Ivermectin administration to livestock would have the greatest impact in West Africa
Credit: Imbahale et al., 2019
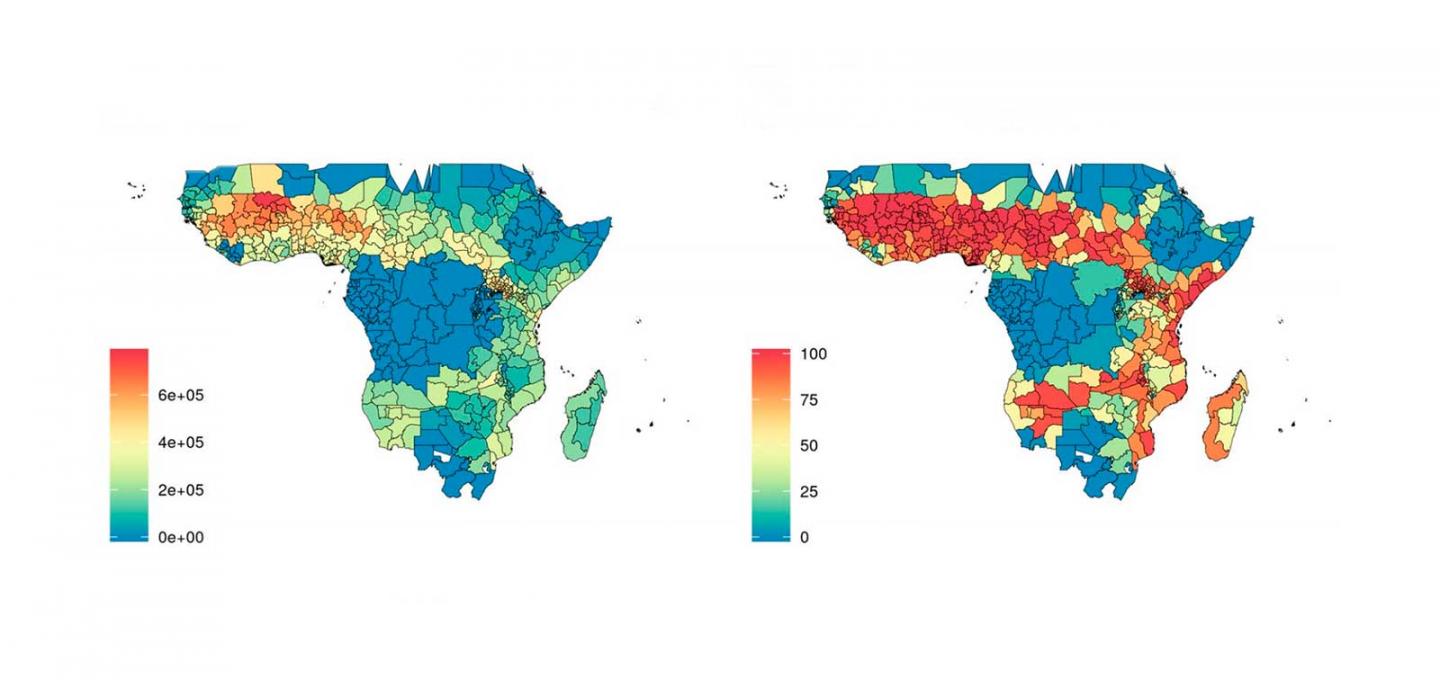
An analysis led by ISGlobal, an institution supported by “la Caixa”, identifies African regions where ivermectin administration to livestock would have the greatest impact on malaria transmission. The results, published, in Scientific Reports, point to West Africa, below the Sahel, where malaria prevalence is very high.
Between 2000 and 2015, an estimated 663 million malaria cases were avoided worldwide, mostly due to the use of insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor spraying. However, these measures do not protect against malaria-transmitting mosquitoes that bite outside, during the day, and can also feed from livestock. Tackling this “residual” transmission will require of strategies that go beyond household walls.
Ivermectin has been used for many years in livestock to control parasites that live on (eg. ticks) or inside (eg. intestinal worms) the animal. Recent studies show that ivermectin can also kill mosquitoes that feed on drug-treated animals, making it an attractive complement tool for vector control, particularly in areas with high malaria transmission.
In this study, ISGlobal researcher Carlos Chaccour and his colleagues performed a mapping exercise to identify African regions where a high malaria prevalence overlaps with high density of livestock and of the Anopheles arabiensis mosquito, which feeds on humans and cattle. In other words, they sought to identify the regions where ivermectin administration to livestock would have the greatest impact on malaria control.
The analysis shows that the West African region under the Sahel (particularly Burkina Faso, Guinea, Benin and Togo) would benefit the most from treating livestock with ivermectin. These regions are also those with the highest malaria prevalence among children under 10 years of age.
“This strategy can provide additional benefits for the community, by improving the overall health of their livestock,” explains Chaccour. In addition, he points out, ivermectin is expected to be effective even against insecticide-resistant mosquitoes.
More studies are needed to evaluate if the strategy is effective in reducing malaria transmission, accepted by communities, and cost-effective. This is precisely one of the aims of BOHEMIA, a project funded by Unitaid and led by ISGlobal. Launched recently, BOHEMIA will assess the impact of mass ivermectin administration in communities and/or livestock in two African countries (Tanzania and Mozambique). “Actually, the regions chosen for BOHEMIA are of special interest for ivermectin use in livestock, according to our maps,” points out Chaccour.
###
Media Contact
Adelaida Sarukhan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




