Researchers evaluate how the new coronavirus rewires human proteins for its own replication, and identify several antiviral drugs ready for clinical trials
Credit: Elizabeth Fischer, Miscroscopy Unit NIH/NIAID
An international team of researchers has analysed how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, hijacks the proteins in its target cells. The research, published in the journal Cell, shows how the virus shifts the cell’s activity to promote its own replication and to infect nearby cells. The scientists also identified seven clinically approved drugs that could disrupt these mechanisms, and recommend that these drugs are immediately tested in clinical trials.
The collaboration included researchers at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the Quantitative Biosciences Institute’s Coronavirus Research Group in the School of Pharmacy at University of California San Francisco (UCSF), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Institut Pasteur, and the Excellence Cluster CIBSS of the University of Freiburg.
Viruses are unable to replicate and spread on their own: they need an organism – their host – to carry, replicate, and transmit them to further hosts. To facilitate this process, viruses need to take control of their host cell’s machinery and manipulate it to produce new viral particles. Sometimes, this hijacking interferes with the activity of the host’s enzymes and other proteins.
Once a protein is produced, enzymes can change its activity by making chemical modifications to its structure. For example, phosphorylation – the addition of a phosphoryl group to a protein by a type of enzyme called a kinase – plays a pivotal role in the regulation of many cell processes, including cell-to-cell communication, cell growth, and cell death. By altering phosphorylation patterns in the host’s proteins, a virus can potentially promote its own transmission to other cells and, eventually, other hosts.
The scientists used mass spectrometry, a tool to analyse the properties of a sample by measuring the mass of its molecules and molecular fragments, to evaluate all host and viral proteins that showed changes in phosphorylation after SARS-CoV-2 infection. They found that 12% of the host proteins that interact with the virus were modified. The researchers also identified the kinases that are most likely to regulate these modifications. Kinases are potential targets for drugs to stop the activity of the virus and treat COVID-19.
The extraordinary behaviour of infected cells
“The virus prevents human cells from dividing, maintaining them at a particular point in the cell cycle. This provides the virus with a relatively stable and adequate environment to keep replicating,” explains Pedro Beltrao, Group Leader at EMBL-EBI.
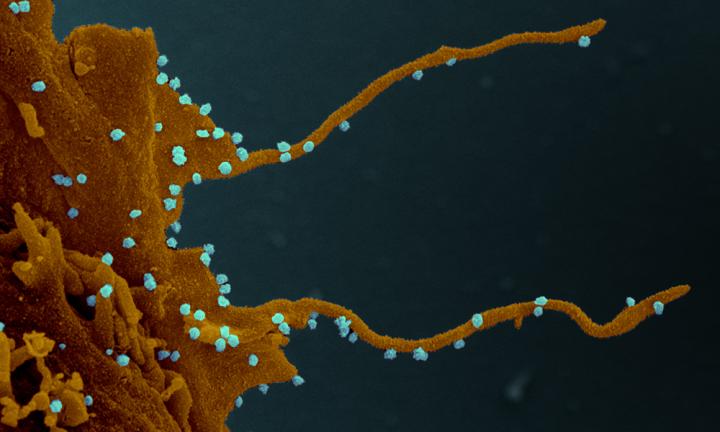
SARS-CoV-2 not only impacts cell division, but also cell shape. One of the key findings from the study is that infected cells exhibit long, branched, arm-like extensions, or filopodia. These structures may help the virus reach nearby cells in the body and advance the infection, but further study is warranted.
“The distinct visualisation of the extensive branching of the filopodia once again elucidates how understanding the biology of virus-host interaction can illuminate possible points of intervention in the disease,” says Nevan Krogan, Director of the Quantitative Biosciences Institute at UCSF and Senior Investigator at Gladstone Institutes.
Old drugs, new treatments
“Kinases possess certain structural features that make them good drug targets. Drugs have already been developed to target some of the kinases we identified, so we urge clinical researchers to test the antiviral effects of these drugs in their trials,” says Beltrao.
In some patients, COVID-19 causes an overreaction of the immune system, leading to inflammation. An ideal treatment would relieve these exaggerated inflammatory symptoms while stopping the replication of the virus. Existing drugs targeting the activity of kinases may be the solution to both problems.
The researchers identified dozens of drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or ongoing clinical trials that target the kinases of interest. Seven of these compounds, primarily anticancer and inflammatory disease compounds, demonstrated potent antiviral activity in laboratory experiments.
“Our data-driven approach for drug discovery has identified a new set of drugs that have great potential to fight COVID-19, either by themselves or in combination with other drugs, and we are excited to see if they will help end this pandemic,” says Krogan.
“We expect to build upon this work by testing many other kinase inhibitors while identifying both the underlying pathways and additional potential therapeutics that may intervene in COVID-19 effectively,” says Kevan Shokat, Professor in the Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at UCSF.
###
European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI)
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is a global leader in the storage, analysis and dissemination of large biological datasets. We help scientists realise the potential of ‘big data’ by enhancing their ability to exploit complex information to make discoveries that benefit humankind.
We are at the forefront of computational biology research, with work spanning sequence analysis methods, multi-dimensional statistical analysis and data-driven biological discovery, from plant biology to mammalian development and disease.
We are part of EMBL and are located on the Wellcome Genome Campus, one of the world’s largest concentrations of scientific and technical expertise in genomics.
Website: http://www.
Quantitative Biosciences Institute (QBI)
The Quantitative Biosciences Institute (QBI) is a University of California organized research unit reporting through the UCSF School of Pharmacy. QBI fosters collaborations across the biomedical and the physical sciences, seeking quantitative methods to address pressing problems in biology and biomedicine. Motivated by problems of human disease, QBI is committed to investigating fundamental biological mechanisms, because ultimately solutions to many diseases have been revealed by unexpected discoveries in the basic sciences.
Website: qbi.ucsf.edu
University of California, San Francisco (UCSF)
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF’s primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area.
Website: ucsf.edu.
Gladstone Institutes
To ensure our work does the greatest good, Gladstone Institutes focuses on conditions with profound medical, economic, and social impact–unsolved diseases. Gladstone is an independent, nonprofit life science research organization that uses visionary science and technology to overcome disease. It has an academic affiliation with UC San Francisco.
Website: gladstone.org.
Authorship and funding: This work was funded by grants from the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, both part of the National Institutes of Health; the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; the Center for Research for Influenza Pathogenesis; the Centers of Excellence for Influenza Research and Surveillance of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; the Centers of Excellence for Integrative Biology of Emerging Infectious Diseases of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (France); F. Hoffmann-LaRoche AG; Vir Biotechnology, Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies (CIBSS), European Research Council (ERC) and the Ron Conway Family. Shokat is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. A complete list of authors and full funding information is available in the Cell paper.
Media Contact
Mehdi Khadraoui
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




