Potential medications to protect mitochondria found with novel screening strategy
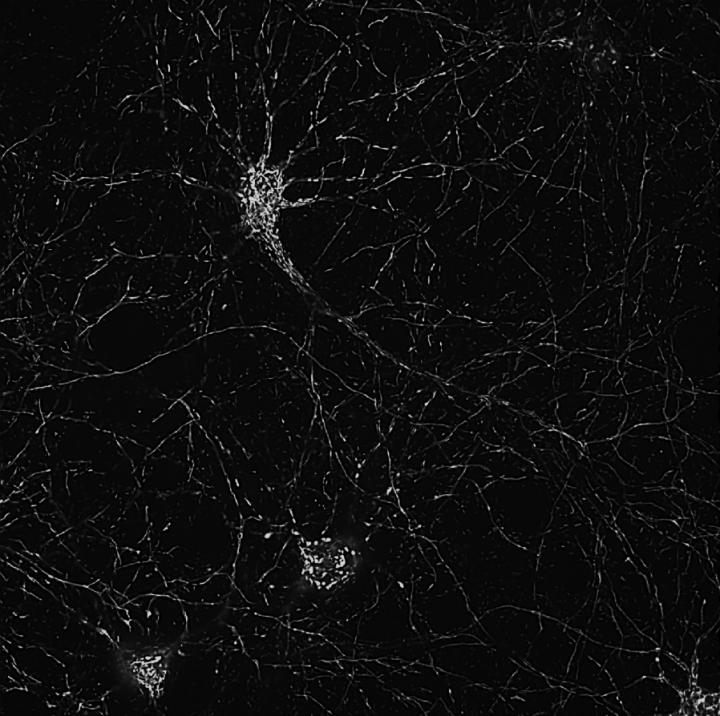
Credit: Ronald Davis Lab at Scripps Research
JUPITER, FL — Jan. 8, 2020 — A sophisticated new screening platform developed by scientists at Scripps Research has enabled them to discover a set of drug-like compounds, including an ingredient found in sore throat lozenges, that may powerfully protect brain cells from dangerous stresses found in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
The screening platform, described in a paper in Science Advances, allows researchers for the first time to rapidly test “libraries” of thousands of molecules to find those that provide broad protection to mitochondria in neurons. Mitochondria are tiny oxygen reactors that supply cells with most of their energy. They are especially important for the health and survival of neurons. Mitochondrial damage is increasingly recognized as a major factor, and in some cases a cause, for diseases of neuronal degeneration such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS.
The scientists, in an initial demonstration of their platform, used it to rapidly screen a library of 2,400 compounds, from which they found more than a dozen that boost the health of neuronal mitochondria and provide broad protection from stresses found in neurodegenerative disorders.
The researchers are now testing the most potent of these mitochondria-protectors in animal models of Alzheimer’s, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and other diseases, with the ultimate goal of developing one or more into new drugs.
“It hasn’t yet been emphasized in the search for effective therapeutics, but mitochondrial failure is a feature of many neurodegenerative disorders and something that must be corrected if neurons are to survive,” says principal investigator Ronald Davis, PhD, professor in the Department of Neuroscience at Scripps Research. “So I’m a big believer that finding mitochondria-protecting molecules is the way to go against these diseases.”
Scientists in prior studies have developed screens for molecules that can enhance mitochondrial function, but only by focusing on mitochondria in cells from outside the brain. A screening system that measures mitochondrial health in mature neurons requires cultures of such neurons, which are relatively difficult to maintain–in part because they do not divide to make new neurons. Davis was convinced, however, that only this more difficult approach, which others including pharmaceutical researchers have avoided, would enable the discovery of compounds that protect brain cells by protecting their mitochondria.
The screening system developed by Davis and his team uses cultured neurons from mouse brains in which mitochondria are labeled with fluorescent tags. Sophisticated microscope imaging and semi-automated image analysis enables the researchers to quickly record mitochondrial numbers, shapes and other visible markers of health in the neurons before and after exposure to different compounds.
In an initial test, the team found that compounds with reported benefits for mitochondria in other cell types had no obvious positive effects for mitochondria in neurons. The researchers then screened their library of 2,400 compounds, which included many existing drug compounds, and found 149 with significant positive effects on neuronal mitochondria.
With further tests the scientists winnowed these “hits” down to a much smaller number, and found several that could robustly protect mouse neuron mitochondria from three stresses known to harm mitochondria in Alzheimer’s: small, toxic clusters of the amyloid beta protein; the neurotransmitter glutamate, which can excite neurons to death; and peroxide, a highly reactive molecule that can be released from damaged mitochondria and go on to harm healthy mitochondria.
The compounds with beneficial effects protected the neuronal mitochondria in some ways more than others, and evidently worked via a variety of biological mechanisms. For example, dyclonine, an anesthetic found in some sore-throat products, protected cultured neurons against glutamate and peroxide toxicity. Dyclonine also increased the energy production of healthy mitochondria as well as the activity of their host neurons’ synapses–connection points to other neurons. Dyclonine seemed so promising that the researchers put it in the water supply of live mice, and again found evidence that it powerfully boosted the health of the mitochondria in the animals’ brains.
“It remains a mystery why dyclonine and other local anesthetics have such effects on mitochondria in neurons–we certainly didn’t anticipate this,” Davis says. “But the compounds we identified give us strong hope that we’ll see beneficial effects when we test them in animal models of specific neurodegenerative diseases, as we’re now doing.”
###
Media Contact
Stacey Singer DeLoye
[email protected]
561-228-2551
Original Source
https:/




