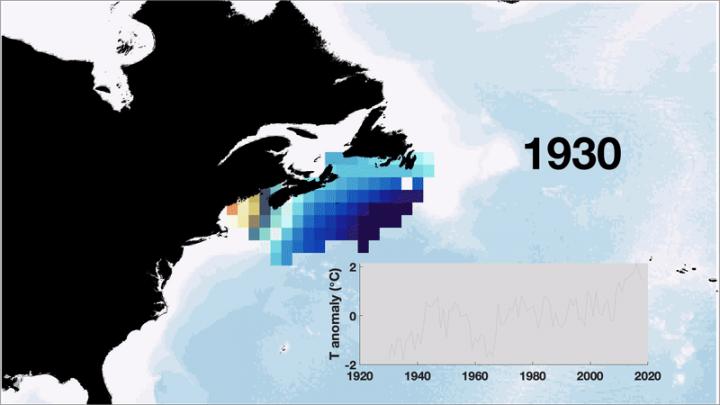
Credit: (Animation by Afonso Gonçalves Neto)
KINGSTON, R.I., — April 20, 2021 — The Northwest Atlantic Shelf is one of the fastest-changing regions in the global ocean, and is currently experiencing marine heat waves, altered fisheries and a surge in sea level rise along the North American east coast. A new paper, “Changes in the Gulf Stream preceded rapid warming of the Northwest Atlantic Shelf,” published in Communications Earth & Environment by recent URI Graduate School of Oceanography graduate Afonso Gonçalves Neto reveals the causes, potential predictability and historical context for these types of rapid changes.
“We used satellite data to show that when the Gulf Stream migrates closer to the underwater plateau known as the Grand Banks of Newfoundland, as it did after 2008, it blocks the southwestward transport of the Labrador Current that would otherwise provide cold, fresh, oxygen-rich water to the North American shelf,” said lead author Gonçalves Neto. This mechanism explains why the most recent decade has been the hottest on record at the edge of the Northeast United States and Canada, as the delivery system of cold water to the region got choked off by the presence of the Gulf Stream.
The URI research team noted the importance of finding that the satellite-observed signature of the Gulf Stream’s position relative to the Grand Banks precedes subsurface shelf warming by over a year. “By monitoring satellite observations for changes near the Grand Banks, we can predict changes coming to the Northeast U.S. shelf with potentially enough lead time to inform fishery management decision-making,” said GSO graduate student and co-author Joe Langan.
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland is hardly a stranger to attention. It was near this feature that an iceberg sank the R.M.S. Titanic, one impetus for creation of the International Ice Patrol. The Ice Patrol has been collecting oceanographic data in this region for over a century, allowing the URI team to put recent satellite observations in a much longer-term context. Though the 2008 shift at the edge of the Grand Banks created warmer and saltier conditions than ever recorded since 1930, there was a similar shift in the 1970s relative to the decades preceding it. Thus, the circulation change directly observed by satellites might have had a precedent about 50 years ago.
Jaime Palter, GSO associate professor of oceanography and co-author of the study, marveled at the long record, and what remains unknown. “We still don’t know what caused the abrupt shift of the circulation near the Grand Banks inferred in the 1970s and observed in 2008, or whether this is the new normal for the circulation and the temperatures of the northeast shelf,” said Palter. “There are modeling studies that suggest that a slowdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation can cause the types of changes we observed, but the connection remains to be made in the observational record.”
###
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation or AMOC is a system of currents that delivers warm ocean waters to northern regions, contributing to the warm climate of Scandinavia and influencing a broad array of northern hemisphere weather phenomena. Climate models show the AMOC circulation slowing if greenhouse gas emissions continue unabated, which–if the link is proven–would continue altering the Northeast U.S. and Canadian shelf waters and impacting fisheries in the future.
Media Contact
Dawn Bergantino
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




