Credit: Dong-Woo Cho (POSTECH)
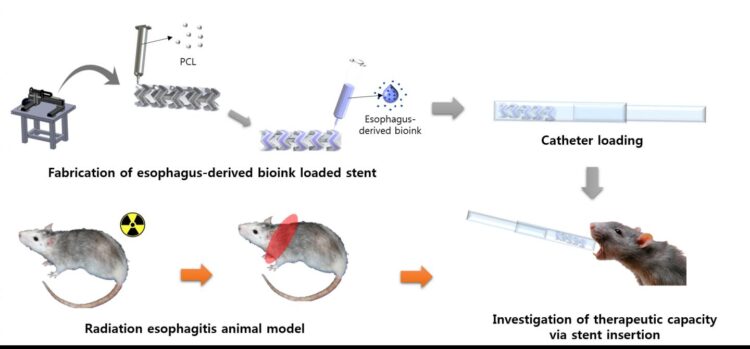
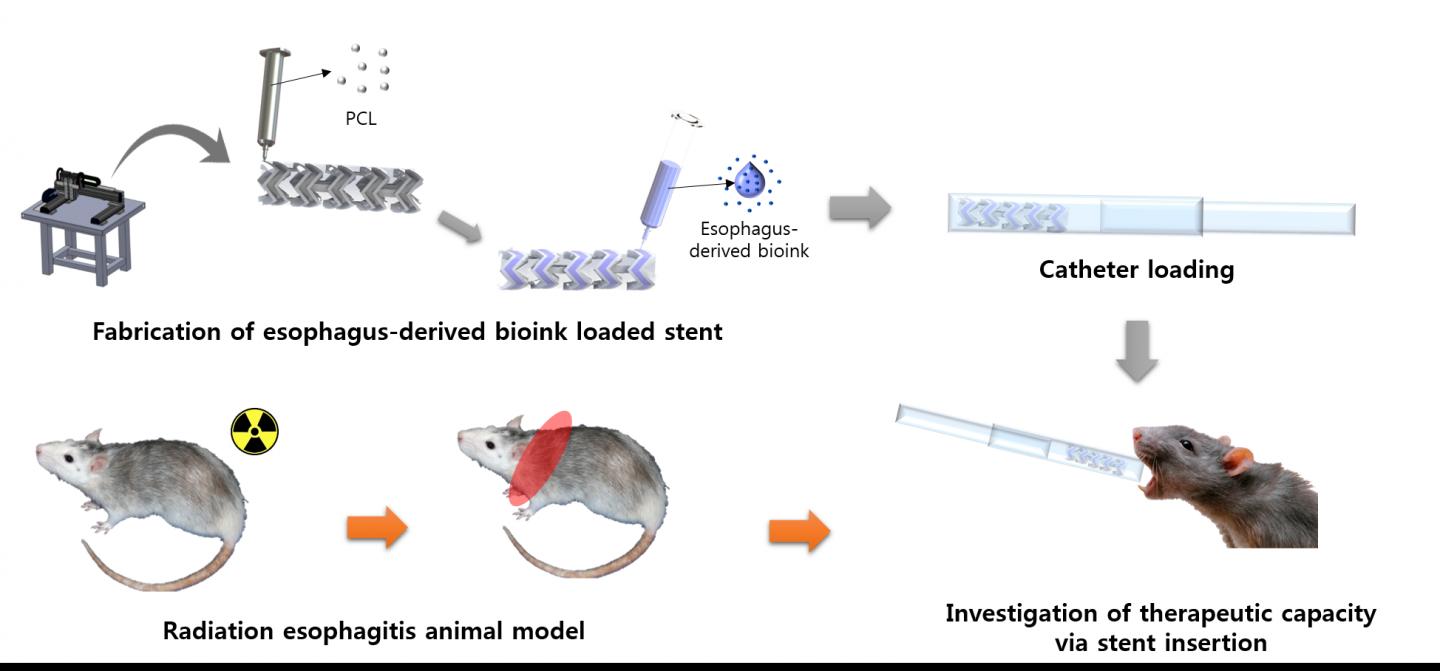
Radiation esophagitis, characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus, is the most common acute adverse effect of radiation therapy that causes swallowing problems. This eventually causes dehydration and leaves the body unfit for further treatment. Unfortunately, no direct cure currently exists for patients suffering from such conditions. To this, a POSTECH research team has developed esophageal stents that biodegrade in the body using 3D printers, opening up the possibility of treating the condition.
A joint research team led by Professor Dong-Woo Cho and Ph.D. candidate Suhun Chae in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at POSTECH and Dr. Dong-Heon Ha of EDmicBio, Inc. has together produced biodegradable stents with esophageal-derived bioink to directly treat radiation esophagitis and verified their therapeutic effects in animal models. These research findings were recently published in Biomaterials, an academic journal with international authority in the biomaterials field.
Various treatment methods are being developed to treat cancer, but radiation therapy is still one of the common treatments along with surgery and chemotherapy. If radiation esophagitis occurs during radiation therapy, treatment is limited to cataclysmic therapy that relieves the pain depending on the symptoms that appear, or inserting a stent to open the swollen esophagus to allow drinking or eating. However, these methods do not treat the damaged tissues directly.
The research team first produced bioink that removed cell components from esophageal tissues and extracted only extracellular matrix through the decellularization process. They produced a dumbbell-type stent that can carry this bioink using a 3D printing system. By inserting this stent into the inflamed esophagus of an animal, they confirmed that it promotes tissue regeneration while mitigating inflammatory reactions.
“The effectiveness of treatment is negated if proper nutrition cannot be delivered due to the pain,” explained Dong-Woo Cho who led the study. He added, “If this esophageal stent implantation is applied clinically, we expect that the patients will have better prognosis and higher quality of life.”
This research was conducted as part of the Research Leader Program the National Research Foundation of Korea and in cooperation with EDmicBio, Inc. which specializes in commercializing 3D organs-on-chips and medical devices.
###
Media Contact
Jinyoung Huh
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.