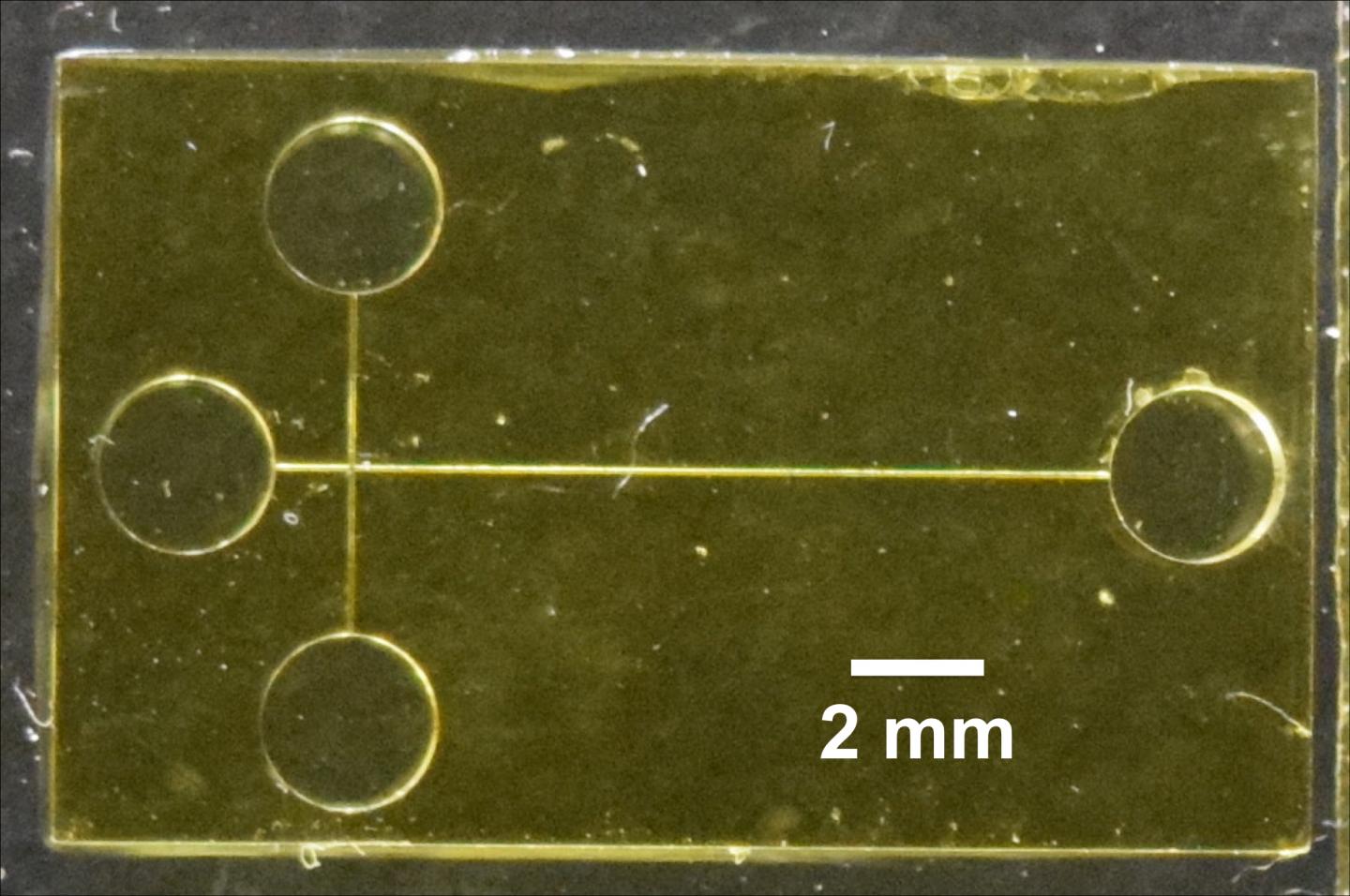
Credit: Adapted from Anal. Chem. 2019, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01395
Preterm birth (PTB) — defined as birth before the 37th week of gestation — is the leading complication of pregnancy. If doctors had a simple, accurate and inexpensive way to identify women at risk for the condition, they could develop better prevention strategies. Now researchers have created a 3D-printed microchip electrophoresis device that can sensitively detect three serum biomarkers of PTB. They report their results in ACS’ journal Analytical Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, PTB affects about 1 in 10 pregnancies worldwide. Preterm infants can suffer complications such as neurological, respiratory and cardiac problems and, in some cases, even death. Scientists have previously identified biomarker peptides and proteins in maternal serum that can fairly accurately predict PTB at 28 weeks of gestation. However, existing methods for detecting the biomarkers are laborious or not very sensitive. In prior research, Adam Woolley and colleagues used a 2D microfluidic device to separate PTB biomarkers by electrophoresis. But making these devices was slow, error-prone and costly. The process also required a clean room, caustic chemicals and highly trained personnel. Therefore, Woolley’s team wanted to develop a 3D-printed microchip device, which would be much simpler, faster and cheaper to make, for separating and detecting fluorescently labeled PTB biomarkers.
The researchers printed their device onto a glass slide using a 3D printer with a custom resin as the ink. To achieve the best separation of three peptide biomarkers by electrophoresis, they optimized the device design, as well as parameters such as applied voltages and buffer identity and composition. The 3D-printed microchip could detect the three PTB biomarkers in the picomolar to low nanomolar range, similar to their 2D microfluidic device. The researchers note that although these detection limits are still higher than the PTB risk levels for the biomarkers, they could increase the sensitivity by adding a component to the device that concentrates the peptides.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health.
The abstract that accompanies this study is available here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




