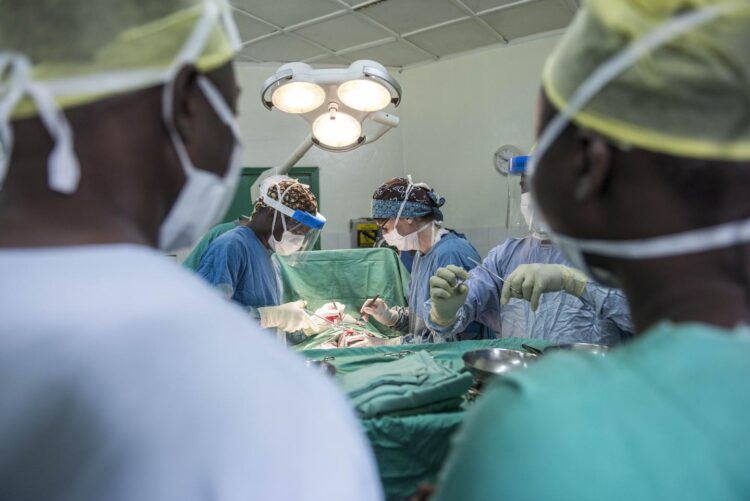
Single blind, randomized clinical trial in Sierra Leone showed that task sharing can expand access to medical care without compromising quality
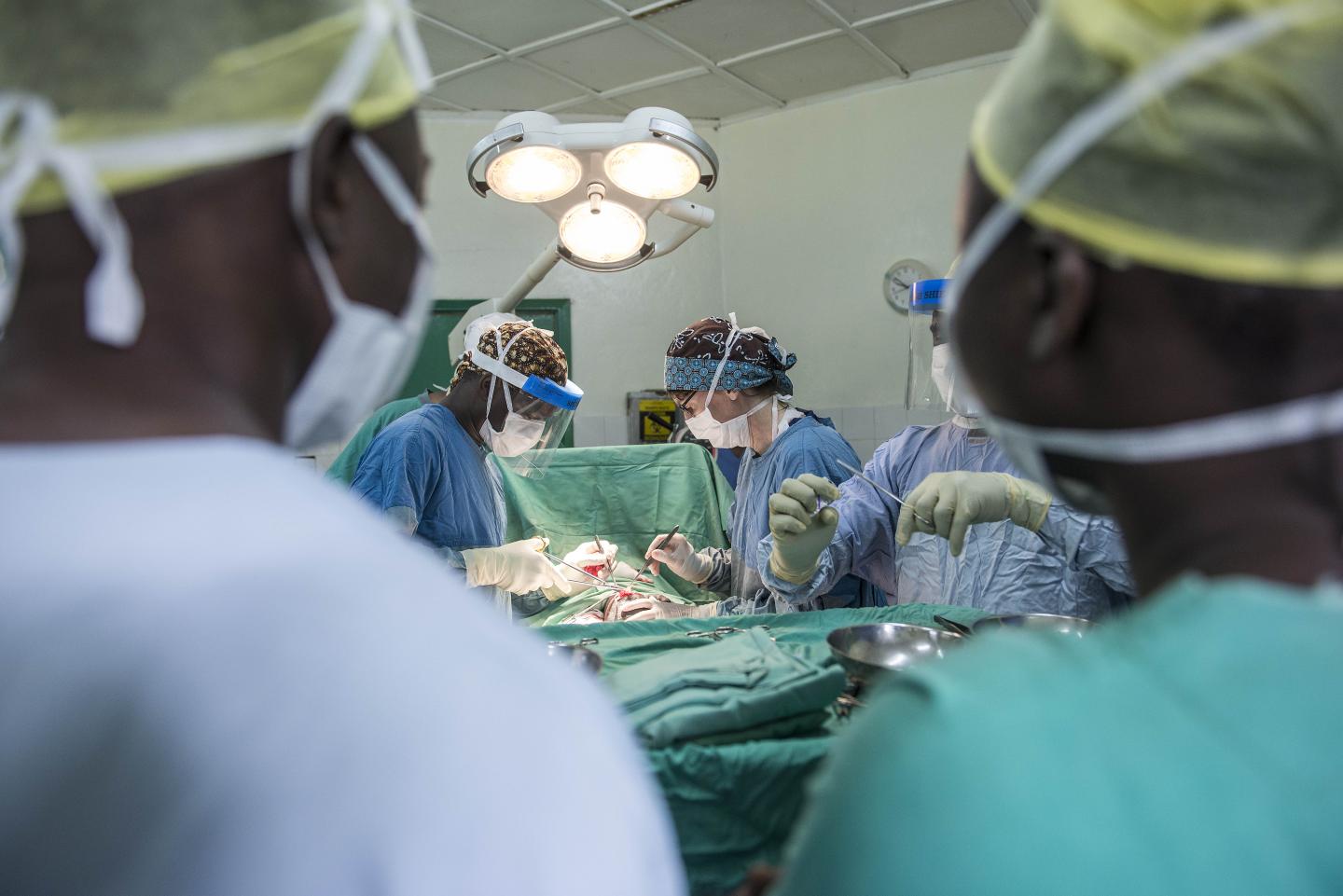
Credit: CapaCare
Many Sub-Saharan countries have a desperate shortage of surgeons, and to ensure that as many patients as possible can be treated, some operations are carried out by medical professionals who are not specialists in surgery.
This approach, called task sharing, is supported by the World Health Organisation, but the practice remains controversial. Now a team of medical researchers from Norway, Sweden, Sierra Leone and the Netherlands shows that groin hernia operations performed by associate clinicians, who are trained medical personnel but not doctors, are just as safe and effective as those performed by doctors. The study has been published in JAMA Network Open.
“The study showed that associate clinicians were not inferior to registered doctors when it comes to recurrence, complications, groin pain or patient satisfaction,” said co-authors Håkon A. Bolkan and Alex van Duinen at the Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine, NTNU.
An estimated 220 million people around the world live with an inguinal hernia, which causes significant suffering and, 40,000 deaths each year.
Twenty million inguinal hernia operations are performed every year, making it the most common general surgical procedure in the world, including in low-income countries like Sierra Leone, where the study was conducted.
Sierra Leone has fewer than one surgeon per 100,000 population. The shortage of surgeons in Sierra Leone means that the country’s medical doctors, who have no specific training in surgery, routinely perform surgical procedures as part of their regular work.
Since 2011, the Norwegian non-profit organization CapaCare has worked with the Sierra Leone Ministry of Health and Sanitation and the United Nations Population Fund to address the shortage in surgical care through task sharing. CapaCare offers a three-year training programme for community health officers, after which they can perform basic lifesaving surgeries, such as groin hernia repairs.
CapaCare graduates are called associate clinicians and their education level is between that of a nurse and a doctor.
The study included 229 men operated on for inguinal hernia between 2017 and 2018 at a district hospital in rural Sierra Leone. The patients were randomly assigned to a doctor or an associate clinician for their surgery and were followed up after two weeks and one year. The researchers also plan a follow-up visit to patients three years after their surgery.
“There were even fewer cases of recurrence in the patients who had been operated on by associate clinicians compared to the group operated on by medical doctors,” Bolkan and van Duinen said. “This was an extremely unexpected finding and task sharing appears to be an attractive option that can help the millions of people suffering from inguinal hernia.”
The researchers’ next step is to develop training programmes for doctors and associate clinicians in order to expand surgical services. Forthcoming studies will be conducted in Sierra Leone and Uganda.
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council. Authors Håkon Bolkan, Alex van Duinen and Thomas Ashley are unpaid members of the CapaCare board.
Publication: “Outcomes after elective inguinal hernia repair performed by associate clinicians versus medical doctors – a randomized, single blinded non-inferiority trial.” Thomas Ashley, Hannah Ashley, Andreas Wladis, Håkon A. Bolkan, Alex J. van Duinen, Jessica H. Beard, Hertta Kalsi, Juuli Palmu, Pär Nordin, Kristina Holm, Michael Ohene-Yeboah, Jenny Löfgren. JAMA Network Open, Many Sub-Saharan countries have a desperate shortage of surgeons, and to ensure that as many patients as possible can be treated, some operations are carried out by medical professionals who are not specialists in surgery.
This approach, called task sharing, is supported by the World Health Organisation, but the practice remains controversial. Now a team of medical researchers from Norway, Sweden, Sierra Leone and the Netherlands shows that groin hernia operations performed by associate clinicians, who are trained medical personnel but not doctors, are just as safe and effective as those performed by doctors. The study has been published in JAMA Network Open.
“The study showed that associate clinicians were not inferior to registered doctors when it comes to recurrence, complications, groin pain or patient satisfaction,” said co-authors Håkon A. Bolkan and Alex van Duinen at the Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine, NTNU.
Training and task sharing as a way to address shortages
An estimated 220 million people around the world live with an inguinal hernia, which causes significant suffering and, 40,000 deaths each year.
Twenty million inguinal hernia operations are performed every year, making it the most common general surgical procedure in the world, including in low-income countries like Sierra Leone, where the study was conducted.
Sierra Leone has fewer than one surgeon per 100,000 population. The shortage of surgeons in Sierra Leone means that the country’s medical doctors, who have no specific training in surgery, routinely perform surgical procedures as part of their regular work.
Since 2011, the Norwegian non-profit organization CapaCare has worked with the Sierra Leone Ministry of Health and Sanitation and the United Nations Population Fund to address the shortage in surgical care through task sharing. CapaCare offers a three-year training programme for community health officers, after which they can perform basic lifesaving surgeries, such as groin hernia repairs.
CapaCare graduates are called associate clinicians and their education level is between that of a nurse and a doctor.
An unexpected finding
The study included 229 men operated on for inguinal hernia between 2017 and 2018 at a district hospital in rural Sierra Leone. The patients were randomly assigned to a doctor or an associate clinician for their surgery and were followed up after two weeks and one year. The researchers also plan a follow-up visit to patients three years after their surgery.
“There were even fewer cases of recurrence in the patients who had been operated on by associate clinicians compared to the group operated on by medical doctors,” Bolkan and van Duinen said. “This was an extremely unexpected finding and task sharing appears to be an attractive option that can help the millions of people suffering from inguinal hernia.”
The researchers’ next step is to develop training programmes for doctors and associate clinicians in order to expand surgical services. Forthcoming studies will be conducted in Sierra Leone and Uganda.
###
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council. Authors Håkon Bolkan, Alex van Duinen and Thomas Ashley are unpaid members of the CapaCare board.
Publication: “Outcomes after elective inguinal hernia repair performed by associate clinicians versus medical doctors – a randomized, single blinded non-inferiority trial.” Thomas Ashley, Hannah Ashley, Andreas Wladis, Håkon A. Bolkan, Alex J. van Duinen, Jessica H. Beard, Hertta Kalsi, Juuli Palmu, Pär Nordin, Kristina Holm, Michael Ohene-Yeboah, Jenny Löfgren. JAMA Network Open, 2021;4(1):32032681
Media Contact
Håkon Angell Bolkan
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.