Study shows how the jellyfish Hydractinia produces eggs and sperm more flexibly than humans
Credit: Dr Tim DuBuc
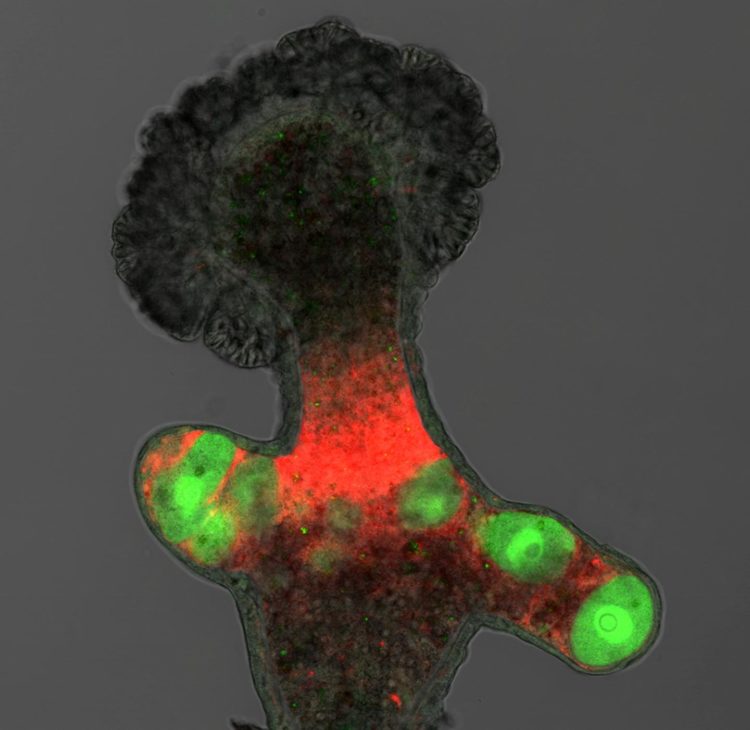
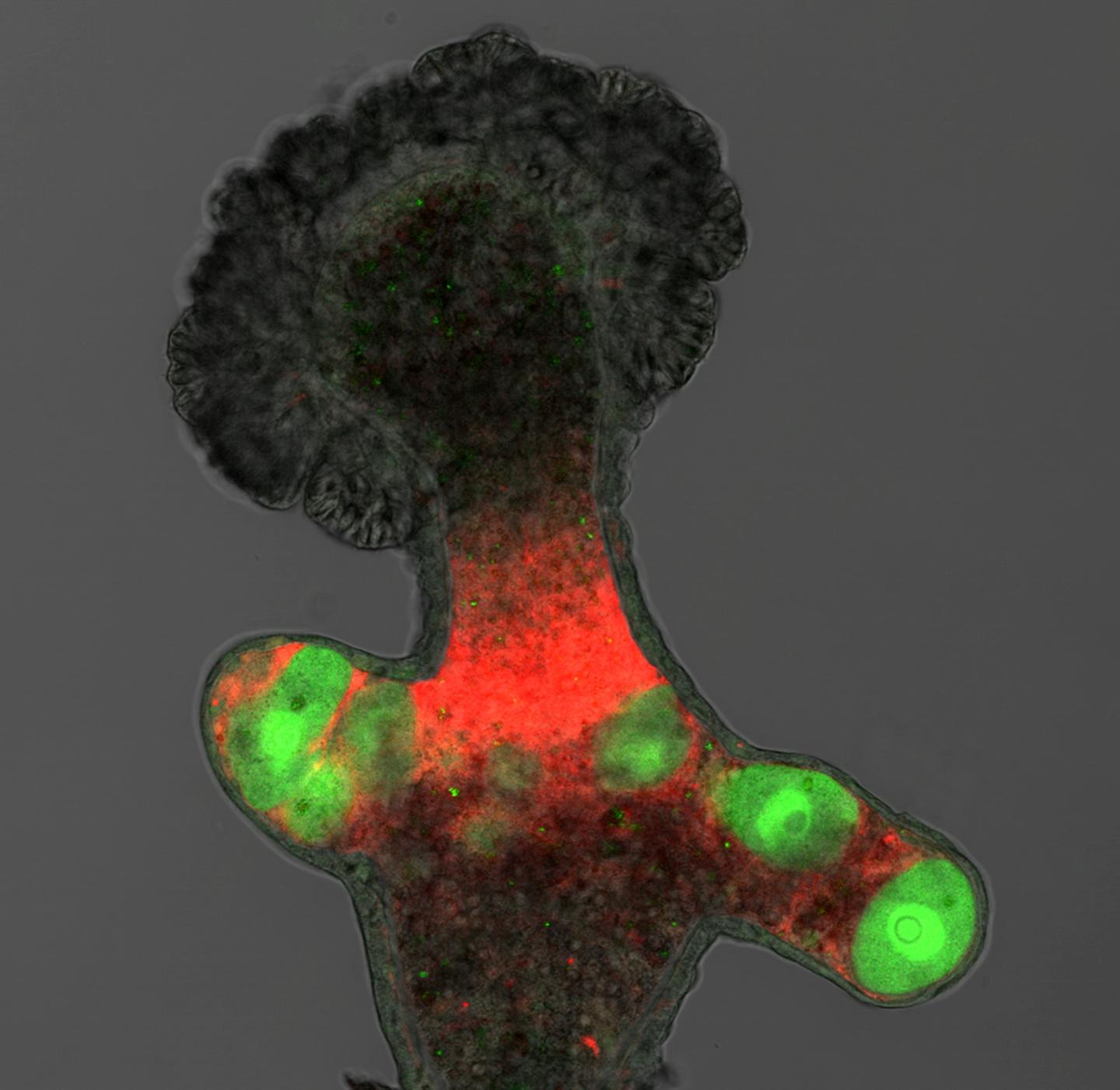
A new study, led by Dr Tim DuBuc and Professor Uri Frank from the Centre for Chromosome Biology at NUI Galway, has found that Hydractinia, a North Atlantic jellyfish that also lives in Galway Bay, reproduces in a similar way to humans but does so far more flexibly.
An article presenting these findings has been published today in the journal Science, with co-authors Dr Andy Baxevanis from the National Human Genome Research Institute of the US National Institutes of Health and Dr Christine Schnitzler from the Whitney Laboratory of Marine Bioscience of the University of Florida.
Most animals, including humans, generate germ stem cells – the exclusive progenitors of eggs and sperm – only once in their lifetime. This process occurs during early embryonic development by setting aside (or ‘sequestering’) a small group of cells. All sperm or eggs that we humans produce during our lives are the descendants of those few cells we sequestered as early embryos. Importantly, there is no way for humans to replenish germ cells that were not sequestered during embryonic development or lost in adult life, resulting in sterility.
In findings that may have implications for the study of human infertility, this research shows that Hydractinia uses a gene called Tfap2 as a ‘switch’ to commit its adult stem cells to produce gametes – eggs and sperm. Humans also use Tfap2 to commit cells to gamete production but only go through this process once, in a narrow time frame during embryonic development. In contrast, Hydractinia performs this process throughout its adult life. Therefore, the loss of germ cells in Hydractinia has no consequences with respect to fertility as its germ cells can be generated throughout its lifetime.
Speaking today, Professor Uri Frank explained: “Looking at the similar, yet more flexible, system of reproduction in Hydractinia broadens our understanding of the issues affecting reproduction in humans. While much of a human’s capacity to reproduce is determined during embryonic development, we see that these jellyfish are far more adaptive and have a much greater capacity to regenerate their reproductive system throughout their adult lives. By looking at these genetically more tractable animals, we hope to understand core processes that control cells’ decisions in development and disease.”
###
The full article is published in Science and available at: https:/
Media Contact
Sheila Gorham
[email protected]
003-539-149-3543
Original Source
http://www.