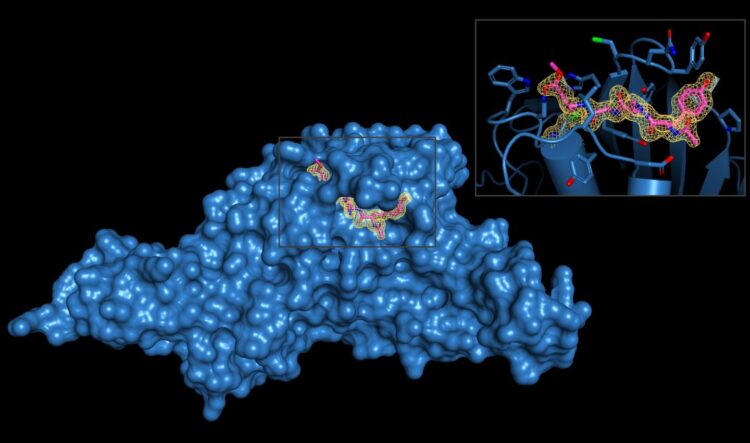
Coronavirus uses enzymatic cutter for virus production and to disable essential immune proteins
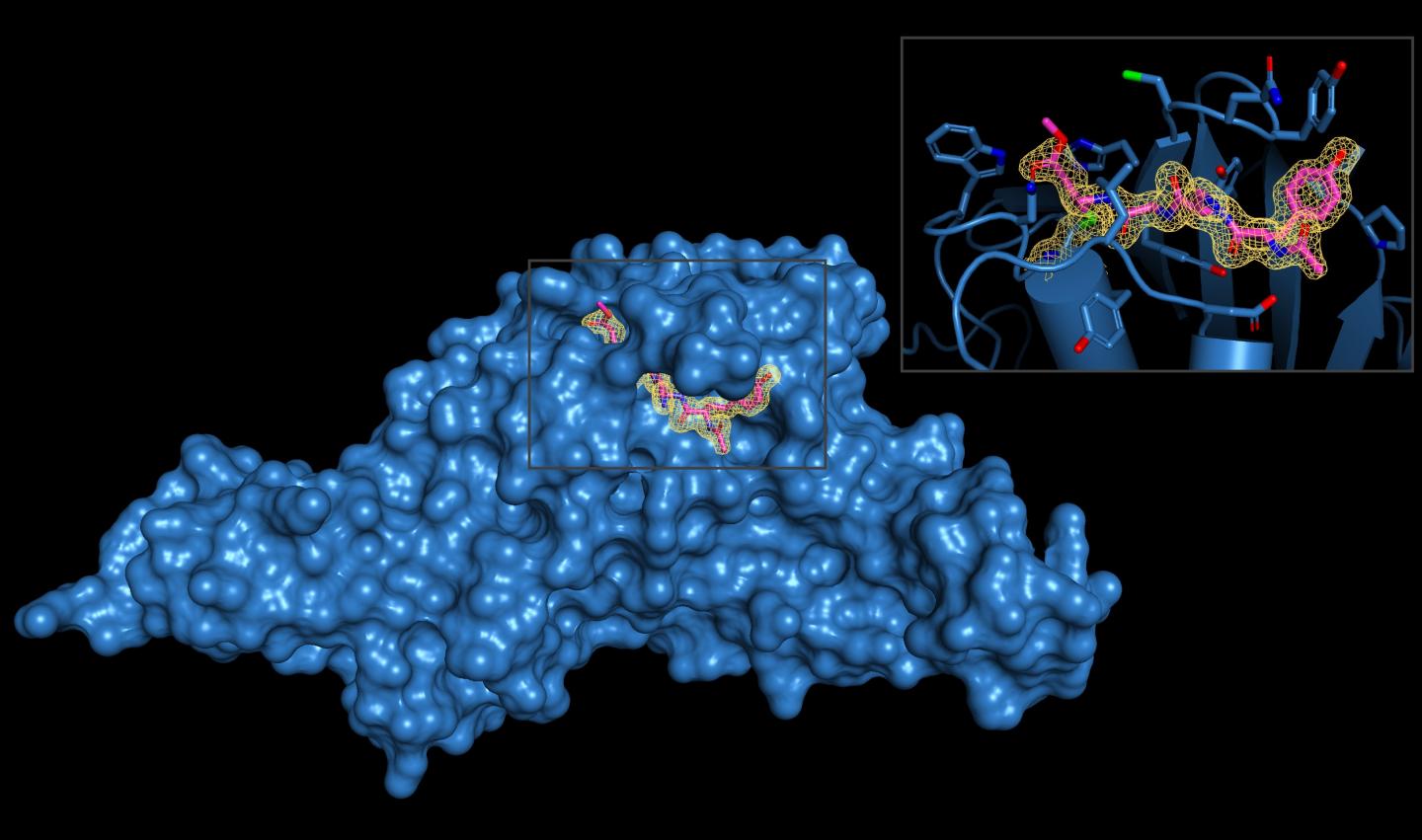
Credit: Image courtesy Shaun K. Olsen, PhD, laboratory at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine)
SAN ANTONIO, Texas, USA – American and Polish scientists, reporting Oct. 16 in the journal Science Advances, laid out a novel rationale for COVID-19 drug design – blocking a molecular “scissor” that the virus uses for virus production and to disable human proteins crucial to the immune response.
The researchers are from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) and the Wroclaw University of Science and Technology. Information gleaned by the American team helped Polish chemists to develop two molecules that inhibit the cutter, an enzyme called SARS-CoV-2-PLpro.
SARS-CoV-2-PLpro promotes infection by sensing and processing both viral and human proteins, said senior author Shaun K. Olsen, PhD, associate professor of biochemistry and structural biology in the Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at UT Health San Antonio.
“This enzyme executes a double-whammy,” Dr. Olsen said. “It stimulates the release of proteins that are essential for the virus to replicate, and it also inhibits molecules called cytokines and chemokines that signal the immune system to attack the infection,” Dr. Olsen said.
SARS-CoV-2-PLpro cuts human proteins ubiquitin and ISG15, which help maintain protein integrity. “The enzyme acts like a molecular scissor,” Dr. Olsen said. “It cleaves ubiquitin and ISG15 away from other proteins, which reverses their normal effects.”
Dr. Olsen’s team, which recently moved to the Long School of Medicine at UT Health San Antonio from the Medical University of South Carolina, solved the three-dimensional structures of SARS-CoV-2-PLpro and the two inhibitor molecules, which are called VIR250 and VIR251. X-ray crystallography was performed at the Argonne National Laboratory near Chicago.
“Our collaborator, Dr. Marcin Drag, and his team developed the inhibitors, which are very efficient at blocking the activity of SARS-CoV-2-PLpro, yet do not recognize other similar enzymes in human cells,” Dr. Olsen said. “This is a critical point: The inhibitor is specific for this one viral enzyme and doesn’t cross-react with human enzymes with a similar function.”
Specificity will be a key determinant of therapeutic value down the road, he said.
The American team also compared SARS-CoV-2-PLpro against similar enzymes from coronaviruses of recent decades, SARS-CoV-1 and MERS. They learned that SARS-CoV-2-PLpro processes ubiquitin and ISG15 much differently than its SARS-1 counterpart.
“One of the key questions is whether that accounts for some of the differences we see in how those viruses affect humans, if at all,” Dr. Olsen said.
By understanding similarities and differences of these enzymes in various coronaviruses, it may be possible to develop inhibitors that are effective against multiple viruses, and these inhibitors potentially could be modified when other coronavirus variants emerge in the future, he said.
###
Activity profiling and structures of inhibitor-bound SARS-CoV-2-PLpro protease provides a framework for anti-COVID-19 drug design
Wioletta Rut, Zongyang Lv, Mikolaj Zmudzinski, Stephanie Patchett, Digant Nayak, Scott J. Snipas, Farid El Oualid, Tony T. Huang, Miklos Bekes, Marcin Drag, Shaun K. Olsen
First published: Oct. 16, 2020, Science Advances
https:/
The Long School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio is named for Texas philanthropists Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long. The school is the largest educator of physicians in South Texas, many of whom remain in San Antonio and the region to practice medicine. The school teaches more than 900 students and trains 800 residents each year. As a beacon of multicultural sensitivity, the school annually exceeds the national medical school average of Hispanic students enrolled. The school’s clinical practice is the largest multidisciplinary medical group in South Texas with 850 physicians in more than 100 specialties. The school has a highly productive research enterprise where world leaders in Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, cancer, aging, heart disease, kidney disease and many other fields are translating molecular discoveries into new therapies. The Long School of Medicine is home to a National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center known for prolific clinical trials and drug development programs, as well as a world-renowned center for aging and related diseases.
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, also referred to as UT Health San Antonio, is one of the country’s leading health sciences universities and is designated as a Hispanic-Serving Institution by the U.S. Department of Education. With missions of teaching, research, patient care and community engagement, its schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions and graduate biomedical sciences have graduated more than 37,000 alumni who are leading change, advancing their fields, and renewing hope for patients and their families throughout South Texas and the world. To learn about the many ways “We make lives better®,” visit http://www.
Stay connected with The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram and YouTube.
To see how we are battling COVID-19, read inspiring stories on Impact.
Media Contact
Will Sansom
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.