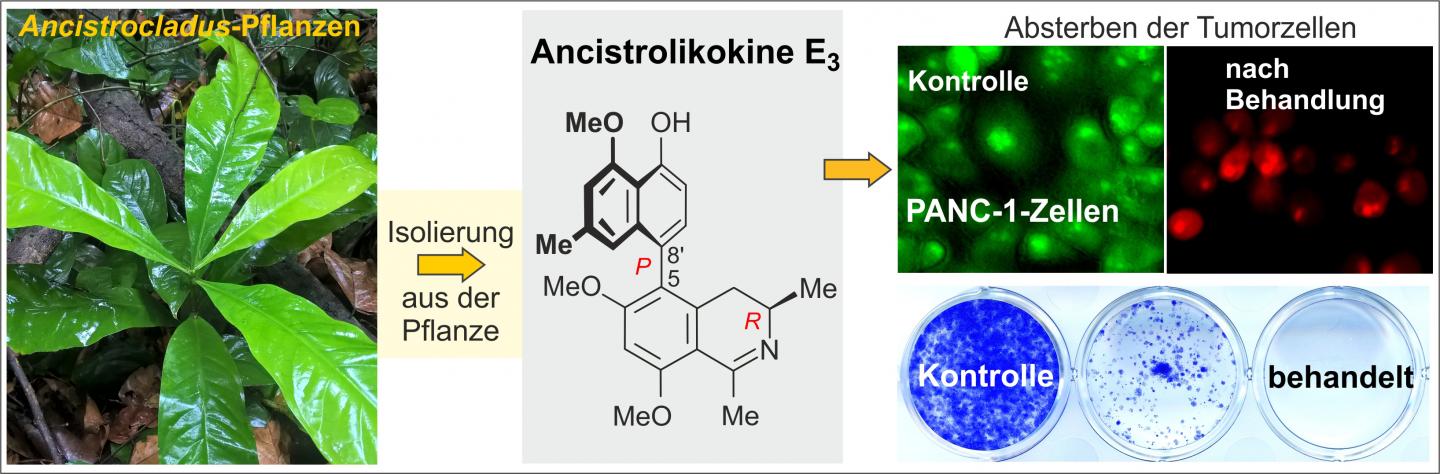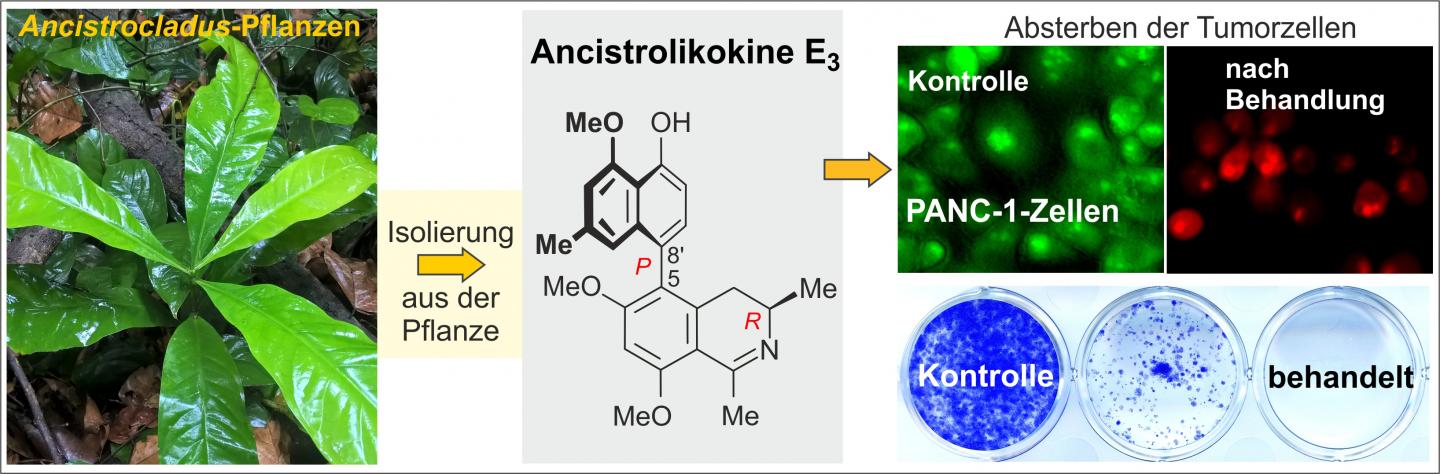
Credit: Pictures: Severin Muyisa / Suresh Awale
Professor Gerhard Bringmann, an expert in natural product chemistry, and his team from the Institute of Organic Chemistry at the Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Germany, together with Professor Suresh Awale and colleagues from the Institute of Natural Medicine of the University of Toyama in Japan have discovered a new, highly effective compound, which is a promising starting point to develop new drugs to treat pancreatic cancer.
A paper recently published in the Journal of Natural Products describes these exciting studies. The prestigious web portal "ACS News Service Weekly PressPac" of the American Chemical Society (ACS) now also presents the new findings to a broader public in a press release of 14 November 2018.
Cancer cells survive by activating the Akt/mTOR signalling pathway
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest forms of cancer, with a five-year survival rate of less than five percent. Because these cancer cells proliferate so aggressively, they deplete nutrients and oxygen in the region of the tumor. Whereas most cells would die under such extreme conditions, pancreatic cancer cells survive by activating a cell signalling pathway called Akt/mTOR.
Some researchers are therefore looking for compounds with antiausterity properties that disrupt this pathway. Substances that are preferably toxic to cancer cells under nutrient deprived conditions are called antiausterity compounds deriving from the Greek word "austerotes".
Alkaloids from rainforest vines
Suresh Awale, Gerhard Bringmann, and their teams previously identified some unusual alkaloids (naturally occurring organic compounds that contain nitrogen) with antiausterity potential from vines found in the Congolese rainforest.
Now the researchers from Würzburg and Japan have isolated and characterized the structure of ancistrolikokine E3 from twigs of the vine Ancistrocladus likoko, thereby identifying another promising new agent, which effectively targets PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cells in the lab.
Dramatic changes to the cancer cells
Ancistrolikokine E3 causes dramatic changes to the morphology of the cancer cells (see upper right illustration), which ultimately kill them. Furthermore, the compound inhibited cancer cell migration and colonization (see lower left illustration) in lab tests, which suggests that the compound could help prevent metastasis formation in patients.
The researchers showed that the compound kills the cancer cells by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway and the autophagy pathway. The studies thus support that ancistrolikokine E3 and other structurally related alkaloids could be promising compounds for anticancer drug development based on the antiausterity strategy.
###
Media Contact
Gerhard Bringmann
[email protected]
49-931-318-5323
@Uni_WUE
https://www.uni-wuerzburg.de/
Original Source
https://go.uniwue.de/likokine http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00733