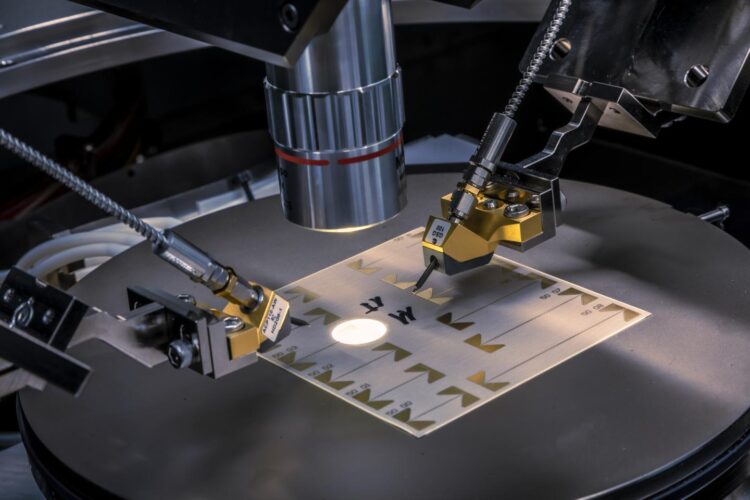
Researchers at TU Graz are specifically looking for ways to embed passive electronic components in three dimensions while guaranteeing safe multifunctionality
Credit: Lunghammer – TU Graz
In smartphones and many other complex, wirelessly networked devices, sophisticated technologies are used to integrate the individual electronic components into the housing. While active components, such as semiconductors, are already well investigated, passive electronic elements such as antennas or filters are lagging behind. This is not only the case for the components itself, but also for their embedding into printed circuit boards (PCBs) or other substrates, in order to achieve higly packed electronic modules. There is also a lack of precise measurement techniques, suitable models and efficient design strategies to predict their behaviour at higher frequencies – for example in 5G systems – and for higher energy densities, especially in power electronics.
This is where the new Christian Doppler Laboratory for Technology-Guided Electronic Component Design and Characterization, or “TONI” for short, comes in. Together with corporate partners Qualcomm, AT&S and Fronius, researchers at Graz University of Technology are specifically looking for ways to embed electronic components in three dimensions while guaranteeing robust and secure multifunctionality. The starting signal for the latest CD lab at TU Graz was given on 27 November 2020. The largest public funding provider is the Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs (BMDW). Including the funds from the three corporate partners, the CD lab has already been financed for seven years with around four million euros.
“Good and efficient hardware is a prerequisite for digitalization and our mobile communication,” emphasises Federal Minister for Digital and Economic Affairs Margarete Schramböck. “This CD laboratory is contributing to this by carrying out research on the fundamentals. The expected benefits include longer battery life, more efficient use of valuable resources and more secure data transmission. Here too, it is clear that research is the basis for entrepreneurial innovation.”
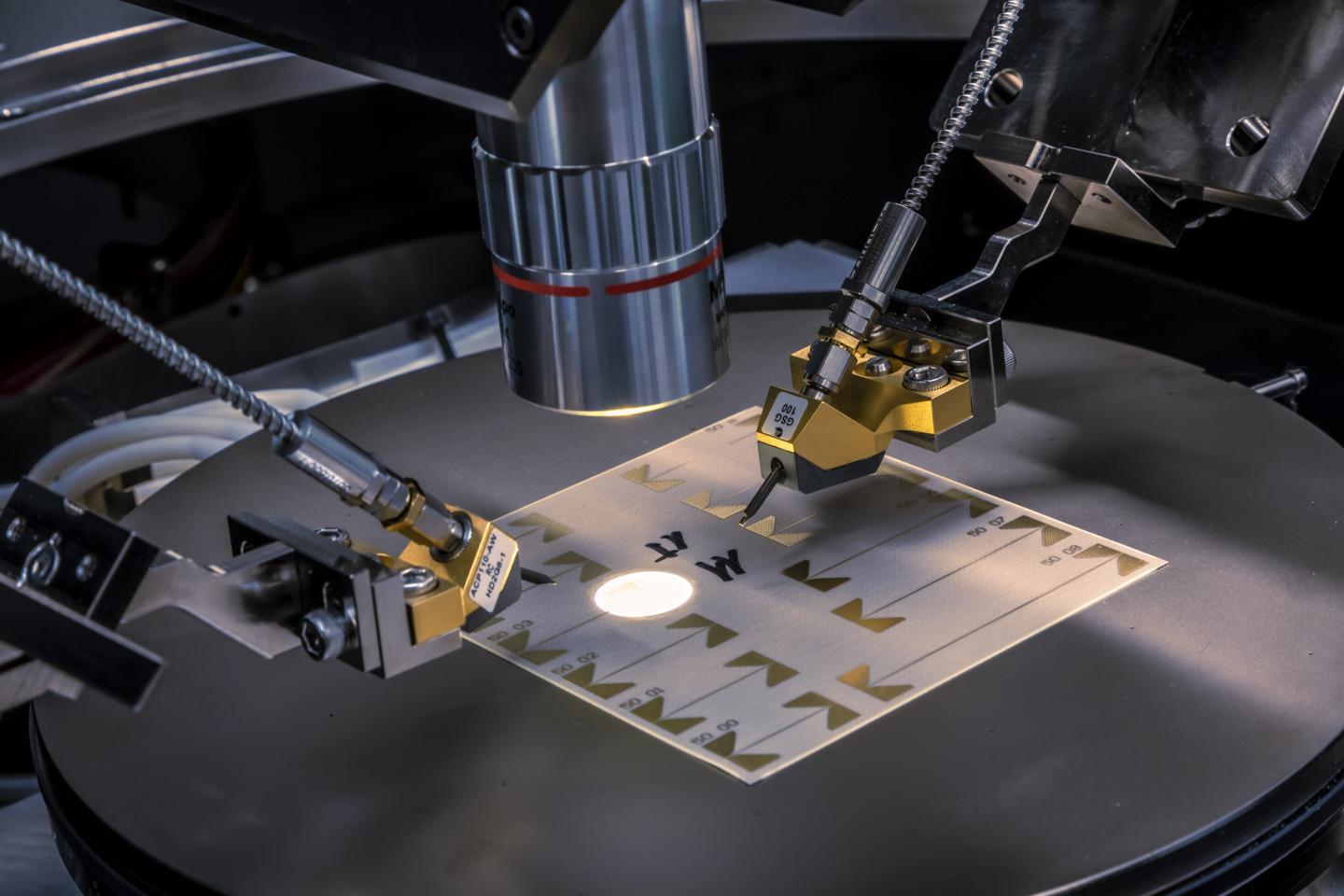
Characterization of little noticed components
Whether smart homes or smart grids, whether healthcare, autonomous driving or space travel, 500 billion devices are expected to be connected to the internet and to communicate wirelessly by 2030. For secure and robust data transmission, more and more transmit and receive channels are being installed together in these devices. This leads to a need for higher integration and a necessary miniaturization of all electronic components. As a result, individual components often have to perform several functions simultaneously, such as antennas that can receive and filter signals at the same time (so-called “filtennas”). Due to the operation of several transmitter units in close proximity, strong electromagnetic interactions are increasingly becoming a problem.
“What still lags far behind the trend towards higher frequencies of operation and expanded multifunctionality is the combination of functionality and integration in the device housing. To achieve this, we now need to focus now more on the passive components, which have often played a secondary role in the past. However, they are just as essential as the semiconductor elements that have already been very well researched,” explains Wolfgang Bösch, head of the new CD lab and also head of the Institute of Microwave and Photonic Engineering at TU Graz. Together with its corporate partners and in cooperation with the Institute of Electronics at TU Graz, the CD lab team is dedicated to the question of how multifunctional and highly integrated components with combined filter and antenna functions can be comprehensively described in theory and manufactured using new technologies.
Correct models instead of trial-and-error
For this purpose, passive components in power electronics as well as in the microwave frequency applications are precisely measured and modelled. “Standard measurement technology reaches its limits here – we have to develop fundamentally new concepts and face the question of how we can measure at all what we have to measure,” says Wolfgang Bösch. New methods for broadband microwave measurements will help to increase the accuracy in production and automatically detect errors in the measurement process. Building on this, new models for embedding passive and active components in printed circuit boards are being researched, with a special focus on the interconnecting elements. And finally, how individual components with their respective electromagnetic fields interfere with each other within the housing will be investigated.
“The objective is to avoid weak points in the circuit design. Developments based on the trial-and-error principle should be a thing of the past, not least for cost reasons. We will therefore develop a simulation and design framework so that all critical parameters are already considered during the development process of such equipment and correct models can be used. This is the only way to guarantee electromagnetic compatibility combined with high integration density and multifunctionality from the outset,” says Bösch.
###
This CD laboratory is anchored in the Field of Expertise “Information, Communication and Computing” at Graz University of Technology (https:/
All 13 CD labs at TU Graz: https:/
In Christian Doppler laboratories, application-oriented basic research is carried out at a high level, with outstanding scientists cooperating with innovative companies. The Christian Doppler Research Society (CDG) is internationally regarded as an example of best practice in promoting this cooperation. Christian Doppler laboratories are jointly funded by the public sector and the participating companies. The most important public funding source is the Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs (BMDW). http://www.
Media Contact
Wolfgang Bösch
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/





