Credit: LSU Health New Orleans
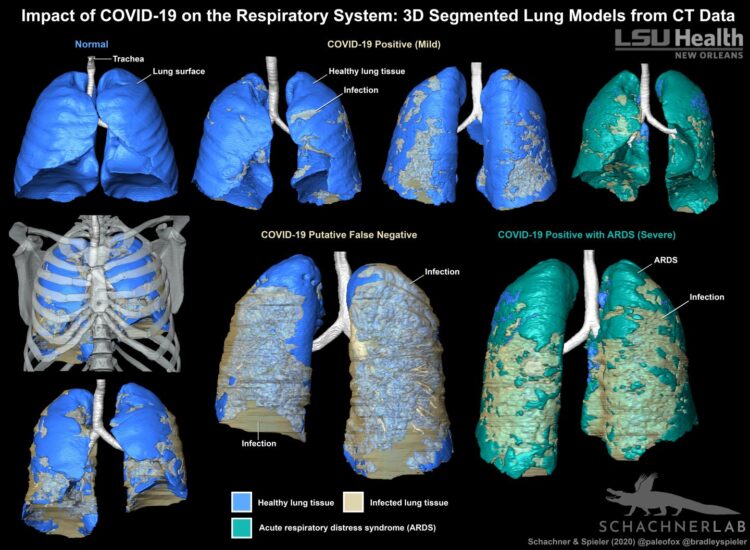
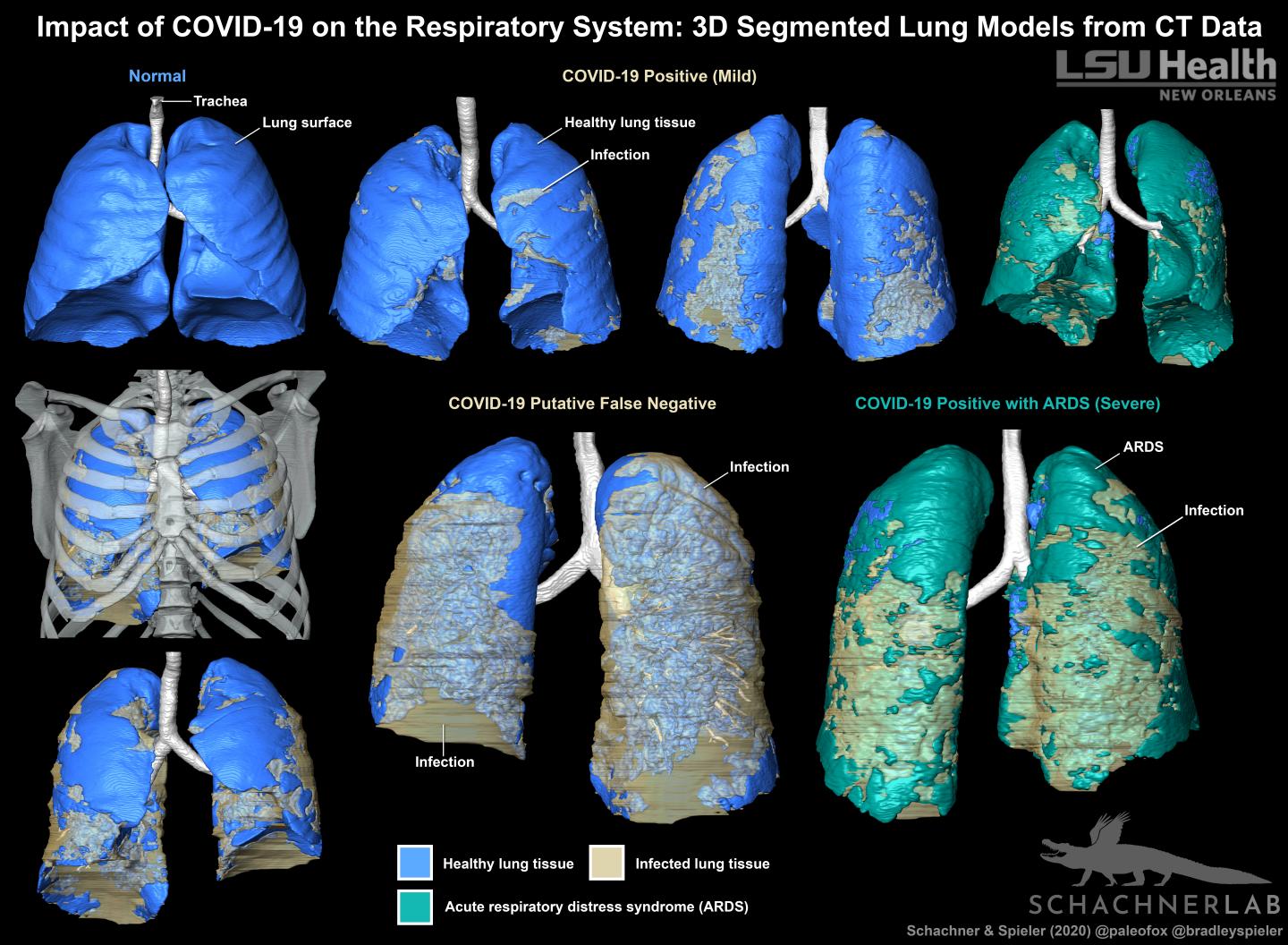
New Orleans, LA — An LSU Health New Orleans radiologist and evolutionary anatomist have teamed up to show the same techniques used for research on reptile and bird lungs can be used to help confirm the diagnosis of COVID-19 in patients. Their paper published in BMJ Case Reports demonstrates that 3D models are a strikingly clearer method for visually evaluating the distribution of COVID-19-related infection in the respiratory system.
Emma R. Schachner, PhD, Associate Professor of Cell Biology & Anatomy, and Bradley Spieler, MD, Vice Chairman of Radiology Research and Associate Professor of Radiology, Internal Medicine, Urology, & Cell Biology and Anatomy at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, created 3D digital models from CT scans of patients hospitalized with symptoms associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
Three patients who were suspected of having COVID-19 underwent contrast enhanced thoracic CT when their symptoms worsened. Two had tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, but one was reverse transcription chain reaction (RT-PCR) negative. But because this patient had compelling clinical and imaging, the result was presumed to be a false negative.
“An array of RT-PCR sensitivities has been reported, ranging from 30-91%,” notes Dr. Spieler. “This may be the result of relatively lower viral loads in individuals who are asymptomatic or experience only mild symptoms when tested. Tests performed when symptoms were resolving have also resulted in false negatives, which seemed to be the result in this case.”
Given diagnostic challenges with respect to false negative results by RT-PCR, the gold standard for COVID-19 diagnostic screening, CT can be helpful in establishing this diagnosis. Importantly, these CT features can range in form and structure and appear to correlate with disease progression. This allows for 3D segmentation of the data in which lung tissue can be volumetrically quantified or airflow patterns could be modeled.
The CT scans were all segmented into 3D digital surface models using the scientific visualization program Avizo (Thermofisher Scientific) and techniques that the Schachner Lab uses for evolutionary anatomy research.
“The full effect of COVID-19 on the respiratory system remains unknown, but the 3D digital segmented models provide clinicians a new tool to evaluate the extent and distribution of the disease in one encapsulated view,” adds Spieler. “This is especially useful in the case where RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 is negative but there is strong clinical suspicion for COVID-19.”
To date, there haven’t been good models of what COVID is doing to the lungs. So, this project focused on the visualization of the lung damage in the 3D models as compared to previous methods that have been published – volume-rendered models and straight 2D screen shots of CT scans and radiographs.
“Previously published 3D models of lungs with COVID-19 have been created using automated volume rendering techniques,” says Dr. Schachner. “Our method is more challenging and time consuming, but results in a highly accurate and detailed anatomical model where the layers can be pulled apart, volumes quantified, and it can be 3D printed.”
The three models all show varying degrees of COVID-19 related infection in the respiratory tissues – particularly along the back of the lungs, and bottom sections. They more clearly show COVID-19-related infection in the respiratory system compared to radiographs (x-rays), CT scans, or RT-PCR testing alone.
###
Schachner and Spieler are now segmenting more models for a larger follow up project.
LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans educates Louisiana’s health care professionals. The state’s flagship health sciences university, LSU Health New Orleans includes a School of Medicine with branch campuses in Baton Rouge and Lafayette, the state’s only School of Dentistry, Louisiana’s only public School of Public Health, and Schools of Allied Health Professions, Nursing, and Graduate Studies. LSU Health New Orleans faculty take care of patients in public and private hospitals and clinics throughout the region. In the vanguard of biosciences research in a number of areas in a worldwide arena, the LSU Health New Orleans research enterprise generates jobs and enormous economic impact. LSU Health New Orleans faculty have made lifesaving discoveries and continue to work to prevent, advance treatment, or cure disease. To learn more, visit http://www.
Media Contact
Leslie Capo
[email protected]
Original Source
http://lsuh.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.