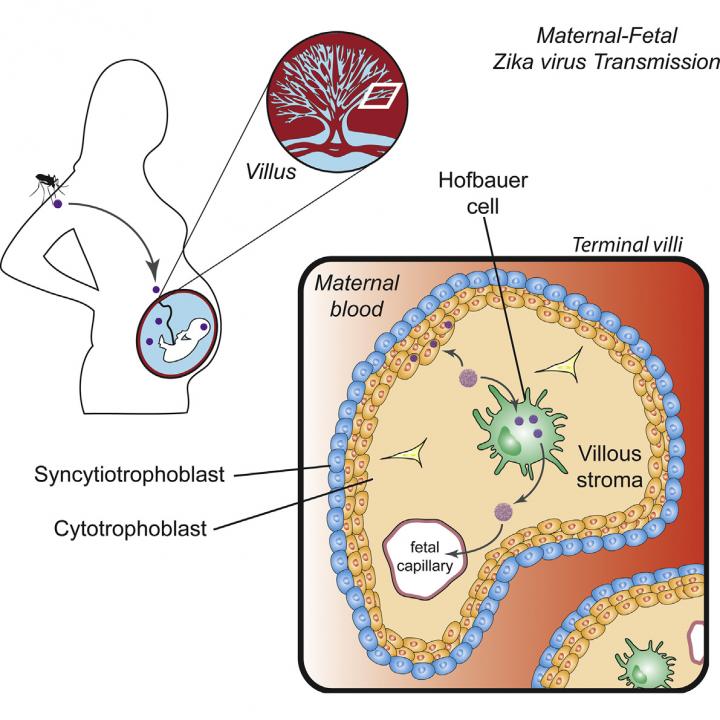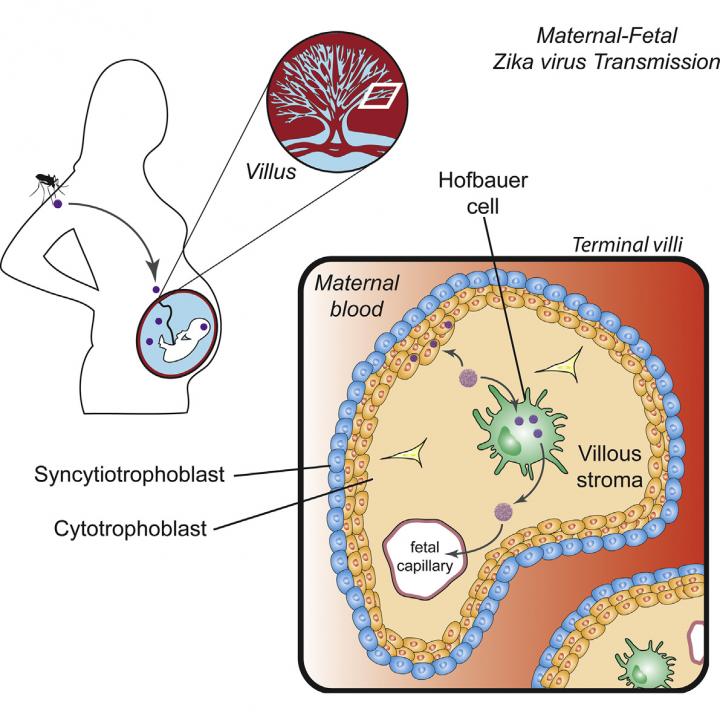
One of Zika's mysteries is how the virus passes from an infected mother, through the placenta, to a developing fetus. The route may not be direct either — transmission via multiple cell types may be necessary. A study appearing May 27, 2016 in Cell Host & Microbe supports the possibility that placental immune cells called Hofbauer cells, which have direct access to fetal blood vessels, are one cell type involved.
"One group has recently discovered viral antigen in Hofbauer cells collected from placental tissue of a fetus that unfortunately died as a result of Zika virus infection," says senior author and Assistant Professor in Pediatrics at the Emory University School of Medicine, Mehul Suthar. "Our study indicates that this cell type may be a target for Zika virus in the placenta and replication in these cells may allow the virus to cross the placental barrier and enter the fetal circulation," adds co-author Rana Chakraborty, a pediatric infectious disease specialist, also at Emory.
The researchers studied a small sample of donated full-term human placentae to identify cell types that might be vulnerable to Zika virus infection (using a strain that is currently circulating in the Caribbean). In addition to Hofbauer cells, which are placental macrophages that originate from the connective tissue (mesenchymal) stem cells of a developing fetus, infection was also detected to a lesser extent in cytotrophoblasts — cells found in the middle layer of the placental barrier.
One explanation for how the virus crosses the placental barrier is by initial infection of syncytiotrophoblasts, the outermost layer of cells that surrounds and nurtures the fetus. However, earlier work (10.1016/j.chom.2016.03.008) has shown that these cells can resist the virus. The work from the Suthar Lab shows that the less-differentiated cytotrophoblasts are permissive for Zika virus infection, suggesting that if the virus is able to cross the syncytiotrophoblast layer, the virus has access to target cells where it can replicate. While Hofbauer cells were identified over a century ago, very little is known about them. Overall, the Zika epidemic has helped to reveal that the placenta is one of the most understudied human organs.
One interesting observation from the study is that the placental cells from the five donors showed different levels of viral replication over time. "A concept that is emerging is how host genetics or other non-viral factors, including nutrition and microbiota, influence your immune response," Suthar says. "What our study suggests is not everyone is predisposed to having the virus replicate in the placenta, but the full meaning of this needs to be explored further."
###
This work was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, Children's Healthcare of Atlanta, Emory Vaccine Center, the Georgia Research Alliance, the Multi-Center NICHD International Maternal Pediatric Adolescent AIDS Clinical Trials Network, and the Center for AIDS Research at Emory University.
Cell Host & Microbe, Quicke and Bowen et al.: "Zika virus infects human placental macrophages" http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(16)30211-6
Cell Press Statement on Data Sharing in Public Health Emergencies
The Cell Press family of journals is committed to ensuring that the global response to public health emergencies is informed by the best available research evidence and data, and as such, we will make all content concerning the Zika virus free to access. We will work in partnership with reviewers to fast-track review all submissions concerning Zika. We will adapt the editorial criteria that we apply to Zika submissions by asking reviewers to evaluate only if the research methods are sound and support the conclusions and if the work will contribute in some way toward resolving the immediate challenges. We will expedite publication of papers that meet these two criteria.
Cell Host & Microbe (@cellhostmicrobe), published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes novel findings and translational studies related to microbes (which include bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses). The unifying theme is the integrated study of microbes in conjunction and communication with each other, their host, and the cellular environment they inhabit. Visit: http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected].
Media Contact
Joseph Caputo
[email protected]
617-397-2802
@CellPressNews
http://www.cellpress.com
The post Zika virus infects human placental macrophages appeared first on Scienmag.