Researchers from Kanazawa University discover that stem cells loaded with antibiotics may represent a novel therapy for implant-related bone infections
Credit: Kanazawa University
Kanazawa, Japan – Bone infections caused by implants are difficult to treat and usually require a prolonged course of antibiotic treatment. In a new study, researchers from Kanazawa University discovered that implant-related bone infections can be effectively treated with a combinational treatment consisting of antibiotics and antibiotic-laden stem cells.
Bone fractures often require implants for stabilization and effective healing of the broken bone. However, implants can cause serious bone infections, such as osteomyelitis, that can only be managed with a prolonged antibiotic treatment. This in turn bears the risk of contributing to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. While major efforts are currently underway to develop new antibiotics that cover these antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a different path has been to study the antibiotic effects of stem cells. One type is the so-called mesenchymal stem cells that naturally reside in the bone marrow and adipose tissue, among others, and that have been shown to possess antimicrobial properties.
“Adipose-derived stem cells, or ADSCs, have the distinct advantage of being abundant in subcutaneous adipose tissues and can thus be easily harvested,” says the corresponding author of the study Tamon Kabata. “The goal of our study was to investigate the therapeutic effects of ADSCs in combination with the antibiotic ciprofloxacin in an animal model of implant-related bone infection.”
To achieve their goal, the researchers first focused on the effects of ciprofloxacin on ADSCs and found an efficient, time-dependent loading of ADSCs with the antibiotic in the first 24 hours with no adverse effects of ciprofloxacin on the function or viability of the stem cells. The researchers then tested the antimicrobial activity of the antibiotic-loaded ADSCs in vitro (in a tube) and found that they effectively decreased the growth of the bacterium S. aureus, which is also the main microbe causing bone implant-related infections.
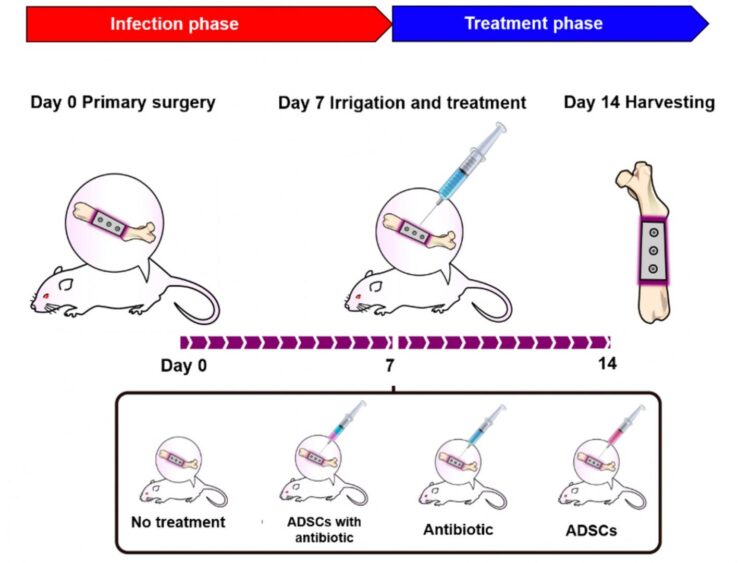
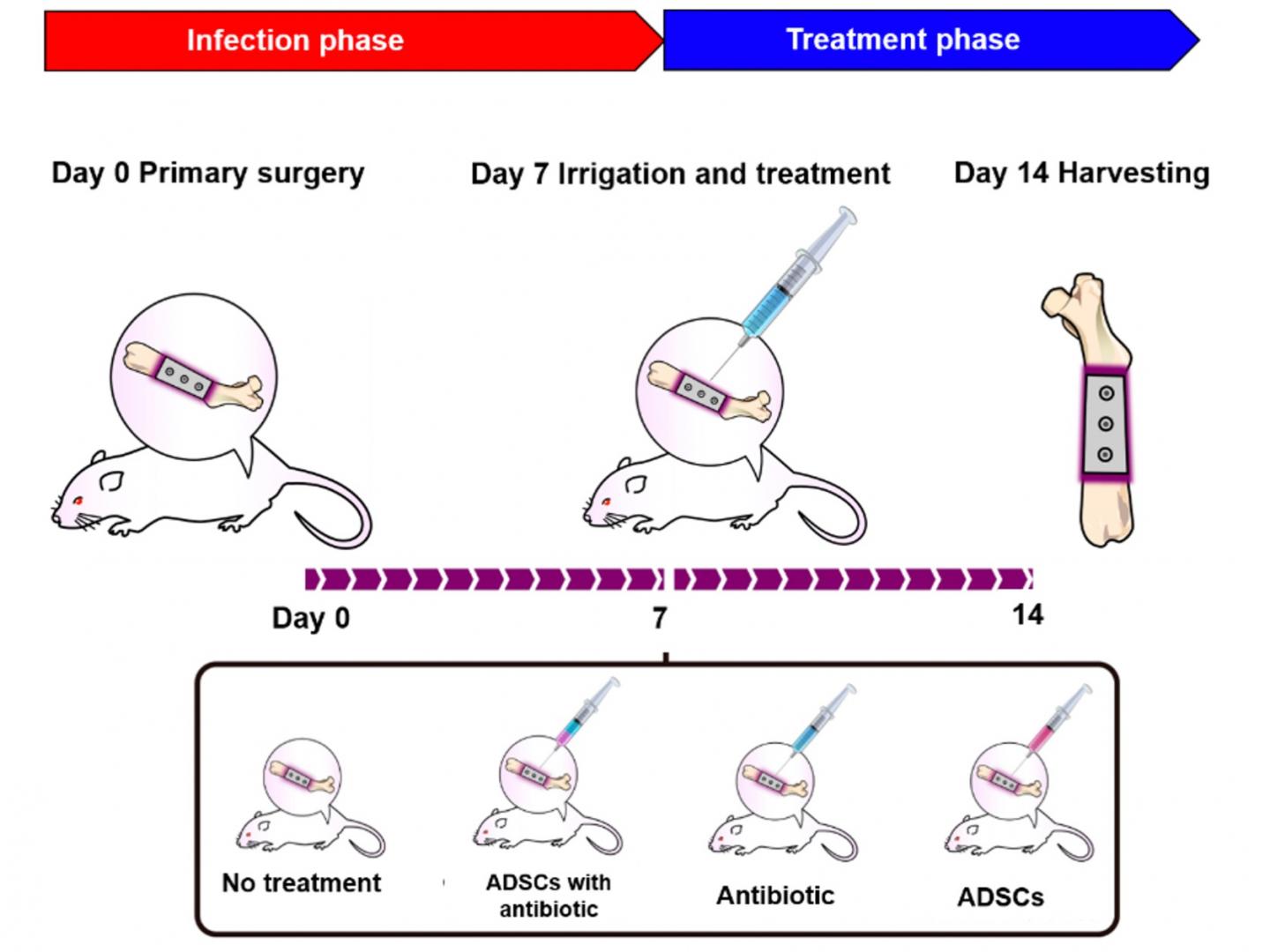
But could this novel approach also mitigate implant-related infection in a living organism? The researchers tested this on rats, who received bone implants using screws coated with S. aureus bacteria. The rats developed osteomyelitis 7 days after surgery. Then, the researchers administered one of the following to the animals: ADSCs loaded with ciprofloxacin, ADSCs alone, ciprofloxacin alone, or no treatment at all. Because osteomyelitis can lead to soft tissue swelling and abscess formation at the site of the infection, the researchers quantified the extent of the disease in the animals and found that only ADSCs loaded with ciprofloxacin presented as an effective treatment. Using the imaging modality micro-computed tomography to visualize the affected bones, the researchers further found that ADSC-loaded ciprofloxacin decreased the appearance of osteolysis, or bone degradation, which is not only important for bone health, but also for the stability of the implant.
“These are striking results that show how ADSCs can efficiently be loaded with antibiotics to exert a strong antimicrobial effect. Our findings suggest a potential novel therapy for implant-associated osteomyelitis, for which conventional treatment with only antibiotics is usually insufficient,” says Kabata.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.