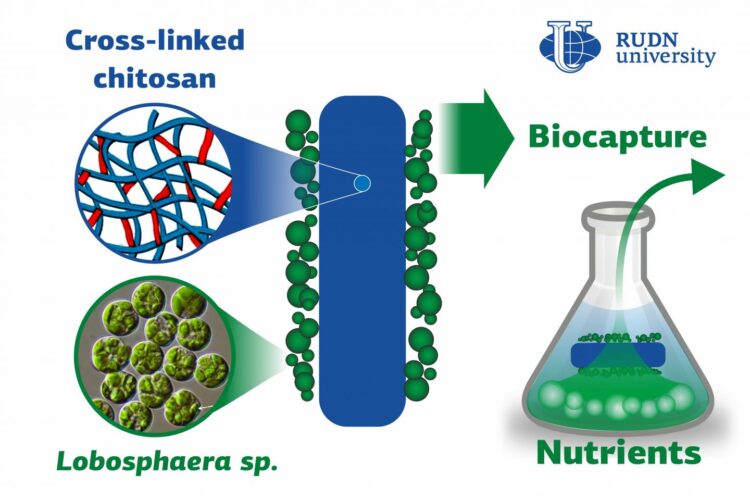
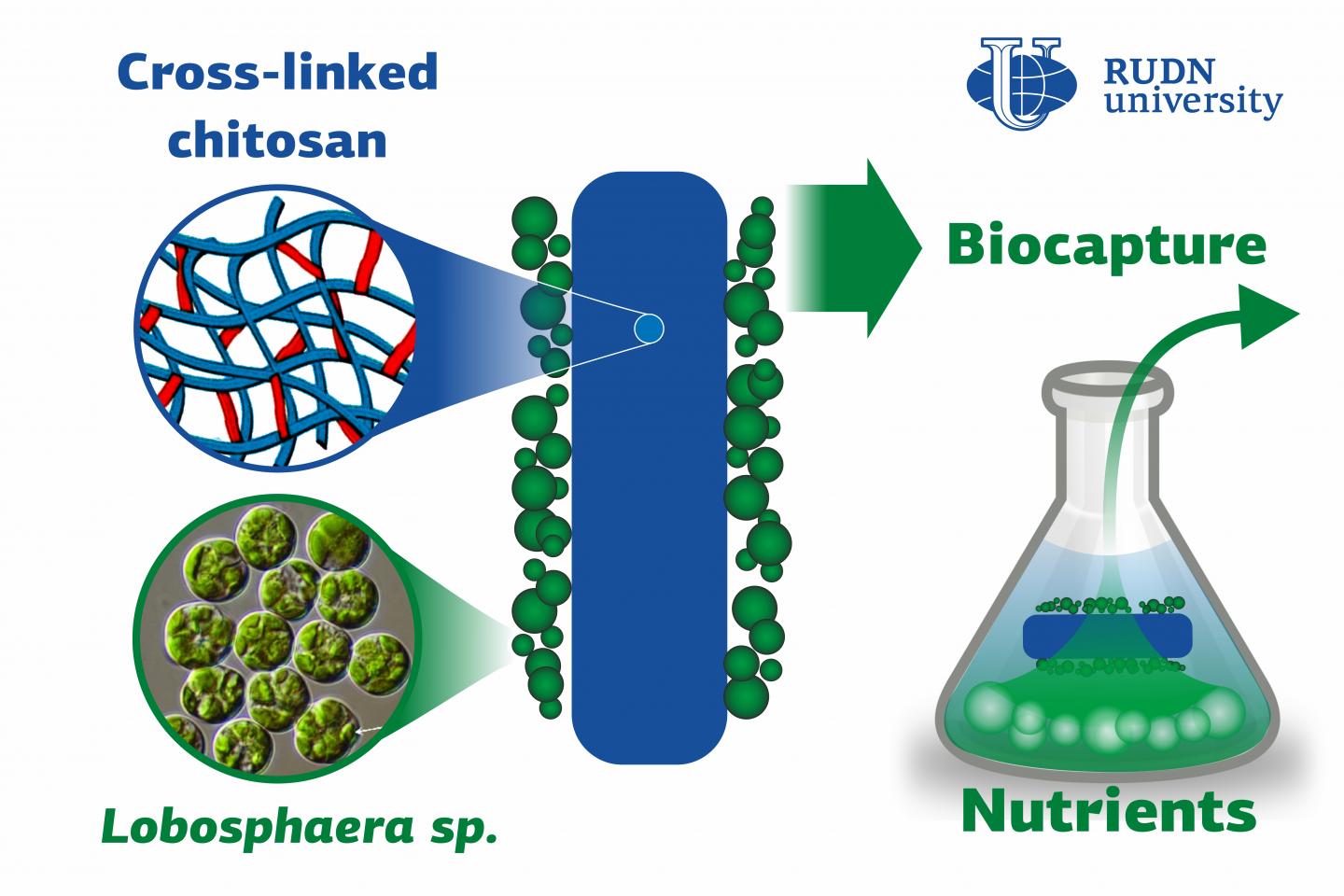
Phosphates and nitrates get to the wastewater together with industrial and household waste, especially detergents. Both substances are parts of phosphorus and nitrogen chemical cycles. However, these cycles are disturbed by human activity, as the growing amounts of phosphates and nitrates cannot be processed by water ecosystems. As a result, these substances turn from useful nutrients to pollutants. Wastewater is treated with special equipment and microorganisms, including microalgae that consume phosphates and nitrates. A team of biotechnologists from RUDN University together with their colleagues from MSU and the Kurchatov Institute developed a biopolymer filter on which useful microalgae can be placed. The polymer is chitosan-based, safe for the algae, biodegradable, and captures chemical elements from wastewater more effectively than its existing analogs.
“Our team was the first to successfully use cross-linked chitosan polymers to immobilize unicellular algae and make them effectively consume nutrients while at the same time not preventing them from growing and photosynthesizing,” said Alexei Solovchenko, a PhD in Biology from the Department of Agrobiotechnology, RUDN University.
Chitosan is a polysaccharide with amino groups and its chemical composition is similar to that of chitin that can be found in shellfish crusts and mushroom cell walls. Chitosan is not water-soluble and therefore can be used to grow algae. However, it is biodegradable. Using an original methodology developed in the Kurchatov Institute, it was cross-linked with glutaraldehyde molecules and thus turned into a strong biocompatible polymer. Then, the team grew the IPPAS C-2047 strain of the Lobosphaera incisa algae on it for seven days.
Based on the results of the seven-day long experiment, the team concluded that a complex of microalgae cells and chitosan-based polymer with a total molecular mass of 600 kDa was more effective than that with a molecular mass of 250 kDa. The algae on the filter captured the nutrients more efficiently than those suspended in the wastewater: specifically, they consumed phosphates 16.7 times and nitrates 1.3 times faster.
Used chitosan biofilters could be repurposed as fertilizers. With time, chitosan would degrade without causing any harm to the environment, while the algae would act as a source of accumulated phosphates and nitrates for the plants.
“Our team has demonstrated that cross-linked chitosan polymers are safe for the environment and effectively support the biocapture of nutrients from wastewater by unicellular algae. When added to a non-toxic medium, the algae biomass could be used as a fertilizer that would gradually release the accumulated nutrients into the soil,” added Alexei Solovchenko from RUDN University.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.