Credit: Image courtesy of Professor Jennifer Clack, University Museum of Zoology, Cambridge
Micro-CT scanning of a tiny snake-like fossil discovered in Scotland has shed new light on the elusive creature, thought to be one of the earliest known tetrapods to develop teeth that allowed it to crush its prey.
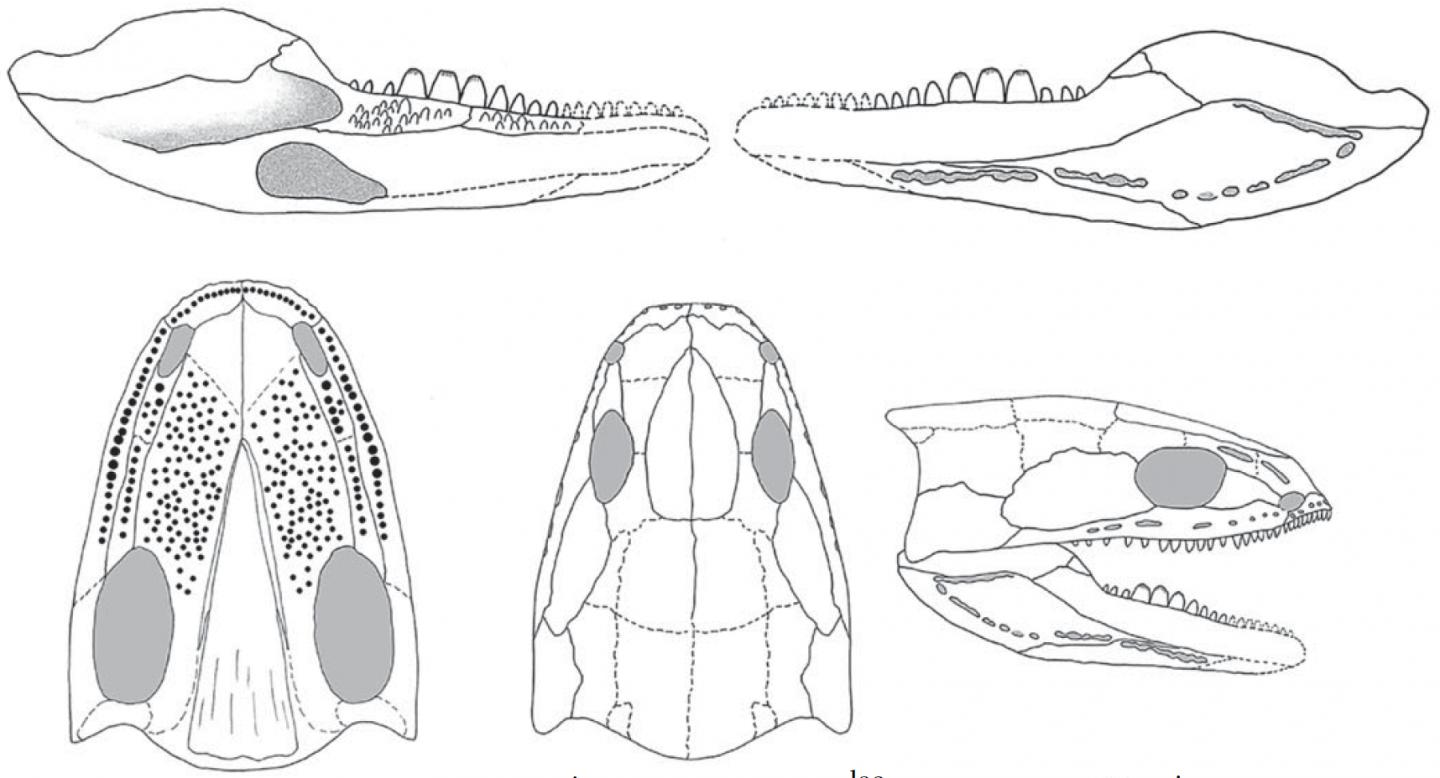
Detailed scans of Acherontiscus caledoniae showed a unique combination of different tooth shapes and sizes as well as a deep lower jaw which scientists believe would have given the creature the ability to pierce, cut and grind the hard-shelled crustaceans that made up its diet.
Scientists led by the University Museum of Zoology in Cambridge alongside the University of Lincoln, the Natural History Museum in London and the University of Southampton, found that the dental pattern of Acherontiscus is at odds with that of several other tetrapods of this period, which tended to have uniform rows of cone-like teeth sometimes curved backwards at the tip. The variation in the shape and size of teeth shown in this fossil displays a level of dental adaptation that is unprecedented in such an early tetrapod.
As co-author Dr Marcello Ruta from the University of Lincoln’s School Of Life Sciences explains: “We found that Acherontiscus preceded the origin of modern tetrapod lineages and joined an array of primitive groups that independently acquired long and often miniaturized bodies, and exhibited either reduced or no limbs.”
The fossil is the only known specimen of this limbless tetrapod, which measured just 6 inches long and existed in swampy marshlands on the outskirts of Edinburgh some 330 million years ago. The delicate nature of the fossil meant that scientists were unable to use mechanical or chemical methods to free its skeleton from the surrounding rock, or study the specimen under a microscope.
Lead author Professor Jennifer Clack from the University Museum of Zoology in Cambridge said: “Using advanced techniques of micro-CT scanning, we were able to make sense of Acherontiscus‘ complex skull, revealing minute anatomical details that allowed us to produce a greatly revised and much more complete reconstruction.
“We were particularly surprised to realize the great variety of shapes and sizes of its teeth. Acherontiscus is the earliest known tetrapod showing a crushing dentition, a feature with a rather discontinuous distribution in fossil and modern tetrapods.”
Fragments in the surrounding matrix have also revealed more about Acherontiscus‘ habitat which will inform further research into the area as co-author Professor John Marshall from the University of Southampton’s School of Ocean and Earth Science explains: “Our study provided impetus for exploring the ecology and environments of the Scottish wetlands where Acherontiscus lived. Analysis of the content of fossil spores from about 0.2 grams of the matrix surrounding the creature suggests that this animal lived close to or within a still water body surrounded by herbaceous plants related to clubmosses. A more distant forest of larger, tree-like relatives of modern quillworts was also present.”
###
The paper Acherontiscus caledoniae: the first heterodont and durophagous tetrapod was published in the Royal Society Open Science journal. The full paper is available at: https:/
Media Contact
Sophie Belcher
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




