Credit: Yotta Kippe/HZB
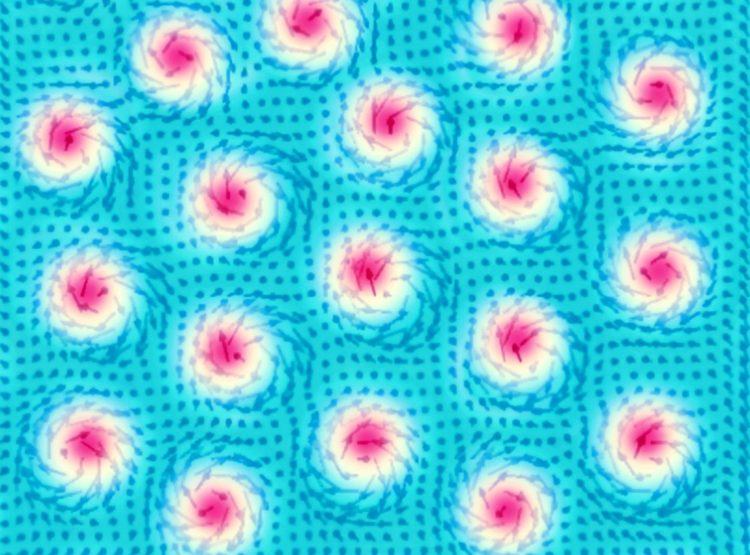
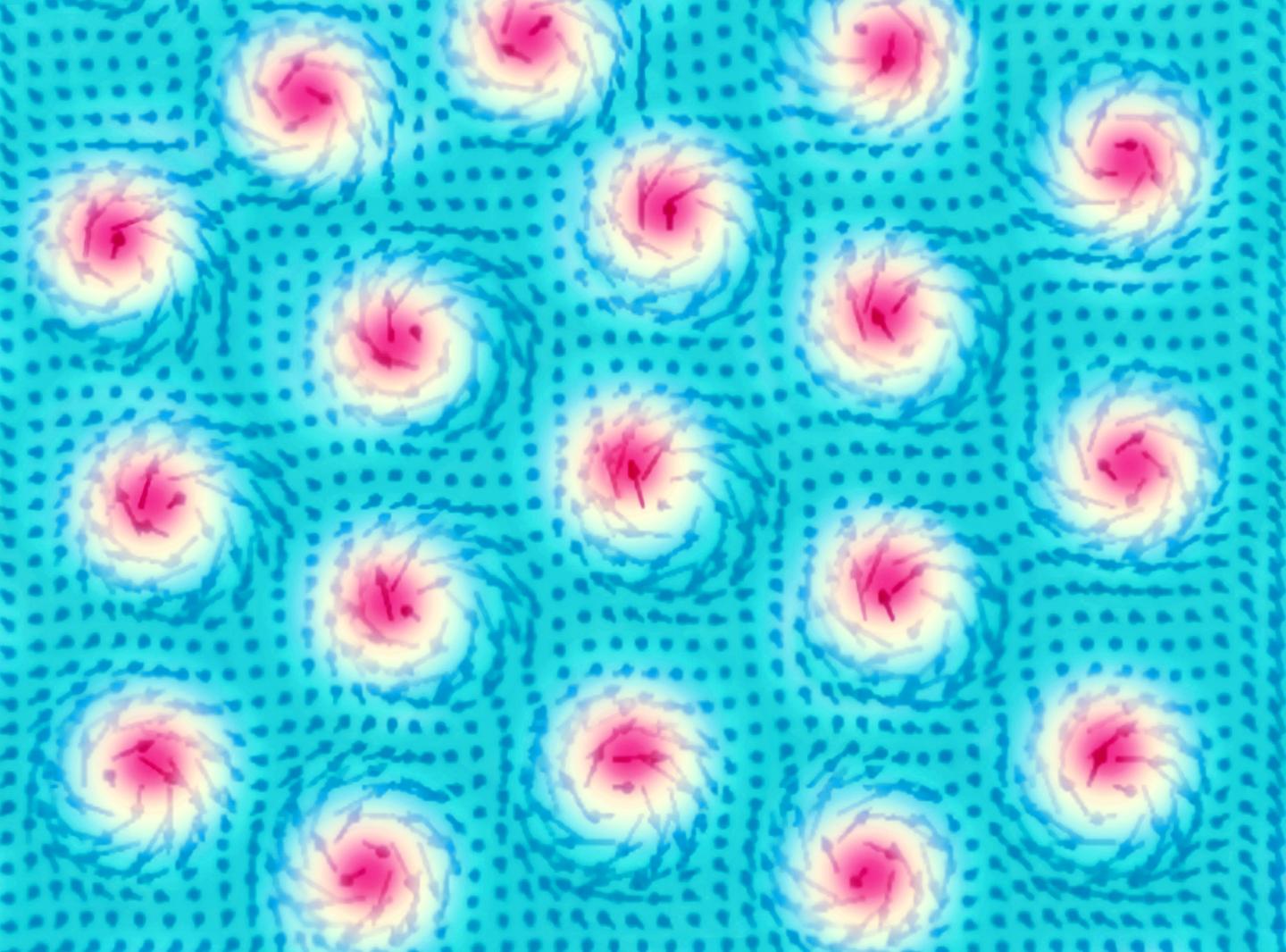
Cu2OSeO3 is a material with unusual magnetic properties. Magnetic spin vortices known as skyrmions are formed within a certain temperature range when in the presence of a small external magnetic field. Currently, moderately low temperatures of around 60 Kelvin (-213 degrees Celsius) are required to stabilise their phase, but it appears possible to shift this temperature range to room temperature. The exciting thing about skyrmions is that they can be set in motion and controlled very easily, thus offering new opportunities to reduce the energy required for data processing.
Theoretical work had predicted that it should be possible to use a high-frequency electric field to excite a group of skyrmions in the sample so that their cores will rotate all together, synchronously like a fish swarm, clockwise or counter-clockwise, or alternatively they can even exhibit a “breathing” motion.
Now a team has succeeded in measuring the dynamics of these skyrmions in detail for the first time using a single-crystal sample of Cu2OSeO3. “Conventional laboratory methods like ferromagnetic resonance, cannot detect directly deflection of the spins in the skyrmion phase and are therefore not suitable for observing selectively their excitations. Therefore, we had to come up with something new”, explains Prof. Christian Back, from Technical University of Munich.
The team succeeded at BESSY II in combining a spin-resolving method with an external microwave field. „The resonant magnetic scattering technique when combined with magnetic vectorial external fields shows where the spins are located in the lattice and how they are oriented in space, and all these for each elemental spin species that may exist in the specimen”, explains Dr. Florin Radu, at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), a physicist who developed and set up the VEKMAG end station in cooperation with partners from the Universität Regensburg, Ruhr University Bochum, and Freie Universität Berlin. The construction and continuing development of the VEKMAG station are supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and HZB.
Using electric field induced ferromagnetic resonance excitation and recording the x-ray intensity of a so called Bragg peak, the research group demonstrated experimentally for the first time that all three characteristic oscillation modes occur in Cu2OSeO3 – the team observed magnetic skyrmions turning clockwise, counterclockwise, and expanding and contracting (“breathing” mode). Those modes can be switched and turned around by changing the frequency of the microwave field: Each dynamic mode is achieved for a certain frequency, which further depends on the external magnetic field as well as on other intrinsic parameters of the sample. “This is a first step towards phase specific characterization of controlled skyrmion’s gyrational motion”, Radu says.
###
Media Contact
Antonia Roetger
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





