Credit: TAN Puchuan
Researchers from the Beijing Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a bionic stretchable nanogenerator (BSNG) that takes inspiration from electric eels.
The scientists hope the new technology will meet the tough demands of wearable equipment applications for stretchability, deformability, biocompatibility, waterproofness and more.
BSNG, which uses technology that mimics the structure of ion channels on the cytomembrane of electric eels’ electrocytes, has two broad applications: Besides providing a potential power source for wearable electronic devices underwater and on land, it can also be used for human motion monitoring due to its excellent flexibility and mechanical responsiveness.
The study was published online in Nature Communications on June 19.
BSNG is based on a mechanically sensitive bionic channel that relies on the stress mismatch between polydimethylsiloxane and silicone. Like its eel counterpart, BSNG can generate an open circuit voltage up to 10 V underwater. It can also generate an open circuit voltage up to 170 V under dry conditions.
BSNG’s bionic structure and material ensure superior stretchability. For example, BSNG maintained stable output performance without attenuation after 50,000 uniaxial tensile tests (tensile rate of 50%).
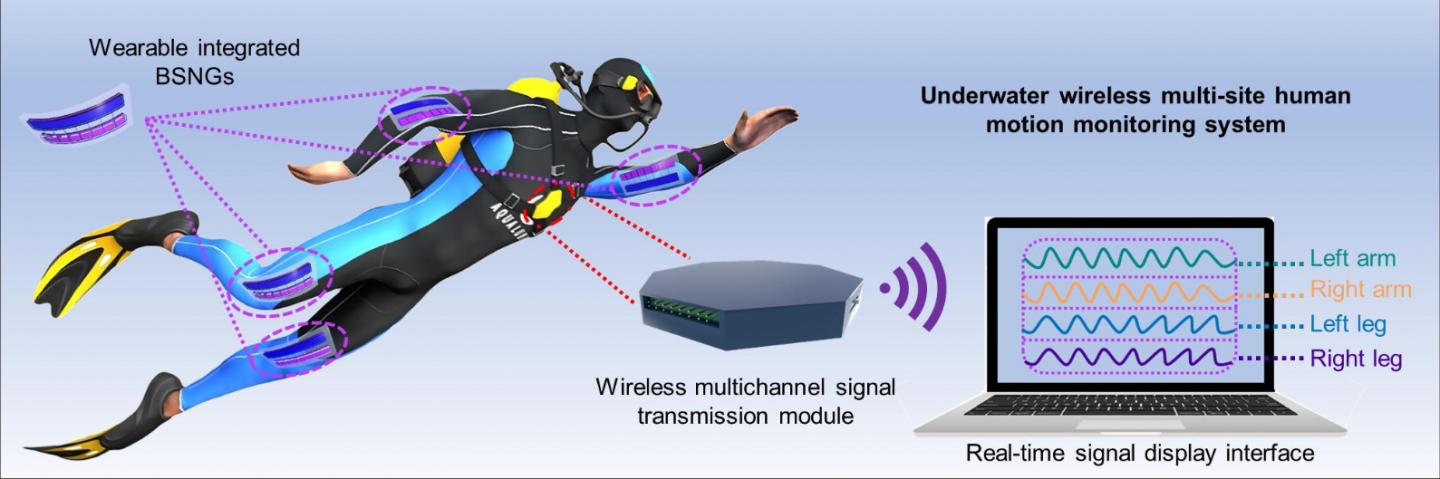
To prove the practicability of the technology, the researchers built an underwater wireless motion monitoring system based on BSNG.
Through this system, the motion signals under different swimming strokes can be synchronously transmitted, displayed and recorded. As for the energy harvester application, researchers achieved underwater rescue based on BSNG.
Wearable integrated BSNGS can collect mechanical energy from human motion and convert it into electrical energy to store in capacitors. In case of emergency, the rescue signal light can be lighted remotely by tapping the alarm trigger in front of the chest.
Due to its excellent properties, BSNG holds great promise for use in electronic skin, soft robots, wearable electronic products and implantable medical devices.
###
Media Contact
TAN Puchuan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




