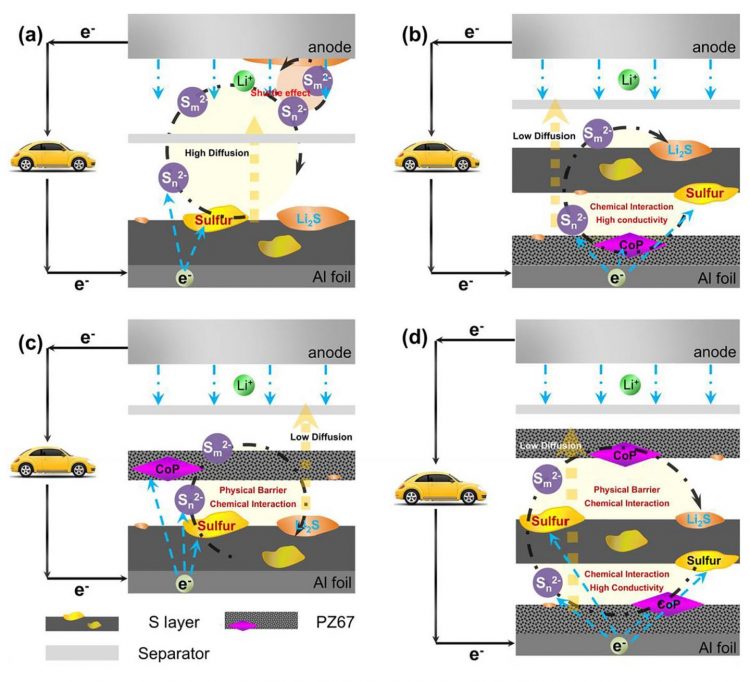
A sandwich-structured electrode enhances reaction kinetics, prohibits shuttling effect, improves lithium sulfur battery performance
Credit: Xing Gao, Siwu Li, Ying Du and Bo Wang
WASHINGTON, D.C., September 30, 2019 — Lithium ion batteries aren’t keeping up with energy demands from higher power electronic devices, electric vehicles and smart electric grids. To develop higher capacity batteries, researchers have looked to lithium sulfur batteries because of sulfur’s high theoretical capacity and energy density.
But there are still several problems to solve before lithium sulfur batteries can be put into practical applications, such as sulfur’s intrinsically low electrical conductivity and the rapid capacity decay caused by polysulfides escaping from the cathode.
The biggest problem is the shuttling effect that occurs during cycling. This effect causes the diffusion of polysulfides from the cathode, creating capacity loss. It also consumes a lot of fresh lithium and electrolytes, and reduces battery performance.
To solve the shuttling problem and improve lithium sulfur battery performance, the authors of a paper published in APL Materials, from AIP Publishing, created a sandwich-structured electrode using a novel material that traps polysulfides and increases the reaction kinetics.
ZIF-67 is a metal-organic framework (MOF) constructed from metal ions or metal clusters and organic ligands. It holds great promise in gas storage and separation, catalysis and energy storage. MOF-derived materials are also attractive in energy storage due to their robust structure, porous surface and high conductivity.
A sandwich-structured electrode with sulfur immobilized in between PZ67 layers, PZ67/S/PZ67, improves the practical energy density of the lithium sulfur battery to three to five times higher than that of lithium ion batteries. The PZ67 is composed of polar materials, and the porous carbon showed a synergistic effect in the chemical interaction, served as a physical barrier, offered a high conductivity to prohibit the polysulfide shuttling effect and enhanced the batteries’ cycling performance.
“The porous PZ67 can not only absorb the polysulfides to form a confinement, it can also improve the kinetics of the actual active materials’ reaction during the battery cycling,” author Siwu Li said. “That means it may also improve the discharge voltage of the battery, and that is a big contribution to improving the energy density of the batteries.”
The sandwich-structured electrode that confines soluble polysulfides could be useful for anyone working to confine soluble materials, Li said. His team plans to continue their work in order to scale up the process of fabricating the hybrid electrode using a hot pressing procedure. They also plan to address instabilities on the anode side of lithium sulfur batteries, possibly by adding a protective layer.
###
The article, “A ZIF-67-derived-sulfur sandwich structure for high performance Li-S batteries,” is authored by Xing Gao, Siwu Li, Ying Du and Bo Wang. The article will appear in the journal APL Materials on Sept. 30, 2019 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5122819). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Materials is an open access journal that features original research on significant topical issues within all areas of materials science. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.