Russian researchers have found MicroRNA molecules potentially capable of repressing the replication of human coronaviruses
Credit: @Nersisyan, et. al.
HSE University researchers have found microRNA molecules that are potentially capable of repressing the replication of human coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2. It turns out that the virus uses miRNA hsa-miR-21-3p to inhibit growth in the first stages of infection in order to delay the active immune response. The results of the research have been published in the journal PeerJ.
After the virus gets inside the cell, it starts actively interacting with various in-cell molecules. One such molecule class is microRNAs (miRNAs), which are small RNAs whose main function is to regulate gene expression. When a virus enters, miRNAs start binding certain parts of its genome RNA, which leads to the destruction of virus RNAs. Such an attack can stop virus replication completely. However, in cases when miRNAs are not very ‘aggressive’, such interactions do not destroy the virus but rather slow down its replication. This scenario is beneficial for the virus since it helps avoid a fast immune response in the cell. And some of the viruses purposefully accumulate host miRNA binding sites. This becomes their advantage: viruses with more binding sites survive and reproduce better, which leads to their evolutionary domination.
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology, Stepan Nersisyan and Alexander Tonevitsky, together with first-year students Narek Engibaryan, Aleksandra Gorbonos, Ksenia Kirdey, and Alexey Makhonin, detected cell miRNAs that are able to bind coronavirus genomes.
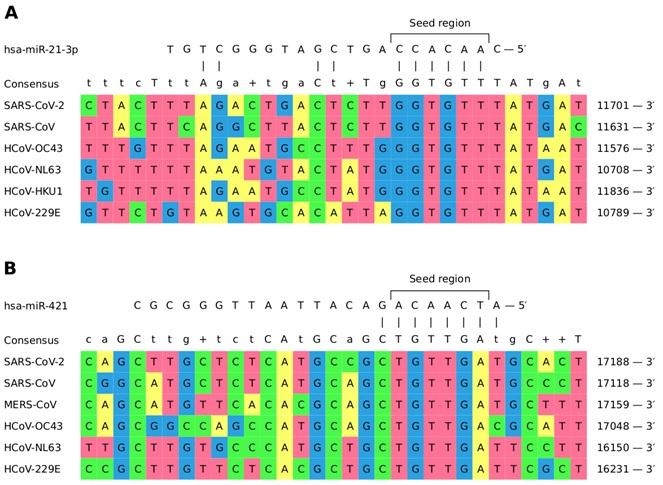
There are seven types of human coronaviruses in total. Four of them (HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-229E) are widespread and cause the common cold, while viruses MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 can cause dangerous atypical pneumonia. The researchers found four families of human miRNAs with detected binding sites with all the viruses under consideration.
The image shows miRNA binding sites hsa-miR-21-3p and hsa-miR-421, which are mutual for six out of seven human coronaviruses.
To find out how the virus can interact with the detected miRNAs, the researchers analysed the available data on miRNA sequences in lungs of mice infected with SARS-CoV. They discovered that the infection leads to an 8-fold increase in the expression of the previously detected miRNA hsa-miR-21-3p.
‘MiRNA hsa-miR-21-3p has big potential for binding all human coronaviruses. But after infection with SARS-CoV, the concentration of this miRNA in the lungs grows a lot. If we assume that this is a mechanism of immune response, it is unclear why the virus does not eliminate the binding sites with cell miRNAs in the process of mutation. On the contrary, we see that the virus ‘accumulates’ them in its genome during the evolution – our research demonstrates that such sites are present in all human coronaviruses and do not mutate considerably. We suppose that this way the virus uses this miRNA to slow down its replication in the early stages of infection in order to delay the active immune response,’ Stepan Nersisyan said.
The next step of the team’s research will be experimental verification of their discoveries. The researchers are also planning to investigate the possibility of medicinal effect on the virus that targets the discovered miRNAs. In particular, they plan to determine whether their artificial introduction or elimination is able to prevent virus reproduction.
###
This link will become live when the embargo lifts. EMBARGOED until 14 September 2020, 7:00 am EST USA.
Media Contact
Liudmila Mezentseva
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




