The synthesized zircon can be used for storage and disposal of radioactive waste; Furthermore, the unusual material, can be used as a reference sample in mineralogical studies
Credit: Ural Federal University
The scientific novelty of the work of scientists from Ural Federal University, Institute of Solid State Chemistry and Geology and Geochemistry of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences lies in the fact that for the first time scientists solved the task of creating zircon with certain spectral properties. To this end, they have worked out the so-called sol-gel method.
It is distinguished by its technological simplicity, controllability of processes and allows synthesizing a larger volume of products with high purity than with other methods.
First, from carbonate of zirconium metal and an organosilicon compound, they obtained a sol – a dispersed medium with the presence of small solid particles, from it – a colloidal system, then, after drying and grinding, a precursor powder of a high degree of homogeneity, which was subjected to further grinding and calcination.
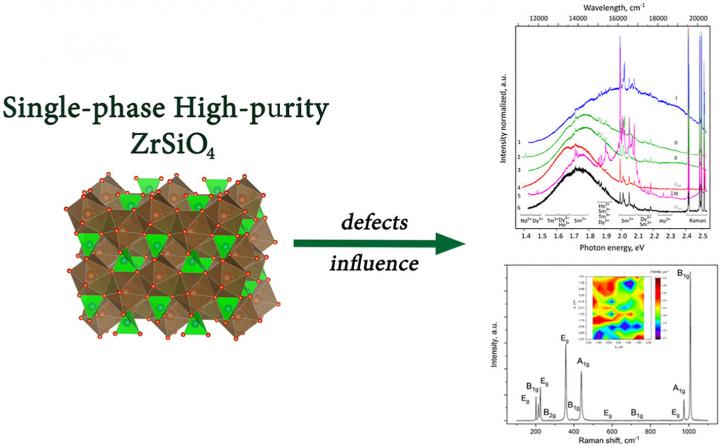
Second, it was found that upon mechanical stirring and sequential annealing – heating to 1550 ° C and further cooling the precursor to room temperature – the number of defects in the synthesized sample decreases and its high purity is achieved.
The range of applications of zircon obtained by the scientists from Yekaterinburg is very wide. Due to its high melting point (above 2000 ° C), chemical resistance, mechanical strength, low expansion coefficient at high temperatures and low thermal conductivity, zircon is useful as a refractory material (for example, for the manufacture of industrial furnaces) and a pigment for the production of heat-resistant paints. The presence of impurities and defects in the structure allows us to consider it as a standard for studying the mechanisms of defect formation in natural zircon crystals.
“Even a small concentration of impurities, such as iron, manganese, titanium, rare earth elements, significantly affects the luminescent properties of zircon, in some cases, the impurities enhance the glow in a certain range of electromagnetic waves. In other words, with the help of impurities, you can give zircon the necessary luminescent properties and use it as a phosphor or to detect the level of radiation damage, since the structure of zircon well “remembers” the radiation dose that it received, ” says Dmitry Zamyatin, senior researcher, Research Laboratory “EXTRA TERRA CONSORTIUM”, UrFU Institute of Physics and Technology.
Furthermore, the synthetic zircon matrix is able to contain large amounts of uranium and thorium. This allows the synthesized zircon to be used as a container for long-term storage and disposal of radioactive elements.
###
Media Contact
Evgeniya Saburova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




