Can sedimentary DNA technology track the long-term dynamics of macro-organism species?
Credit: Michinobu Kuwae, CMES, Ehime University
Long-term variability in the ‘abundance’ of a macro-organism could provide fundamental information for evaluating its evolution, its responses to climate changes and human impact, enabling management and preservation strategies. Biological monitoring in aquatic systems has provided evidence of long-term variability in the abundance of macro-organisms. However, almost all such records span less than a century; there are none which span centuries or more. Aquatic bottom sediments have provided records of species abundance on longer time scales, although previous studies addressed marine fish species using fossil remains (mainly fish scales) and reconstructed abundance for only seven fish taxons. Thus, there remains a distinct lack of information on long-term changes in abundance for many marine fish species and other macro-organisms in aquatic systems.
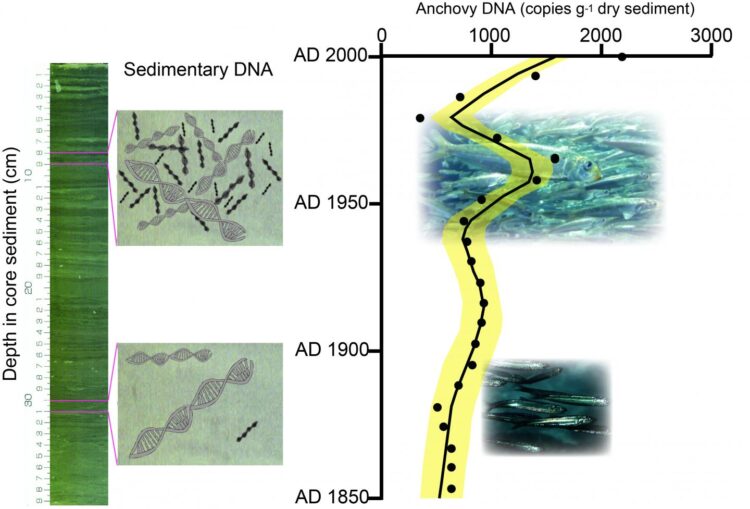
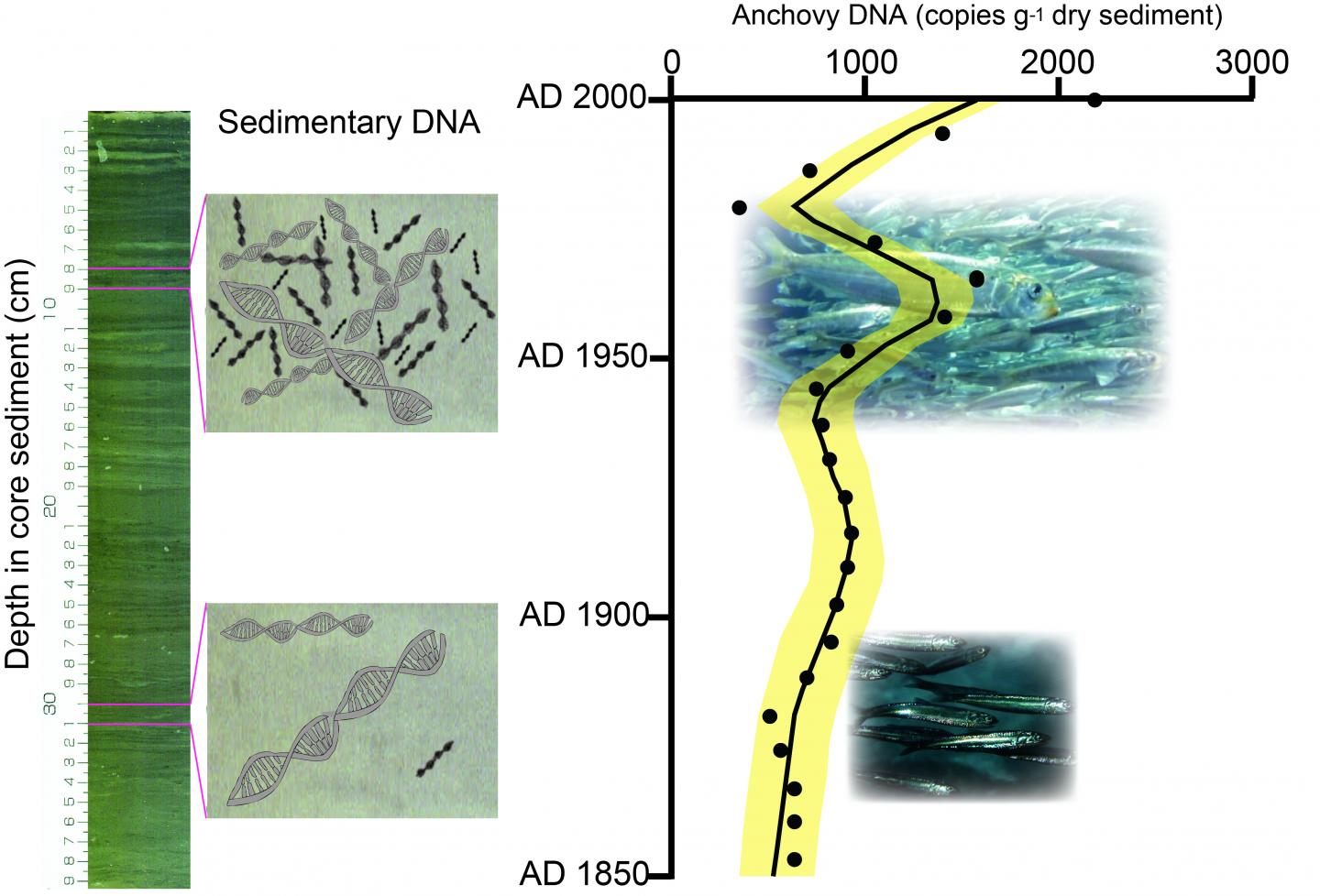
This study focused on an approach using sedimentary DNA which is a potentially powerful tool for reconstructing lengthy records of fish species. We first tested the existence of fish DNA in the marine sediment sequences in a Japanese bay. Then we tested the utility of sedimentary DNA in reconstructing past fish abundance by comparing fish sedimentary DNA concentrations with fish scale concentrations and landing data.
Sediment core samples collected from Beppu Bay in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan, were used to quantify sedimentary DNA of three major fish species (Japanese anchovy, Japanese sardine, and jack mackerel) by applying quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) methods. The result showed that the DNA of these fish species were detected in sediment sequences spanning the last 300 years. Observed temporal changes in fish DNA concentrations on decadal and centennial time scales are consistent with those of landings in Japan for all three species and with those of sardine fish scale concentrations. Thus, sedimentary DNA could be used to track decadal-centennial dynamics of fish abundance in marine.
Using environmental DNA is a widely accepted approach for biological monitoring that is easy, fast and inexpensive without the need for taxonomic expertise for the physical identification of a species. However, such monitoring started only recently; the data collection interval not being less than 10 years. In contrast, the use of sedimentary DNA is expected to instantly obtain lengthy retrospective monitoring data of abundance if the water has a sedimentary basin in which DNA is continuously deposited and stably preserved. This approach has not been used because it remains unclear whether sedimentary DNA concentrations reflect the abundance of an aquatic species. Our findings suggest that the use of sedimentary DNA is a viable technique for tracking past changes in fish abundance, and also could be used to reconstruct the abundance of macro-organisms inhabiting water. Sedimentary DNA technology could support monitoring efforts during the 21st century as a potential tool for decifering the long-term dynamics of macro-organisms before the monitoring started or at a place lacking lengthy monitering observations.
###
Media Contact
Public Relations Division
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.