Credit: Image by WANG Dangge
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy using the antibody that combats the programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) shows great potential and is causing a revolution in clinical cancer management. Unfortunately, only a subset of treated patients responds to current ICB therapies, likely due to the immunological tolerance of tumors. Therefore, developing a practical strategy to combat this immunological tolerance and amplify ICB therapies has become a priority.
To meet this challenge, scientists from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a tumor enzymatic microenvironment-activatable antibody nanoparticle for robust cancer immunotherapy. This research was published online in Science Immunology.
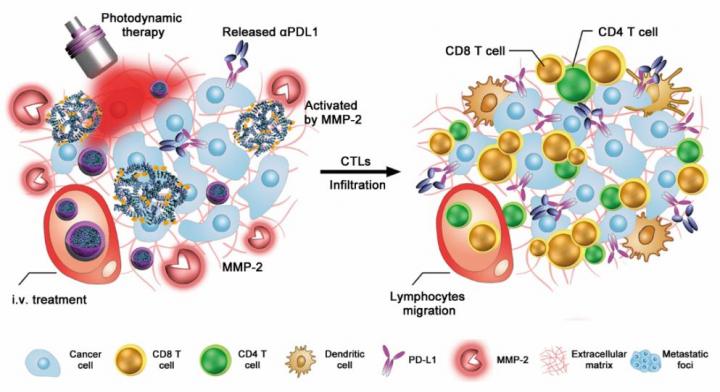
In this study, Prof. YU Haijun, Prof. LI Yaping and their colleagues engineered the antibody nanoparticles by integrating anti-PD-L1 antibody (αPDL1) and indocyanine green (ICG) into one single nanoplatform. ICG is a clinically approved fluorophore for fluorescence imaging in live surgery and photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy (PDT). The antibody nanoparticles remain inert in blood circulation and protect αPDL1 from binding with normal tissues. Once accumulated at the tumor site through the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, the antibody nanoparticles become activated to release αPDL1 for tumor-specific PD-L1 blockading.
Moreover, the scientists revealed that the antibody nanoparticles triggered the release of tumor antigens and promoted intratumoral infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) through the ICG-based PDT effect. “This is crucial for cancer immunotherapy since CTLs have been well-identified as the killer of tumor cells,” explained Prof. YU, co-corresponding author of the study.
Finally, they showed that the antibody nanoparticles not only boost antitumor immunity with great efficiency, but also elicit long-term immune memory effects in BALB/c mice, thus leading to remarkable tumor regression.
In particular, the antibody nanoparticle-mediated combination of ICB and PDT therapy effectively suppressed tumor growth and metastasis to the lung and lymph nodes when using a 4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/C mouse model, which resulted in survival for >70% of the mice for more than 65 days, compared to complete mouse death in 42 days for the free αPDL1 group.
“We provided a robust antibody nanoplatform for priming the antitumor immunity and inhibiting the immune checkpoint, which could be readily adapted to other immune checkpoint inhibitors for enhanced ICB therapies. Given the simplicity of the nanostructures, our study has the potential of being translated into future generations of cancer immunotherapy,” Prof. YU said.
###
Media Contact
YU Haijun
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.




