Researchers aim to better explain the way plasmas interact with biological materials to help pave the way for plasma use in wound healing and cancer therapy
Credit: Natalia Yu. Babaeva
WASHINGTON, November 24, 2020 — Plasma medicine is an emerging field, as plasmas show promise for use in a wide range of therapies from wound healing to cancer treatment. Plasma jets are the main plasma sources typically used in plasma-surface applications. Before applications can progress, however, a better understanding of how plasma jets modify the surfaces of biological tissue is required.
To help with this understanding, researchers from the Russian Academy of Sciences conducted computer simulations of the interaction between an atmospheric pressure plasma jet with a surface that has properties similar to blood serum. They present their analysis in the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing.
“While using the plasma jets for the purpose of plasma medicine, it is important to know that the presence or absence of the treated surface in vicinity of a jet significantly influences jet parameters,” said Natalia Babaeva, one of the authors. “For example, the wounds with blood serum can have different properties. These properties can also vary during the plasma treatment.”
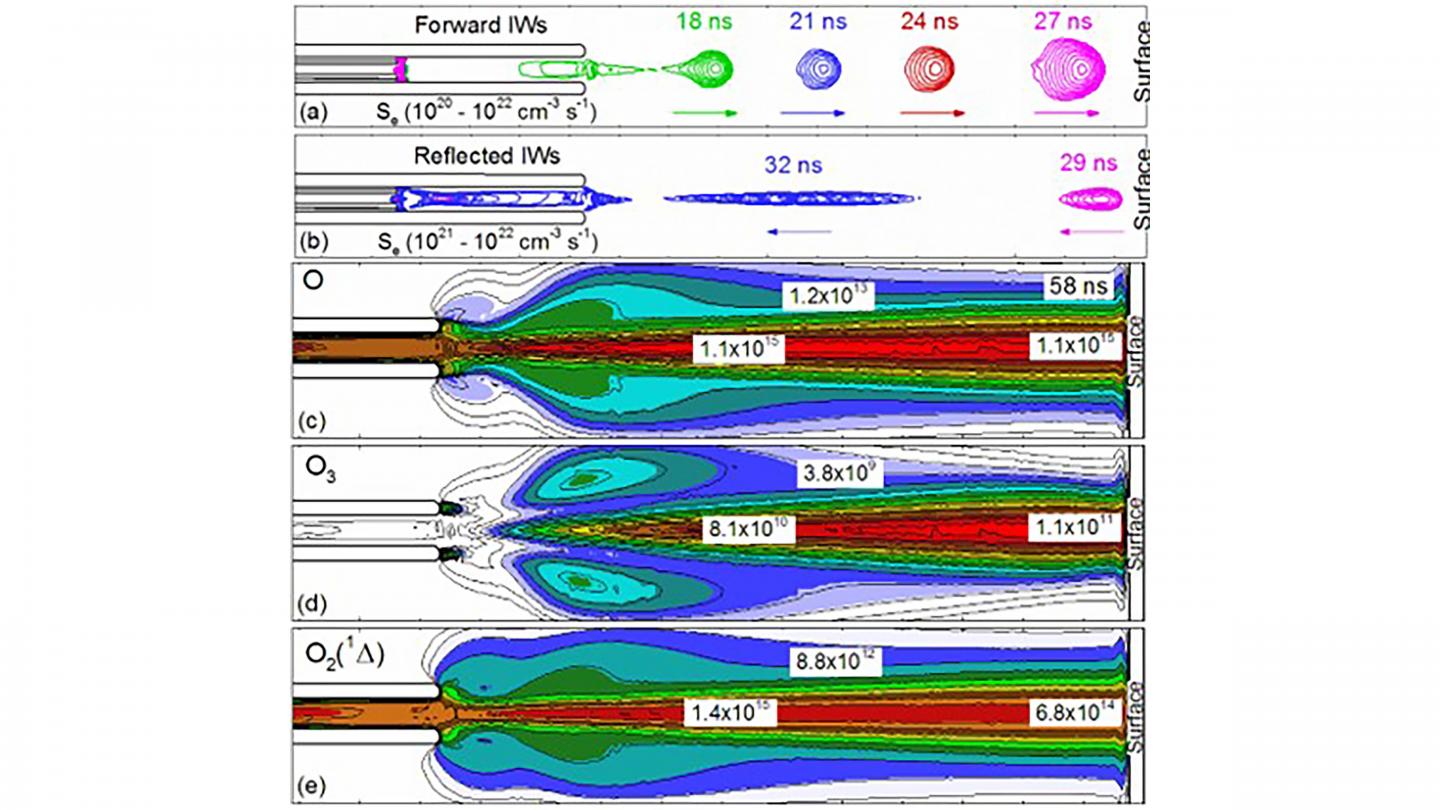
Depending on the characteristics of the tissue being treated, the plasma jet can behave in a number of different ways. The ionization waves produced by plasma jets may reflect back and forth, or they can spread over the tissue as surface discharge.
For the type of plasma Babaeva and her team studied, they found that the biomaterial-like surface can lead to multiple reflections of the plasma jet, and with each passage, the number of electrons and radicals — a type of very reactive molecule — increases. Specifically, the radicals identified are oxygen, hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide, ozone, and nitric oxide, also known as reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species.
“Reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species are important for the actions of antimicrobial drugs, cancer, and wound healing therapies,” Babaeva said, adding that they both play an active role in the immune systems of animals and plants.
Quantifying these radicals and understanding the direction and magnitude of their flow is important for optimizing plasmas for use in biomedical applications, where the ability to control their behavior to some degree is crucial. The team’s simulations provide the means to predict this behavior.
“This prediction is very important, as it determines the plasma treatment potential,” Babaeva said. “Our research adds some knowledge on the particular behavior of the jet in the presence of highly conductive surfaces.”
###
The article, “Reactive fluxes delivered by plasma jets to conductive dielectric surfaces during multiple reflections of ionization waves,” is authored by Natalia Yu. Babaeva and George V. Naidis. The article will appear in the Journal of Applied Physics on Nov. 24, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0019350). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.