Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new technique for creating devices out of a water-based hydrogel material that can be patterned, folded and used to manipulate objects. The technique holds promise for use in “soft robotics” and biomedical applications.
“This work brings us one step closer to developing new soft robotics technologies that mimic biological systems and can work in aqueous environments,” says Dr. Michael Dickey, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the work.
“In the nearer term, the technique may have applications for drug delivery or tissue scaffolding and directing cell growth in three dimensions, for example,” says Dr. Orlin Velev, INVISTA Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State, the second senior author of the paper.
The technique they’ve developed uses hydrogels, which are water-based gels composed of water and a small fraction of polymer molecules. Hydrogels are elastic, translucent and – in theory – biocompatible. The researchers found a way to modify and pattern sections of hydrogel electrically by using a copper electrode to inject positively charged copper ions into the material. Those ions bond with negatively charged sites on the polymer network in the hydrogel, essentially linking the polymer molecules to each other and making the material stiffer and more resilient. The researchers can target specific areas with the electrodes to create a framework of stiffened material within the hydrogel. The resulting patterns of ions are stable for months in water.
“The bonds between the biopolymer molecules and the copper ions also pull the molecular strands closer together, causing the hydrogel to bend or flex,” Velev says. “And the more copper ions we inject into the hydrogel by flowing current through the electrodes, the further it bends.”
The researchers were able to take advantage of the increased stiffness and bending behavior in patterned sections to make the hydrogel manipulate objects. For example, the researchers created a V-shaped segment of hydrogel. When copper ions were injected into the bottom of the V, the hydrogel flexed – closing on an object as if the hydrogel were a pair of soft tweezers. By injecting ions into the back side of the hydrogel, the tweezers opened – releasing the object.
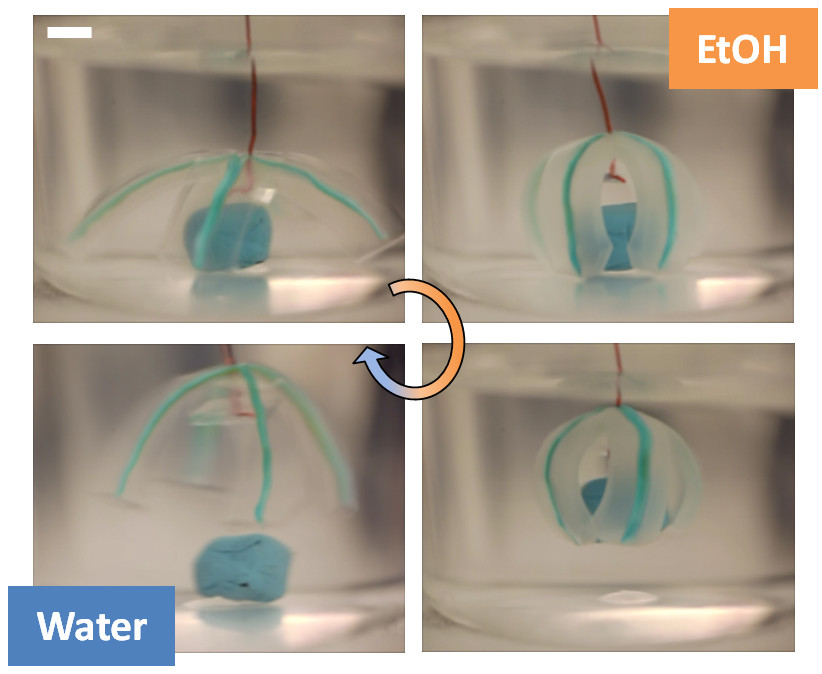
The researchers also created a chemically actuated “grabber” out of an X-shaped segment of hydrogel with a patterned framework on the back of the X. When the hydrogel was immersed in ethanol, the non-patterned hydrogel shrank. But because the patterned framework was stiffer than the surrounding hydrogel, the X closed like the petals of a flower, grasping an object. When the X-shaped structure was placed in water, the hydrogel expanded, allowing the “petals” to unfold and release the object. Video of the hydrogels in action is available here.
“We are currently planning to use this technique to develop motile, biologically compatible microdevices,” Velev says.
“It’s also worth noting that this technique works with ions other than copper, such as calcium, which are biologically relevant,” Dickey says.
The paper, “Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting,” was published online Aug. 2 in Nature Communications. Lead authors of the paper are Dr. Etienne Palleau, a former postdoctoral researcher at NC State, and Daniel Morales, a Ph.D. student at NC State. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation’s Research Triangle Materials Research Science and Engineering Center and DS/DGA-France.
In 2011, Velev and Dickey published research on their development of gel-like memory devices that function in wet environments.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by North Carolina State University.