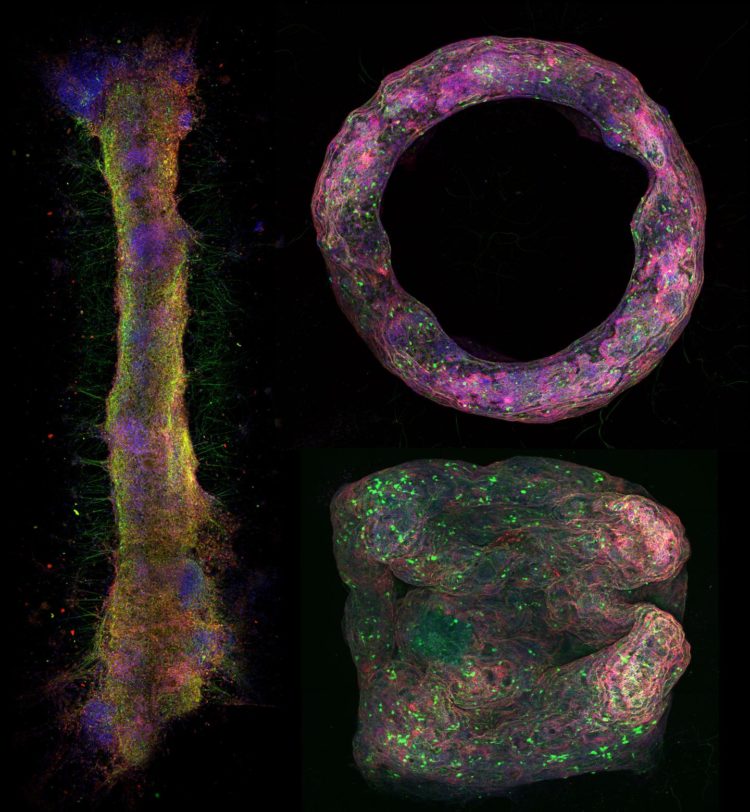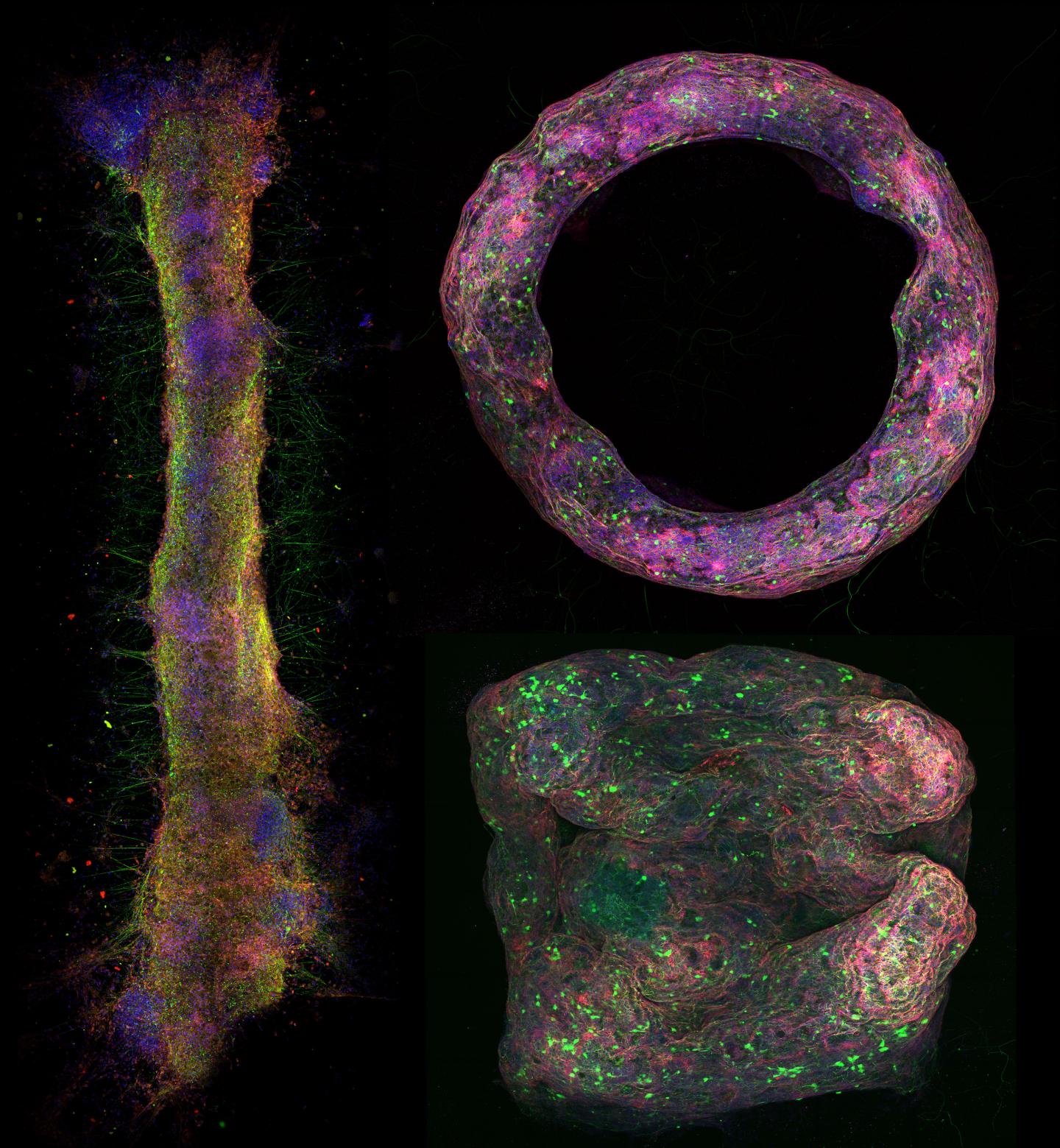
Credit: University of Illinois Department of Bioengineering
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have successfully used stem cells to engineer living biohybrid nerve tissue to develop 3D models of neural networks with the hopes of gaining a better understanding of how the brain and these networks work.
The first author, Gelson Pagan-Diaz-Diaz, likens the produced tissue to a computer processing unit, which provided the basic principle to today’s supercomputer. Pagan-Diaz is a graduate student in Prof. Rashid Bashir’s group in the Department of Bioengineering at the Grainger College of Engineering. Bashir is also the Dean of the College. “Being able to form 3-dimensional tissue consisting of neurons can give us the ability to develop tissue models for drug screening or processing units for biological computers”, Pagan-Diaz said.
The brain is challenging to study in an actual person, but being able to understand how these networks develop using a 3D model outside the body promises to give researchers a new tool to better understand how it works. These models will be able to help understand how abnormalities form, e.g. what gives rise to diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
The team was able to give 3D geometry to the living tissue made of neurons which optogenetics, so they could be activated with blue light. These tissues could be used to study complex behaviors that happen in the brain and how these tissues react with new drugs being developed. It could also mean less reliant on animals to test these drugs in the future.
“If we can control how these neurons communicate with each other, if we can train them using optogenetics, if we can program them, then we can potentially use to perform engineering functions,” Bashir said. “In the future, our hope is that by being able to design these neural tissue, we can begin to realize biological processing units and biological computers, similar to the brain.”
The project was funded through an NSF Science and Technology Center EBICS (Emergent Behaviors of Integrated Cellular Systems) and published this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. It was inspired by work done five years ago in developing functioning muscles, where researchers in Bashir’s lab, developed bio bots that can walk when stimulated with electricity or light.
This new work was performed by interdisciplinary team consists of Pagan-Diaz, Bashir, Karla Ramos-Cruz from bioengineering, Richard Sam from the School of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Mikhail Kandel and Prof. Gabriel Popescu from electrical and computer engineering, and Onur Aydin and Prof. Taher Saif from mechanical science and engineering.
In this study, the team developed neural tissue mimics that can form different shapes. The team used hydrogels and fibrin to make millimeter to centimeter scale structures that doesn’t have rigid scaffolds and can be molded into a number of desired shapes.
“It’s a bundle of hundreds to thousands of microns of cells that contains a lot of populations with a genetic makeup similar to in vivo tissues,” Pagan-Diaz explained. “As we continue develop these bio-fabrication methods, we should be able to capture a lot of the phenomena that happens in vivo. Once we can prove that, we will be able to mimic the morphology that we see in the brain. Once we show that the tissue engineered outside the body is similar to the tissue in the body, then we can then fabricate them over and over again.”
Besides drug testing, the team is especially interested in being able to recapitulate the way these networks might develop learning and memory.
“Being able to fabricate these tissue mimics outside the body allows us to characterize and study their electrical activity in great detail,” Pagan-Diaz emphasized. “the broad set of design rules due to the 3D structure and shapes gives you a lot more experimental freedom and open up new avenues of research in neuroscience, medicine, and engineering applications.”
###
Media Contact
Gelson Pagan-Diaz
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.