Partnered with machine learning, brain scans reveal how people understand objects in our world
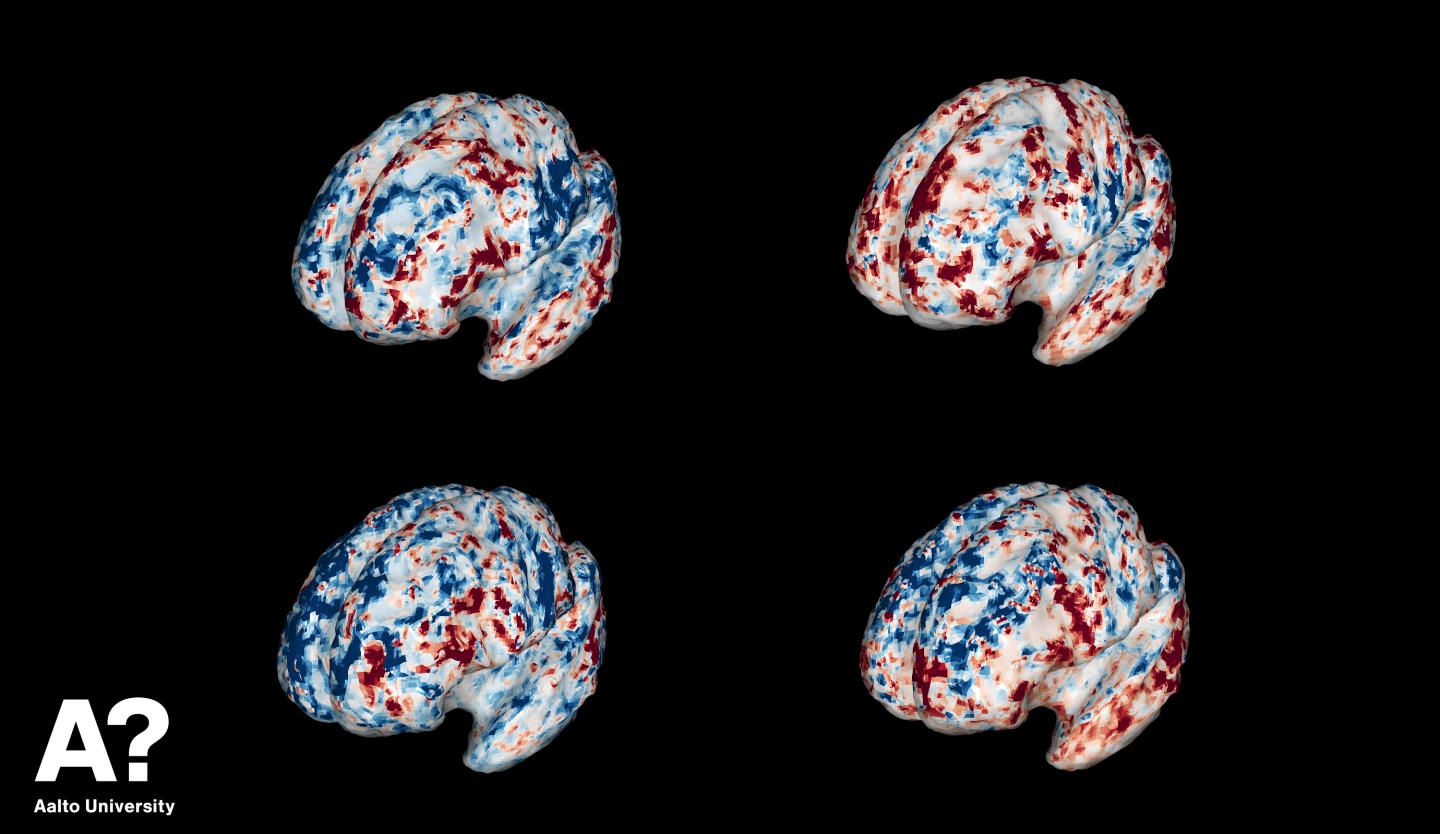
Credit: Sasa L. Kivisaari
What’s an s-shaped animal with scales and no legs? What has big ears, a trunk and tusks? What goes ‘woof’ and chases cats? The brain’s ability to reconstruct facts – ‘a snake’, ‘an elephant’ and ‘a dog’ – from clues has been observed using brain scanning by researchers at Aalto university. Their study was published today in Nature Communications.
In the research, test subjects were given three clues to help them guess what familiar objects the clues described. In addition to well-known animals, the clues depicted vegetables, fruits, tools and vehicles. The familiar objects and concepts described in the clues were never presented directly to the test subjects.
The researchers at Aalto University demonstrated that brain activation patterns contained more information about the features of the concept than had been presented as clues. The researchers concluded that the brain uses environmental clues in an agile way to activate a whole range of the target concept’s properties that have been learned during life.
‘This is a very important skill in nature because it enables a quick response based on small amount of information. For example, we automatically avoid a wiggly thing on a rocky shore because we know that a snake may be poisonous,’ says Sasa Kivisaari, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Aalto University.
The study used a huge amount of internet-based material to map the meaningful features associated with different concepts. Machine learning was used to create a model that describes the relationship between these features and brain activation patterns. Based on the model, brain activation patterns could be used to accurately deduce which concept the test subject was thinking of. For example, the activation patterns could be used to infer whether the clues led the subject to think of an elephant or a dog.
Understanding our differences to detect memory disorders
The method can be used to address the question why people understand or perceive the same concept differently.
‘The organization of meanings in the brain differs from person to person and can also affect how easy or hard it is for them to understand each other,’ says Professor Riitta Salmelin.
The research may also play a role in detecting memory disorders.
‘Combining and understanding meaningful information seems to involve the same brain areas that are damaged in early Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, the method we use may also be applied to the early detection of memory disorders,’ says Kivisaari.
Professor Riitta Salmelin’s research team studies the neural basis of processing of language and meaningful information at the Department of Neuroscience and Biomedical Engineering at Aalto University. The research has been supported by the Academy of Finland, the Aalto Brain Centre and the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation.
###
Further information:
Visualisation of the model used in the study: https:/
Sasa Kivisaari
Postdoctoral Researcher, Academy of Finland
Aalto University
[email protected]
Tel: +358 50 432 2828
Riitta Salmelin
Professor
Aalto University
[email protected]
Tel: +358 50 344 2745
Media Contact
Dr. Sasa Kivisaari
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




