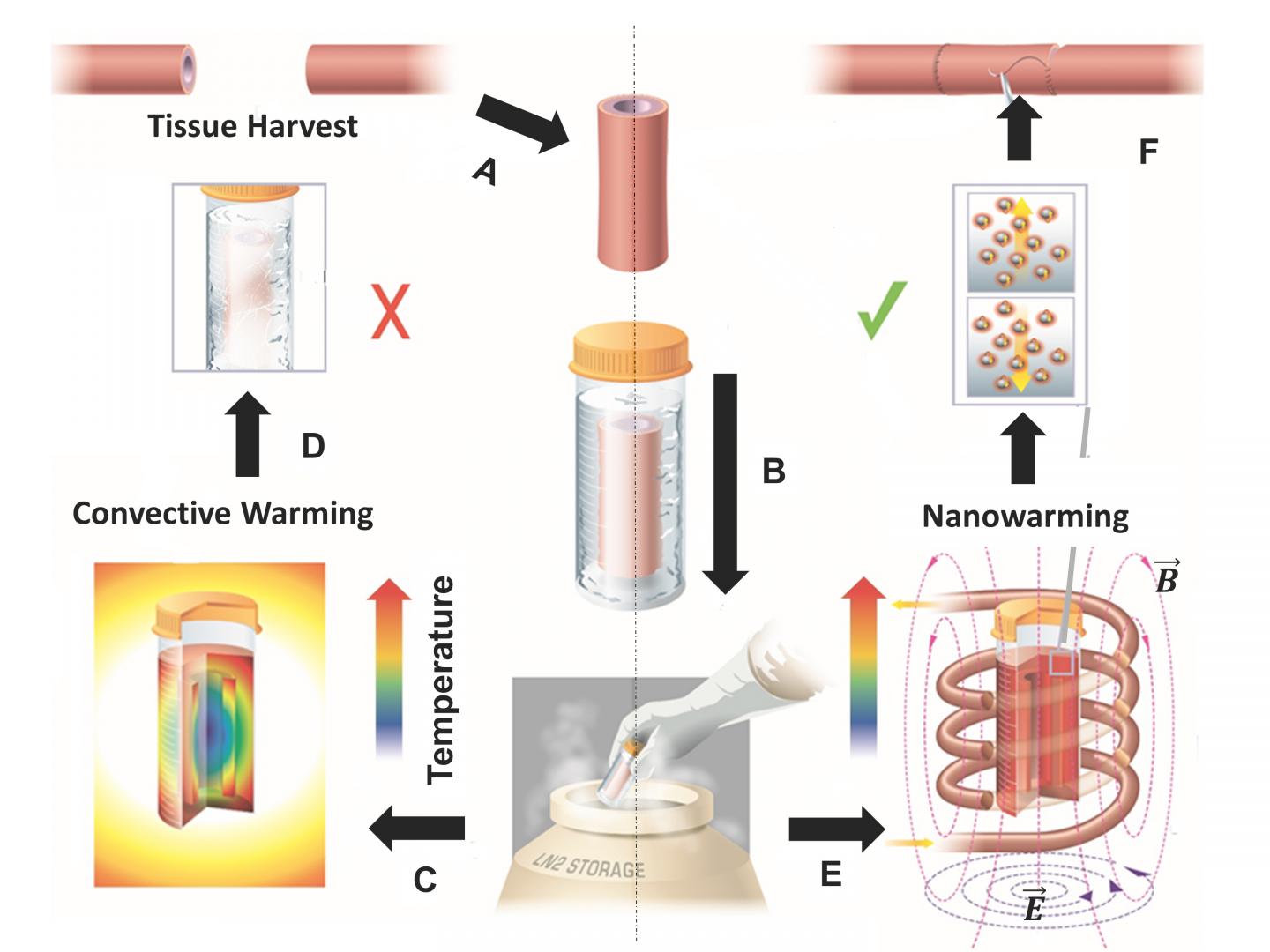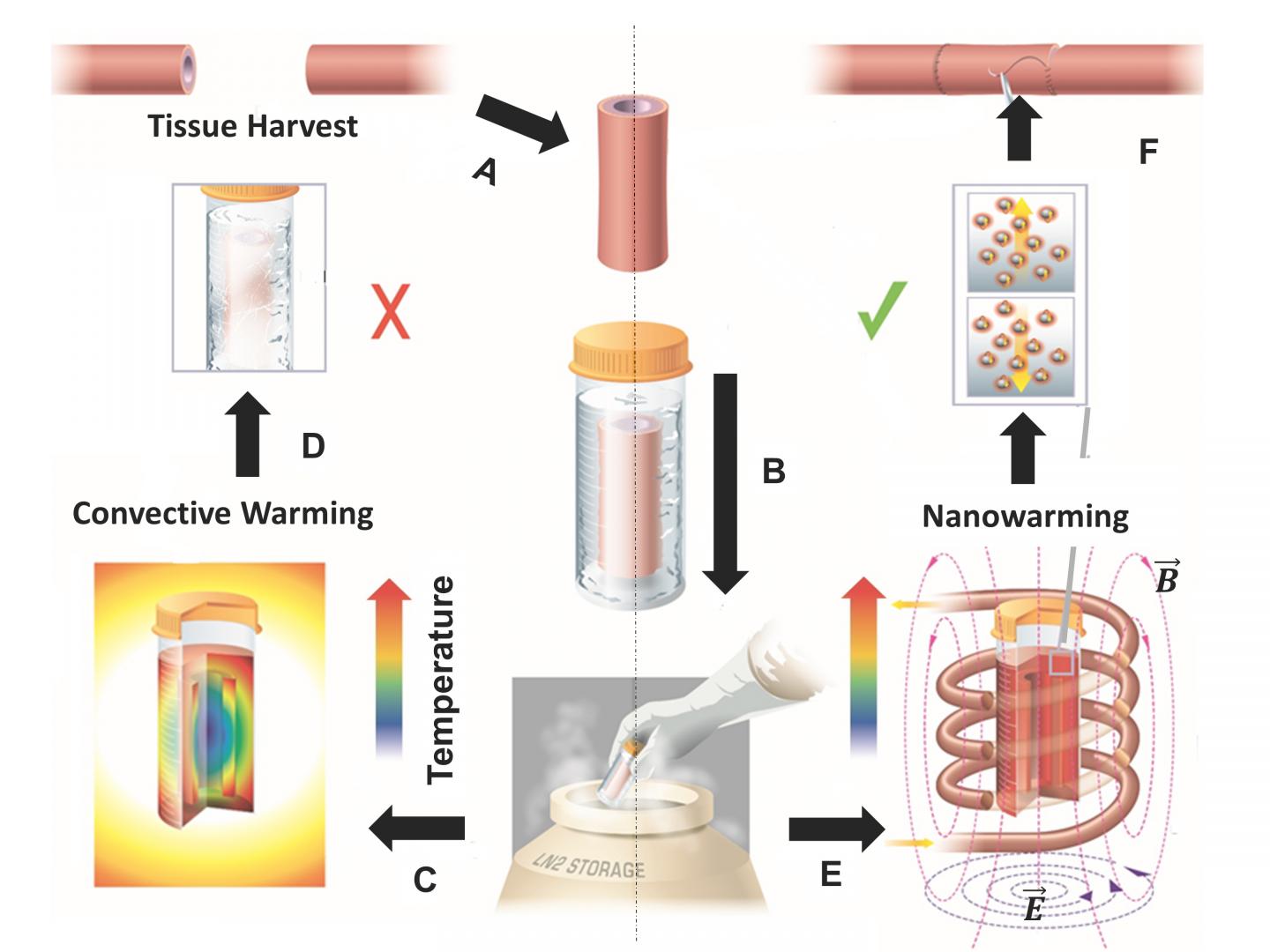
Credit: Manuchehrabadi et al., Science Translational Medicine (2017)
Overcoming a major hurdle in transplant medicine, a new study reveals that nanotechnology can be used to rapidly rewarm cryogenically treated samples without damaging delicate frozen tissues, which may someday help make organ cryopreservation a reality. More than 60% of the hearts and lungs donated for transplantation must be discarded annually, because these tissues cannot be kept on ice for longer than four hours. According to recent estimates, if only half of unused organs were successfully transplanted, transplant waiting lists could be eliminated within two years. Long-term preservation methods like vitrification – which involves super-cooling biological samples to a glassy state – could establish tissue storage banks and reduce transplant rejection rates, greatly facilitating the process to find matching donors when needed. Unfortunately, while sophisticated cryopreservation methods exist to keep samples cold, tissues often suffer damage and even crack during the thawing process. Navid Manuchehrabadi and colleagues developed a unique approach to quickly warm up frozen tissues without compromising their cellular viability. The researchers mixed silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles into a solution and generated uniform heat throughout the samples by applying an external magnetic field. After rewarming, none of the tissues displayed signs of harm, unlike control samples rewarmed slowly over ice. What's more, the nanoparticles were successfully washed away from the sample following thawing. The scientists also tested their set-up using frozen human skin cells, segments of pig heart tissue, and sections of pig arteries in larger-sized volumes amounting to 50 milliliters. Although scaling up the system to accommodate whole organs will require further optimization, the authors say the technology might be applied beyond cryogenics, including delivering lethal pulses of heat to cancer cells.
###
Media Contact
Science Press Package Team
[email protected]
202-326-6440
@AAAS
http://www.aaas.org
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag